Miller MF410034T Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire
Ce manuel convient également à

Spoolmatic - Pro
15A And 30A
Processes
OM-264 713D 2015−08
MIG (GMAW) Welding
File: MIG (GMAW)
Visit our website at
www.MillerWelds.com
Description
Semi-Automatic, Air-Cooled,
MIG (GMAW) Welding Gun
R

Miller Electric manufactures a full line
of welders and welding related equipment.
For information on other quality Miller
products, contact your local Miller distributor to receive the latest full
line catalog or individual specification sheets. To locate your nearest
distributor or service agency call 1-800-4-A-Miller, or visit us at
www.MillerWelds.com on the web.
Thank you and congratulations on choosing Miller. Now you can get
the job done and get it done right. We know you don’t have time to do
it any other way.
That’s why when Niels Miller first started building arc welders in 1929,
he made sure his products offered long-lasting value and superior
quality. Like you, his customers couldn’t afford anything less. Miller
products had to be more than the best they could be. They had to be the
best you could buy.
Today, the people that build and sell Miller products continue the
tradition. They’re just as committed to providing equipment and service
that meets the high standards of quality and value established in 1929.
This Owner’s Manual is designed to help you get the most out of your
Miller products. Please take time to read the Safety precautions. They
will help you protect yourself against potential hazards on the worksite.
We’ve made installation and operation quick
and easy. With Miller you can count on years
of reliable service with proper maintenance.
And if for some reason the unit needs repair,
there’s a Troubleshooting section that will
help you figure out what the problem is. The
parts list will then help you to decide the
exact part you may need to fix the problem.
Warranty and service information for your
particular model are also provided.
Miller is the first welding
equipment manufacturer in
the U.S.A. to be registered to
the ISO 9001 Quality System
Standard.
Working as hard as you do
− every power source from
Miller is backed by the most
hassle-free warranty in the
business.
From Miller to You
Mil_Thank 2009−09

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 −SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR GMAW WELDING GUNS − READ BEFORE USING 1........
1-1. Symbol Usage 1........................................................................
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards 1..................................................................
1-3. Proposition 65 Warnings 2...............................................................
1-4. Principal Safety Standards 2.............................................................
1-5. EMF Information 2......................................................................
SECTION 2 − MESURES DE SÉCURITÉ VISANT LES PISTOLETS DE SOUDAGE GMAW − À LIRE AVANT
UTILISATION 3................................................................................
2-1. Signification des symboles 3.............................................................
2-2. Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc 3......................................................
2-3. Proposition californienne 65 Avertissements 4...............................................
2-4. Principales normes de sécurité 4..........................................................
2-5. Informations relatives aux CEM 4.........................................................
SECTION 3 − DEFINITIONS 7...................................................................
3-1. Additional Safety Symbols And Definitions 7................................................
3-2. Miscellaneous Symbols And Definitions 7...................................................
SECTION 4 − SPECIFICATIONS 8................................................................
4-1. Gun Specifications 8....................................................................
4-2. Duty Cycle And Overheating 8............................................................
SECTION 5 − INSTALLATION 8..................................................................
5-1. Connecting To 24 Volt Weld Control 8......................................................
5-2. Connecting To 115 Volt Weld Control 9.....................................................
5-3. Removing Top Cover Of Pistol Grip Gun 9..................................................
5-4. Installing Wire Spool And Threading Welding Wire 10..........................................
5-5. Adjusting Drive Roll And Spool Brake Pressure 11............................................
5-6. Rotating Canister 11.....................................................................
5-7. Installing Gas Supply 12..................................................................
SECTION 6 − OPERATION 13....................................................................
6-1. Gun Controls 13.........................................................................
6-2. Gun Pressure Roll Tension Setting 13.......................................................
6-3. Shielding Gas 14........................................................................
SECTION 7 − MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING 14...........................................
7-1. Replacing Canister Inlet Guide 15..........................................................
7-2. Replacing Spool Canister 15..............................................................
7-3. Replacing Head Tube Liner 16.............................................................
7-4. Removing Diffuser In Air And Water-Cooled Pistol-Grip Guns 16................................
7-5. Changing Gun Contact Tip 17.............................................................
7-6. Gun Drive Assembly Maintenance 17.......................................................
7-7. Troubleshooting 18......................................................................
SECTION 8 − ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS 20........................................................
SECTION 9 − PARTS LIST 22.....................................................................
SECTION 10 − PARTS LIST INCLUDING CONSUMABLES 26........................................
WARRANTY


OM-264 713 Page 1
SECTION 1 −SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR GMAW
WELDING GUNS − READ BEFORE USING
SR7 (MIG) 2013-09
Protect yourself and others from injury — read, follow, and save these important safety precautions and operating instructions.
1-1. Symbol Usage
DANGER! − Indicates a hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. The
possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols
or explained in the text.
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury. The possible
hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols or ex-
plained in the text.
NOTICE − Indicates statements not related to personal injury.
. Indicates special instructions.
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! ELECTRIC
SHOCK, MOVING PARTS, and HOT PARTS hazards. Consult sym-
bols and related instructions below for necessary actions to avoid the
hazards.
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards
The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual
to call attention to and identify possible hazards. When you
see the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions
to avoid the hazard. The safety information given below is
only a summary of the more complete safety information
found in the welding power source Owner’s Manual. Read
and follow all Safety Standards.
Only qualified persons should install, operate, maintain, and
repair this unit.
During operation, keep everybody, especially children, away.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
D Always wear dry insulating gloves.
D Insulate yourself from work and ground.
D Do not touch live electrode or electrical parts.
D Replace worn, damaged, or cracked guns or cables.
D Turn off welding power source before changing contact tip or gun
parts.
D Keep all covers and handle securely in place.
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous.
D Keep your head out of the fumes.
D Ventilate area, or use breathing device. The
recommended way to determine adequate
ventilation is to sample for the composition and quantity of fumes
and gases to which personnel are exposed.
D Read and understand the Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) and the
manufacturer’s instructions for adhesives, coatings, cleaners,
consumables, coolants, degreasers, fluxes, and metals.
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
D Do not weld near flammable material.
D Do not weld on containers that have held com-
bustibles, or on closed containers such as
tanks, drums, or pipes unless they are properly prepared ac-
cording to AWS F4.1 and AWS A6.0 (see Safety Standards).
D Watch for fire; keep extinguisher nearby.
D Read and understand the Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) and the
manufacturer’s instructions for adhesives, coatings, cleaners,
consumables, coolants, degreasers, fluxes, and metals.
BUILDUP OF GAS can injure or kill.
D Shut off compressed gas supply when not in
use.
D Always ventilate confined spaces or use ap-
proved air-supplied respirator.
MOVING PARTS can injure.
D Keep away from moving parts.
D Keep away from pinch points such as drive
rolls.
Arc rays from the welding process produce intense
visible and invisible (ultraviolet and infrared) rays
that can burn eyes and skin. Sparks fly off from the
weld.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin.
D Wear an approved welding helmet fitted with a proper shade of filter
lenses to protect your face and eyes from arc rays and sparks
when welding or watching (see ANSI Z49.1 and Z87.1 listed in
Safety Standards).
D Wear approved safety glasses with side shields under your
helmet.
D Use protective screens or barriers to protect others from flash,
glare and sparks; warn others not to watch the arc.
D Wear body protection made from durable, flame-resistant material
(leather, heavy cotton, wool). Body protection includes oil-free
clothing such as leather gloves, heavy shirt, cuffless trousers, high
shoes, and a cap.
HOT PARTS can burn.
D Allow gun to cool before touching.
D Do not touch hot metal.
D Protect hot metal from contact by others.

OM-264 713 Page 2
NOISE can damage hearing.
Noise from some processes or equipment can
damage hearing.
D Check for noise level limits exceeding those
specified by OSHA.
D Use approved ear plugs or ear muffs if noise level is high.
D Warn others nearby about noise hazard.
WELDING WIRE can injure.
D Keep hands and body away from gun tip when
trigger is pressed.
READ INSTRUCTIONS.
D Read and follow all labels and the Owner’s
Manual carefully before installing, operating, or
servicing unit. Read the safety information at
the beginning of the manual and in each
section.
D Use only genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer.
D Perform maintenance and service according to the Owner’s
Manuals, industry standards, and national, state, and local
codes.
1-3. Proposition 65 Warnings
Welding or cutting equipment produces fumes or gases
which contain chemicals known to the State of California to
cause birth defects and, in some cases, cancer. (California
Health & Safety Code Section 25249.5 et seq.)
This product contains chemicals, including lead, known to
the state of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after use.
1-4. Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
is available as a free download from the American Welding Society at
http://www.aws.org or purchased from Global Engineering Documents
(phone: 1-877-413-5184, website: www.global.ihs.com).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protec-
tion, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036 (phone: 212-642-4900, web-
site: www.ansi.org).
Safe Practices for the Preparation of Containers and Piping for Welding
and Cutting, American Welding Society Standard AWS F4.1, from Glob-
al Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184, website: www.glo-
bal.ihs.com).
Safe Practices for Welding and Cutting Containers that have Held Com-
bustibles, American Welding Society Standard AWS A6.0, from Global
Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184,
website: www.global.ihs.com).
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protec-
tion Association, Quincy, MA 02269 (phone: 1-800-344-3555, website:
www.nfpa.org and www. sparky.org).
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1,
from Compressed Gas Association, 14501 George Carter Way, Suite
103, Chantilly, VA 20151 (phone: 703-788-2700, website:
www.cganet.com).
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, CSA Standard
W117.2, from Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 5060
Spectrum Way, Suite 100, Ontario, Canada L4W 5NS (phone:
800-463-6727, website: www.csa-international.org).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protec-
tion, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036 (phone: 212-642-4900, web-
site: www.ansi.org).
Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot
Work, NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire Protection Association,
Quincy, MA 02269 (phone: 1-800-344-3555, website: www.nfpa.org.
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Standards for General Indus-
try, Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1910, Subpart Q,
and Part 1926, Subpart J, from U.S. Government Printing Office, Super-
intendent of Documents, P.O. Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250-7954
(phone: 1-866-512-1800) (there are 10 OSHA Regional Offices—
phone for Region 5, Chicago, is 312-353-2220, website:
www.osha.gov).
1-5. EMF Information
Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized electric
and magnetic fields (EMF). The current from arc welding (and allied pro-
cesses including spot welding, gouging, plasma arc cutting, and induc-
tion heating operations) creates an EMF field around the welding circuit.
EMF fields may interfere with some medical implants, e.g. pacemakers.
Protective measures for persons wearing medical implants have to be
taken. For example, restrict access for passers−by or conduct individu-
al risk assessment for welders. All welders should use the following pro-
cedures in order to minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding
circuit:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them, or using a
cable cover.
2. Do not place your body between welding cables. Arrange cables
to one side and away from the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cables around your body.
4. Keep head and trunk as far away from the equipment in the
welding circuit as possible.
5. Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as
possible.
6. Do not work next to, sit or lean on the welding power source.
7. Do not weld whilst carrying the welding power source or wire
feeder.
About Implanted Medical Devices:
Implanted Medical Device wearers should consult their doctor and the
device manufacturer before performing or going near arc welding, spot
welding, gouging, plasma arc cutting, or induction heating operations.
If cleared by your doctor, then following the above procedures is recom-
mended.

OM-264 713 Page 3
SECTION 2 − MESURES DE SÉCURITÉ VISANT LES
PISTOLETS DE SOUDAGE GMAW − À LIRE AVANT
UTILISATION
SR7(MIG)_2013−09 fre
Pour écarter les risques de blessure pour vous−même et pour autrui — lire, appliquer et ranger en lieu sûr ces consignes relatives
aux précautions de sécurité et au mode opératoire.
2-1. Signification des symboles
DANGER! − Indique une situation dangereuse qui si on
l’évite pas peut donner la mort ou des blessures graves.
Les dangers possibles sont montrés par les symboles
joints ou sont expliqués dans le texte.
Indique une situation dangereuse qui si on l’évite pas
peut donner la mort ou des blessures graves. Les dan-
gers possibles sont montrés par les symboles joints ou
sont expliqués dans le texte.
NOTE − Indique des déclarations pas en relation avec des blessures
personnelles.
. Indique des instructions spécifiques.
Ce groupe de symboles veut dire Avertissement! Attention! DANGER
DE CHOC ELECTRIQUE, PIECES EN MOUVEMENT, et PIECES
CHAUDES. Consulter les symboles et les instructions ci-dessous y
afférant pour les actions nécessaires afin d’éviter le danger.
2-2. Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc
Les symboles présentés ci-après sont utilisés tout au long du
présent manuel pour attirer votre attention et identifier les ris-
ques de danger. Lorsque vous voyez un symbole, soyez vigi-
lant et suivez les directives mentionnées afin d’éviter tout
danger. Les consignes de sécurité présentées ci-après ne
font que résumer l’information contenue dans les normes de
sécurité énumérées dans le manuel d’utilisation du poste de
soudage. Veuillez lire et respecter toutes ces normes de sé-
curité.
L’installation, l’utilisation, l’entretien et les réparations ne
doivent être confiés qu’à des personnes qualifiées.
Au cours de l’utilisation, tenir toute personne à l’écart et plus
particulièrement les enfants.
UN CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE peut tuer.
D Porter toujours des gants secs et isolants.
D S’isoler de la pièce et de la terre.
D Ne jamais toucher une électrode ou des pièces
électriques sous tension.
D Remplacer les pistolets ou câbles de soudage qui sont endom-
magés, usés ou craquelés.
D Mettre la soudeuse hors tension avant de remplacer un bec con-
tact ou des pièces de pistolet.
D S’assurer que tous les couvercles et poignées sont fermement
assujettis.
LES VAPEURS ET LES FUMÉES
peuvent être nocives.
D Éloigner sa tête des endroits renfermant des
vapeurs.
D Aérer la zone de travail ou porter un appareil re-
spiratoire. Pour déterminer la bonne ventila-
tion, il est recommandé de procéder à un
prélèvement pour la composition et la quantité
de fumées et de gaz auxquels est exposé le
personnel.
D Lire et comprendre les fiches de données de sécurité et les instruc-
tions du fabricant concernant les adhésifs, les revêtements, les
nettoyants, les consommables, les produits de refroidissement, les
dégraisseurs, les flux et les métaux.
LE SOUDAGE peut causer un incen-
die ou une explosion.
D Ne pas souder à proximité de matériaux inflam-
mables.
D Ne pas effectuer le soudage sur des conteneurs fermés tels que
des réservoirs, tambours, ou conduites, à moins qu’ils n’aient été
préparés correctement conformément à AWS F4.1 et AWS A6.0
(voir les Normes de Sécurité).
D Prendre garde aux incendies et toujours avoir un extincteur à
proximité.
D Lire et comprendre les fiches de données de sécurité et les
instructions du fabricant concernant les adhésifs, les revêtements,
les nettoyants, les consommables, les produits de refroidissement,
les dégraisseurs, les flux et les métaux.
L’ACCUMULATION DE VAPEURS
peut causer des lésions ou la mort.
D Quand on n’utilise pas le gaz comprimé de
protection, fermer le robinet de la bouteille.
D Assurer toujours la ventilation des zones fer-
mées ou utiliser un appareil respiratoire avec
alimentation en air.
Les PIÈCES MOBILES peuvent
causer des blessures.
D Ne pas s’approcher des organes mobiles.
D Ne pas s’approcher des points de coincement
tels que des rouleaux de commande.
LE RAYONNEMENT DE L’ARC peut
brûler les yeux et la peau.
Le rayonnement de l’arc du procédé de soudage
génère des rayons visibles et invisibles intenses
(ultraviolets et infrarouges) susceptibles de provoquer des brûlures
dans les yeux et sur la peau. Des étincelles sont projetées pendant le
soudage.
D Porter un casque de soudage approuvé muni de verres filtrants
approprié pour protéger visage et yeux pendant le soudage
(voir ANSI Z49.1 et Z87.1 énuméré dans les normes de sécurité).
D Porter des lunettes de sécurité avec écrans latéraux même sous
votre casque.

OM-264 713 Page 4
D Avoir recours à des écrans protecteurs ou à des rideaux pour
protéger les autres contre les rayonnements les éblouissements
et les étincelles ; prévenir toute personne sur les lieux de ne pas
regarder l’arc.
D Porter un équipement de protection pour le corps fait d’un matériau
résistant et ignifuge (cuir, coton robuste, laine). La protection du
corps comporte des vêtements sans huile comme par ex. des
gants de cuir, une chemise solide, des pantalons sans revers, des
chaussures hautes et une casquette.
LES PIÈCES CHAUDES peuvent
provoquer des brûlures.
D Laisser refroidir le pistolet avant de le toucher.
D Ne pas toucher d’objets métalliques chauds.
D Abriter les objets métalliques contre tout con-
tact par les personnes à proximité.
Le BRUIT peut endommager l’ouie.
Le bruit des processus et des équipements peut
affecter l’ouïe.
D Vérifier si les niveaux de bruit excèdent les lim-
ites spécifiées par l’OSHA.
D Utiliser des bouche-oreilles ou des serre-tête antibruit approuvés si
le niveau de bruit est élevé.
D Avertir les personnes à proximité au sujet du danger inhérent au
bruit.
LES FILS DE SOUDAGE peuvent
provoquer des blessures.
D Éloigner les mains et le corps de la buse du pis-
tolet après avoir appuyé sur la gâchette.
LIRE LES INSTRUCTIONS.
D Lire et appliquer les instructions sur les
étiquettes et le Mode d’emploi avant
l’installation, l’utilisation ou l’entretien de
l’appareil. Lire les informations de sécurité au
début du manuel et dans chaque section.
D N’utiliser que les pièces de rechange recommandées par le cons-
tructeur.
D Effectuer l’entretien en respectant les manuels d’utilisation,
les normes industrielles et les codes nationaux, d’état et locaux.
2-3. Proposition californienne 65 Avertissements
Les équipements de soudage et de coupage produisent des
fumées et des gaz qui contiennent des produits chimiques
dont l’État de Californie reconnaît qu’ils provoquent des
malformations congénitales et, dans certains cas, des
cancers. (Code de santé et de sécurité de Californie, chapitre
25249.5 et suivants)
Ce produit contient des éléments chimiques, dont le plomb,
reconnus par l’État de Californie pour leur caractère
cancérogène ainsi que provoquant des malformations
congénitales ou autres problèmes de procréation. Se laver
les mains après toute manipulation.
2-4. Principales normes de sécurité
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
is available as a free download from the American Welding Society at
http://www.aws.org or purchased from Global Engineering Documents
(phone: 1-877-413-5184, website: www.global.ihs.com).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protec-
tion, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036 (phone: 212-642-4900, web-
site: www.ansi.org).
Safe Practices for the Preparation of Containers and Piping for Welding
and Cutting, American Welding Society Standard AWS F4.1, from Glob-
al Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184, website: www.glo-
bal.ihs.com).
Safe Practices for Welding and Cutting Containers that have Held Com-
bustibles, American Welding Society Standard AWS A6.0, from Global
Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184,
website: www.global.ihs.com).
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protec-
tion Association, Quincy, MA 02269 (phone: 1-800-344-3555, website:
www.nfpa.org and www. sparky.org).
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1,
from Compressed Gas Association, 14501 George Carter Way, Suite
103, Chantilly, VA 20151 (phone: 703-788-2700, website:
www.cganet.com).
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, CSA Standard
W117.2, from Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 5060
Spectrum Way, Suite 100, Ontario, Canada L4W 5NS (phone:
800-463-6727, website: www.csa-international.org).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protec-
tion, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036 (phone: 212-642-4900, web-
site: www.ansi.org).
Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot
Work, NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire Protection Association,
Quincy, MA 02269 (phone: 1-800-344-3555, website: www.nfpa.org.
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Standards for General Indus-
try, Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1910, Subpart Q,
and Part 1926, Subpart J, from U.S. Government Printing Office, Super-
intendent of Documents, P.O. Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250-7954
(phone: 1-866-512-1800) (there are 10 OSHA Regional Offices—
phone for Region 5, Chicago, is 312-353-2220, website:
www.osha.gov).
2-5. Informations relatives aux CEM
Le courant électrique qui traverse tout conducteur génère des champs
électromagnétiques (CEM) à certains endroits. Le courant de soudage
crée un CEM autour du circuit et du matériel de soudage. Le courant
issu d’un soudage à l’arc (et de procédés connexes, y compris le
soudage par points, le gougeage, le découpage plasma et les
opérations de chauffage par induction) crée un champ
électromagnétique (CEM) autour du circuit de soudage. Des mesures
de protection pour les porteurs d’implants médicaux doivent être prises:
Limiter par exemple tout accès aux passants ou procéder à une
évaluation des risques individuels pour les soudeurs. Tous les
soudeurs doivent appliquer les procédures suivantes pour minimiser
l’exposition aux CEM provenant du circuit de soudage:
1 Rassembler les câbles en les torsadant ou en les attachant avec
du ruban adhésif ou avec une housse.
2 Ne pas se tenir au milieu des câbles de soudage. Disposer les
câbles d’un côté et à distance de l’opérateur.
3 Ne pas courber et ne pas entourer les câbles autour de votre
corps.

OM-264 713 Page 5
4 Maintenir la tête et le torse aussi loin que possible du matériel du
circuit de soudage.
5 Connecter la pince sur la pièce aussi près que possible de la
soudure.
6 Ne pas travailler à proximité d’une source de soudage, ni
s’asseoir ou se pencher dessus.
7 Ne pas souder tout en portant la source de soudage ou le
dévidoir.
En ce qui concerne les implants médicaux :
Les porteurs d’implants doivent d’abord consulter leur médecin avant
de s’approcher des opérations de soudage à l’arc, de soudage par
points, de gougeage, du coupage plasma ou de chauffage par induc-
tion. Si le médecin approuve, il est recommandé de suivre les procédu-
res précédentes.

OM-264 713 Page 6

OM-264 713 Page 7
SECTION 3 − DEFINITIONS
3-1. Additional Safety Symbols And Definitions
. Some symbols are found only on CE products.
Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards as shown by the symbols.
Safe1 2012−05
3-2. Miscellaneous Symbols And Definitions
V
Volts
I
1
Primary Current
A
Amperes
X
Duty Cycle
I
2
Rated Welding
Current
U
2
Conventional
Load Voltage
U
1
Primary Voltage
IP
Degree Of
Protection
Percent
Notes

OM-264 713 Page 8
SECTION 4 − SPECIFICATIONS
4-1. Gun Specifications
Wire Diameter
Range
Approximate
Wire Feed
Range
Cooling
Method
Maximum
Spool Size
Weld Circuit Rating
Overall
Dimensions
Weight
.030 Thru 1/16 in.
(0.8 Thru 1.6 mm)
Aluminum Wire
70 To 900 ipm
(1.7 To 23
mpm)
Air Cooled
4 in. (102 mm)
Diameter
100 Volts, 200 Amperes,
100% Duty Cycle
Using Argon Shielding Gas
Length: 15-3/8 in.
(390 mm)
Width: 2-1/2 in.
(64 mm)
Height: 10-3/4 in.
(273 mm)
2.9 lb
(1.3 kg)
Gun Only
15A Model:
9 lb (4.1 kg)
Gun With Cable
30A Model:
14 lb (6.4 kg)
Gun With Cable
4-2. Duty Cycle And Overheating
Duty Cycle is percentage of 10 min-
utes that unit can weld at rated load
without overheating.
NOTICE − Exceeding duty cycle
can damage unit and void warranty.
Ref. sduty1 5/95
6 Minutes Welding 4 Minutes Resting
Continuous Welding
Air-Cooled Models
100% Duty Cycle At 200 Amperes Using Argon 60% Duty Cycle At 250 Amperes Using Argon
SECTION 5 − INSTALLATION
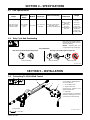
5-1. Connecting To 24 Volt Weld Control
Ref. T0050 / 150 917-G
1 Gas Hose
Connect fitting to regulator/flowme-
ter (see Section 5-7).
2 24 Volt Weld Control
3 Trigger Control Cord
Insert plug into receptacle, and
tighten threaded collar.
4 Weld Cable
Connect to positive (+) weld output
terminal on welding power source
according to its Owner’s Manual.
Tools Needed:
1-1/8, 5/8 in.
1
2
3
4

OM-264 713 Page 9
5-2. Connecting To 115 Volt Weld Control
Ref. T0050 / 149 549-A / 149 966-J
1 115 Volt Weld Control
2 Gas Hose
Connect to regulator/flowmeter.
3 Trigger Control Cord
Insert plug into receptacle, and
tighten threaded collar.
4 Weld Cable
5 Positive (+) Weld Output
Terminal In Control
Connect weld cable to positive (+)
weld output terminal in weld control.
Reinstall weld control wrapper.
Left Side
Wrapper Off
5
6
1
2
3
4
3
Tools Needed:
1-1/8, 5/8 in.
5-3. Removing Top Cover Of Pistol Grip Gun
1 Top Cover Triangular Boss
Push up on triangular boss to open
door. Door hinges on handle.
To open door fully, push up on door
until it clicks into position.
. If door is pushed too far it will
separate from handle. If this
happens the door can be rein-
stalled.
Push door back into original posi-
tion to close.
T0054-B
1

OM-264 713 Page 10
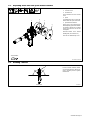
5-4. Installing Wire Spool And Threading Welding Wire
Ref. T0052-B / T0061
1 Pressure Arm Lever
. To release drive roll pressure,
pull back on pressure arm
lever. While pulled back, shift to
left onto shoulder to lock into
place.
2 Canister Inlet Guide
3 Drive Roll Grove
4 Top Cover
5 Thumbscrew (Canister
Rotation)
Loosen thumbscrew to rotate can-
ister (see Section 5-6).
6 Canister
7 Spool Brake Thumbnut
If necessary, turn thumbnut coun-
terclockwise slightly to install spool.
8 Canister Cover
9 Thumbscrew (Canister Cover)
Loosen thumbscrew and remove
cover.
10 Wire Spool
Loosen wire from spool, cut off bent
wire, and pull 6 in. (150 mm) of wire
off spool.
11 Contact Tip
Thread wire through canister inlet
guide, along drive roll groove, and
out contact tip.
Install spool so wire feeds off
bottom.
Close and secure pressure arm
lever.
Reinstall top cover and canister
cover.
Tools Needed:
11
4
6
7
8
9
10
5
1
2
3

OM-264 713 Page 11
5-5. Adjusting Drive Roll And Spool Brake Pressure
Ref. T0051 / T0052-B
Tools Needed:
1
2
4
3
1 Top Cover
2 Canister Cover
3 Thumbscrew
Loosen thumbscrew and remove
cover.
4 Spool
Cut welding wire off at contact tip.
Retract wire onto spool and secure.
5 Spool Brake Thumbnut
Grasp spool in one hand and turn
while adjusting spool brake thumb-
nut. When a slight force is needed
to turn spool, tension is set. Do not
overtighten.
Reinstall canister cover. Thread
welding wire (see Section 5-4).
Turn Off unit. Reinstall top cover.
5
5-6. Rotating Canister
150 433-A
1 Canister
Loosen canister rotation thumb-
screw (see Section 5-4). Move can-
ister to desired position. Tighten
thumbscrew.
1
Rear View

OM-264 713 Page 12
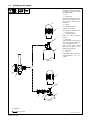
5-7. Installing Gas Supply
ssb3.1* 5/94 − 158 697-A
Obtain gas cylinder and chain to
running gear, wall, or other station-
ary support so cylinder cannot fall
and break off valve.
1 Cap
2 Cylinder Valve
Remove cap, stand to side of valve,
and open valve slightly. Gas flow
blows dust and dirt from valve.
Close valve.
3 Cylinder
4 Regulator/Flowmeter
Install so face is vertical.
. Delivery pressure range must
not exceed 60 psi.
5 Gas Hose Connection
Fitting has 5/8-18 right-hand
threads.
6 Flow Adjust
Typical flow rate is 20 cfh (cubic feet
per hour). Check wire manufactur-
er’s recommended flow rate.
Make sure flow adjust is closed
when opening cylinder to avoid
damage to the flowmeter.
7CO
2
Adapter
8 O-Ring
Install adapter with O-ring between
regulator/flowmeter and CO
2
cylinder.
Tools Needed:
1-1/8, 5/8 in.
CO
2
Gas
7 8
3
1
2
4
5
6
1
2
3
Argon Gas
OR

OM-264 713 Page 13
SECTION 6 − OPERATION
6-1. Gun Controls
1 Trigger
Press trigger to energize welding
power source contactor
(if applicable), start shielding gas
flow, and begin wire feed.
2 Wire Speed Control
Use control to fine adjust wire feed
speed set on wire feeder Weld
Speed control. The numbers
around the control are for reference
only.
1
2
Ref. T0050
6-2. Gun Pressure Roll Tension Setting
. Aluminum series specific -
Pressure roll tension setting
ensures smooth wire feeding
action.
. Gun Pressure Roll Tension is
factory set to 4XXX.
1 Pressure Roll Adjustment
Screw
Wire tension should be set to 4XXX
for 4000 series aluminum wire.
Rotate Pressure Roll Adjustment
Screw fully counterclockwise until
indicator line on adjustment knob
lines up with indicator line on handle
in the 4XXX position.
Wire tension should be set to 5XXX
for 5000 series aluminum and stain-
less wire.
Rotate Pressure Roll Adjustment
Screw fully clockwise until indicator
line on adjustment knob lines up
with indicator line on handle in the
5XXX position.
. Small diameter (.035) 5000
series wire may run better on
the 4XXX setting.
1
Ref. T0050
Tools Needed:

OM-264 713 Page 14
6-3. Shielding Gas
sb5.1 6/92 − S-0621-C / Ref. T0050
1 Shielding Gas Cylinder
2 Valve
3 Gun Trigger
Open valve on cylinder just before
welding.
Gun trigger turns weld output and
gas flow on and off (see Section
6-1).
Close valve on cylinder when
finished welding.
1
2
3
SECTION 7 − MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
. Maintain more often
during severe conditions.
! Disconnect power
before maintaining.
n = Check Z = Change ~ = Clean l = Replace
* To be done by Factory Authorized Service Agent
Reference
Every
3
Months
l Damaged Or Unreadable
Labels
l Repair Or Replace
Cracked Weld Cable
~ Clean And Tighten Weld
Terminals
n Check Gun Cable
l Damaged Gas Hose l Damaged Or Cracked
Plug
Every
6
Months
~ Clean Drive Rolls ~ Blow Out Or Vacuum
Inside
After
Each
Spool
Of Wire
~ Gun Liner

OM-264 713 Page 15
7-1. Replacing Canister Inlet Guide
Ref. T0051-B / T0052-B
1 Top Cover
2 Pressure Arm Lever
Cut off welding wire where it enters
pressure roll assembly area.
3 Nozzle
Pull wire out nozzle.
4 Thumbscrew
5 Canister Cover
Loosen thumbscrew and remove
cover.
6 Wire Spool
7 Spool Brake Thumbnut
Loosen thumbnut, retract wire onto
spool, secure, and remove spool.
8 Canister Inlet Guide
Turn counterclockwise to remove.
Install new guide.
Reinstall spool and thread welding
wire (see Section 5-4).
Close pressure arm lever. Adjust
spool brake pressure and drive roll
pressure if necessary.
Reinstall covers.
Tools Needed:
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
3
7-2. Replacing Spool Canister
Ref. T0051-B
1 Top Cover
2 Pressure Arm Lever
Cut off welding wire where it enters
pressure roll assembly area.
3 Nozzle
Pull wire out nozzle.
4 Thumbscrew (Canister
Rotation)
Turn thumbscrew counterclock-
wise three full turns.
5 Spool Canister
Remove as shown. Push new can-
ister into wire drive housing until ful-
ly seated. Tighten thumbscrew.
Install spool and thread welding
wire (see Section 5-4).
Close pressure arm lever. Adjust
spool brake pressure and drive roll
pressure as necessary.
Reinstall covers.
Tools Needed:
1
3
5
2
4

OM-264 713 Page 16
7-3. Replacing Head Tube Liner
Ref. T0055-B
If changing wire size, change gun
drive roll accordingly.
1 Cover
2 Head Tube
Remove head tube from gun.
3 Liner
Pull liner out of head tube.
Insert new liner into head tube and
reinstall head tube onto gun.
. A twisting motion may be need-
ed to feed liner thru head tube.
2
3
1
2
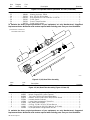
7-4. Removing Diffuser In Air-Cooled Pistol-Grip Guns
Ref. T0027
! Turn Off welding power source.
! Water in gun parts can cause elec-
tric shock and can lower weld
quality.
1 Nozzle
2 FasTip
To remove, see Section 7-5.
3 Diffuser
Remove diffuser and replace.
Tools Needed:
3/8 in.
12 3
Air Cooled Head Tube Assembly
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
La page charge ...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
Miller MF410034T Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire
- Ce manuel convient également à
dans d''autres langues
- English: Miller MF410034T Owner's manual
Documents connexes
-
Miller MF370133T Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller ME470121T Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller ME140205T Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller MF510108T Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller SPOOLMATIC 15A Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller SPOOLMATIC 15A Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller MH170316T Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller MG460083T Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller TWIN WIRE SUBARC TORCHES CE Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller TWIN WIRE SUBARC TORCHES CE Le manuel du propriétaire



































