Miller LC499801 Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire
Ce manuel convient également à

OM-210 540C
September 2003
Auto Axcess 450
Processes
Description
MIG (GMAW) Welding
Pulsed MIG (GMAW-P)
Flux Cored (FCAW) Welding
Automatic Welding
Automatic Welding Interface And
Arc Welding Power Source
Visit our website at
www.MillerWelds.com

Miller Electric manufactures a full line
of welders and welding related equipment.
For information on other quality Miller
products, contact your local Miller distributor to receive the latest full
line catalog or individual catalog sheets. To locate your nearest
distributor or service agency call 1-800-4-A-Miller, or visit us at
www.MillerWelds.com on the web.
Thank you and congratulations on choosing Miller. Now you can get
the job done and get it done right. We know you don’t have time to do
it any other way.
That’s why when Niels Miller first started building arc welders in 1929,
he made sure his products offered long-lasting value and superior
quality. Like you, his customers couldn’t afford anything less. Miller
products had to be more than the best they could be. They had to be the
best you could buy.
Today, the people that build and sell Miller products continue the
tradition. They’re just as committed to providing equipment and service
that meets the high standards of quality and value established in 1929.
This Owner’s Manual is designed to help you get the most out of your
Miller products. Please take time to read the Safety precautions. They
will help you protect yourself against potential hazards on the worksite.
We’ve made installation and operation quick
and easy. With Miller you can count on years
of reliable service with proper maintenance.
And if for some reason the unit needs repair,
there’s a Troubleshooting section that will
help you figure out what the problem is. The
parts list will then help you to decide the
exact part you may need to fix the problem.
Warranty and service information for your
particular model are also provided.
Miller is the first welding
equipment manufacturer in
the U.S.A. to be registered to
the ISO 9001:2000 Quality
System Standard.
Working as hard as you do
− every power source from
Miller is backed by the most
hassle-free warranty in the
business.
From Miller to You
Mil_Thank 7/03

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-1. Symbol Usage 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-3. Additional Symbols For Installation, Operation, And Maintenance 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-4. California Proposition 65 Warnings 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-5. Principal Safety Standards 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-6. EMF Information 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 2 − CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ − À LIRE AVANT UTILISATION 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-1. Signification des symboles 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-2. Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-3. Autres symboles relatifs à l’installation, au fonctionnement et à l’entretien de l’appareil. 7. . . . . . . . . . .
2-4. Principales normes de sécurité 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-5. Information sur les champs électromagnétiques 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 3 − INSTALLATION 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-1. Specifications 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-2. Dimensions And Weight 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-3. Duty Cycle And Overheating 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-4. Volt-Ampere Curves 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-5. Selecting A Location 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-6. Connection Diagram 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-7. Rear Panel Receptacles And Circuit Breakers 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-8. Connecting To Weld Terminals 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-9. Selecting Weld Cable Sizes* 13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-10. Peripheral Receptacle Functions 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-11. Electrical Service Guide 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-12. Connecting Input Power 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-13. Touch Sensor Operation 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 4 − OPERATION 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-1. Operational Terms 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-2. Front Panel Controls (See Section 4-3) 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-3. Front Panel Controls - Continued (See Section 4-2) 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-4. Front Panel Switches 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-5. Special Teach Mode (Use With Section 4-6) 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-6. Special Teach Mode (Use With Section 4-5) 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-7. Pulse Welding Terms 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-8. Teach Data Points 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-9. Pulse Weld Data Library − .035 Steel, 90% Argon, 10% CO2 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-10. Pulse Weld Data Library − .035 Steel, 98% Argon, 2% CO2 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-11. Pulse Weld Data Library − .035 Steel, 98% Argon, 2% Oxygen 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-12. Pulse Weld Data Library − .045 Steel, 90% Argon, 10% CO2 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-13. Pulse Weld Data Library − .045 Steel, 98% Argon, 2% CO2 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-14. Pulse Weld Data Library − .045 Steel, 98% Argon, 2% Oxygen 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-15. Pulse Weld Data Library − .052 Steel, 90% Argon, 10% CO2 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-16. Pulse Weld Data Library − .052 Steel, 98% Argon, 2% CO2 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-17. Pulse Weld Data Library − .052 Steel, 98% Argon, 2% Oxygen 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-18. Pulse Weld Data Library − .062 Steel, 90% Argon, 10% CO2 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-19. Pulse Weld Data Library − .062 Steel, 98% Argon, 2% CO2 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-20. Pulse Weld Data Library − .062 Steel, 98% Argon, 2% Oxygen 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-21. Pulse Weld Data Library − .045 Metal Core, 90% Argon, 10% CO2 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-22. Pulse Weld Data Library − .052 Metal Core, 90% Argon, 10% CO2 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-23. Pulse Weld Data Library − .062 Metal Core, 90% Argon, 10% CO2 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-24. Set Value Mode 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 5 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR SERVICING 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-1. Symbol Usage 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-2. Servicing Hazards 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-3. California Proposition 65 Warnings 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-4. EMF Information 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 6 − MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-1. Routine Maintenance 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-2. Blowing Out Inside Of Unit 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-3. Front Panel Error Messages 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-4. Removing Cover and Measuring Input Capacitor Voltage 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-5. Weld Process Board PC4 Diagnostic LED’s 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-6. Diagnostic LED’s On Process Board PC4 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-7. Motor Board PC6 Diagnostic LED’s And Dip Switch Settings 33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-8. Diagnostic LED’s On Motor Board PC6 33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-9. Display Module PC7 Diagnostic LED’s 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-10. Diagnostic LED’s On Display Module PC7 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-11. Automation Module PC9 Diagnostic LED’s 35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-12. Diagnostic LED’s On Automation Module PC9 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-13. Network Status Table 37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-14. Robot Calibration Mode 38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-15. Robot Override Mode 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-16. Troubleshooting 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
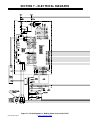
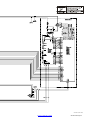
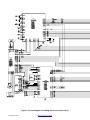
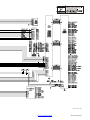
SECTION 7 − ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
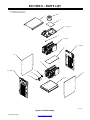
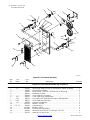
SECTION 8 − PARTS LIST 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
WARRANTY

OM-210 540 Page 1
Return To Table Of Contents
SECTION 1 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING
som _8/03
1-1. Symbol Usage
Means Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards
with this procedure! The possible hazards are shown in
the adjoining symbols.
Y Marks a special safety message.
. Means “Note”; not safety related.
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! possible
ELECTRIC SHOCK, MOVING PARTS, and HOT PARTS hazards.
Consult symbols and related instructions below for necessary actions
to avoid the hazards.
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards
Y The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual to
call attention to and identify possible hazards. When you see
the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions to
avoid the hazard. The safety information given below is only
a summary of the more complete safety information found in
the Safety Standards listed in Section 1-5. Read and follow all
Safety Standards.
Y Only qualified persons should install, operate, maintain, and
repair this unit.
Y During operation, keep everybody, especially children, away.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal shocks
or severe burns. The electrode and work circuit is
electrically live whenever the output is on. The input
power circuit and machine internal circuits are also
live when power is on. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the
wire, wire reel, drive roll housing, and all metal parts touching the
welding wire are electrically live. Incorrectly installed or improperly
grounded equipment is a hazard.
D Do not touch live electrical parts.
D Wear dry, hole-free insulating gloves and body protection.
D Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulating mats
or covers big enough to prevent any physical contact with the work
or ground.
D Do not use AC output in damp areas, if movement is confined, or if
there is a danger of falling.
D Use AC output ONLY if required for the welding process.
D If AC output is required, use remote output control if present on
unit.
D Disconnect input power or stop engine before installing or
servicing this equipment. Lockout/tagout input power according to
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 (see Safety Standards).
D Properly install and ground this equipment according to its
Owner’s Manual and national, state, and local codes.
D Always verify the supply ground − check and be sure that input
power cord ground wire is properly connected to ground terminal in
disconnect box or that cord plug is connected to a properly
grounded receptacle outlet.
D When making input connections, attach proper grounding conduc-
tor first − double-check connections.
D Frequently inspect input power cord for damage or bare wiring −
replace cord immediately if damaged − bare wiring can kill.
D Turn off all equipment when not in use.
D Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or poorly spliced cables.
D Do not drape cables over your body.
D If earth grounding of the workpiece is required, ground it directly
with a separate cable.
D Do not touch electrode if you are in contact with the work, ground,
or another electrode from a different machine.
D Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair or replace damaged
parts at once. Maintain unit according to manual.
D Wear a safety harness if working above floor level.
D Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
D Clamp work cable with good metal-to-metal contact to workpiece
or worktable as near the weld as practical.
D Insulate work clamp when not connected to workpiece to prevent
contact with any metal object.
D Do not connect more than one electrode or work cable to any
single weld output terminal.
SIGNIFICANT DC VOLTAGE exists after removal of
input power on inverters.
D Turn Off inverter, disconnect input power, and discharge input
capacitors according to instructions in Maintenance Section
before touching any parts.
Welding produces fumes and gases. Breathing
these fumes and gases can be hazardous to your
health.
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous.
D Keep your head out of the fumes. Do not breathe the fumes.
D If inside, ventilate the area and/or use exhaust at the arc to remove
welding fumes and gases.
D If ventilation is poor, use an approved air-supplied respirator.
D Read the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) and the
manufacturer’s instructions for metals, consumables, coatings,
cleaners, and degreasers.
D Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated, or while
wearing an air-supplied respirator. Always have a trained watch-
person nearby. Welding fumes and gases can displace air and
lower the oxygen level causing injury or death. Be sure the breath-
ing air is safe.
D Do not weld in locations near degreasing, cleaning, or spraying op-
erations. The heat and rays of the arc can react with vapors to form
highly toxic and irritating gases.
D Do not weld on coated metals, such as galvanized, lead, or
cadmium plated steel, unless the coating is removed from the weld
area, the area is well ventilated, and if necessary, while wearing an
air-supplied respirator. The coatings and any metals containing
these elements can give off toxic fumes if welded.

OM-210 540 Page 2
Return To Table Of Contents
Arc rays from the welding process produce intense
visible and invisible (ultraviolet and infrared) rays
that can burn eyes and skin. Sparks fly off from the
weld.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin.
D Wear a welding helmet fitted with a proper shade of filter to protect
your face and eyes when welding or watching (see ANSI Z49.1
and Z87.1 listed in Safety Standards).
D Wear approved safety glasses with side shields under your
helmet.
D Use protective screens or barriers to protect others from flash and
glare; warn others not to watch the arc.
D Wear protective clothing made from durable, flame-resistant mate-
rial (leather and wool) and foot protection.
Welding on closed containers, such as tanks,
drums, or pipes, can cause them to blow up. Sparks
can fly off from the welding arc. The flying sparks, hot
workpiece, and hot equipment can cause fires and
burns. Accidental contact of electrode to metal objects can cause
sparks, explosion, overheating, or fire. Check and be sure the area is
safe before doing any welding.
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
D Protect yourself and others from flying sparks and hot metal.
D Do not weld where flying sparks can strike flammable material.
D Remove all flammables within 35 ft (10.7 m) of the welding arc. If
this is not possible, tightly cover them with approved covers.
D Be alert that welding sparks and hot materials from welding can
easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas.
D Watch for fire, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
D Be aware that welding on a ceiling, floor, bulkhead, or partition can
cause fire on the hidden side.
D Do not weld on closed containers such as tanks, drums, or pipes,
unless they are properly prepared according to AWS F4.1 (see
Safety Standards).
D Connect work cable to the work as close to the welding area as
practical to prevent welding current from traveling long, possibly
unknown paths and causing electric shock and fire hazards.
D Do not use welder to thaw frozen pipes.
D Remove stick electrode from holder or cut off welding wire at
contact tip when not in use.
D Wear oil-free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy
shirt, cuffless trousers, high shoes, and a cap.
D Remove any combustibles, such as a butane lighter or matches,
from your person before doing any welding.
FLYING METAL can injure eyes.
D Welding, chipping, wire brushing, and grinding
cause sparks and flying metal. As welds cool,
they can throw off slag.
D Wear approved safety glasses with side
shields even under your welding helmet.
BUILDUP OF GAS can injure or kill.
D Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
D Always ventilate confined spaces or use
approved air-supplied respirator.
HOT PARTS can cause severe burns.
D Do not touch hot parts bare handed.
D Allow cooling period before working on gun or
torch.
MAGNETIC FIELDS can affect pacemakers.
D Pacemaker wearers keep away.
D Wearers should consult their doctor before
going near arc welding, gouging, or spot
welding operations.
NOISE can damage hearing.
Noise from some processes or equipment can
damage hearing.
D Wear approved ear protection if noise level is
high.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high
pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can explode. Since
gas cylinders are normally part of the welding
process, be sure to treat them carefully.
CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
D Protect compressed gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechani-
cal shocks, slag, open flames, sparks, and arcs.
D Install cylinders in an upright position by securing to a stationary
support or cylinder rack to prevent falling or tipping.
D Keep cylinders away from any welding or other electrical circuits.
D Never drape a welding torch over a gas cylinder.
D Never allow a welding electrode to touch any cylinder.
D Never weld on a pressurized cylinder − explosion will result.
D Use only correct shielding gas cylinders, regulators, hoses, and fit-
tings designed for the specific application; maintain them and
associated parts in good condition.
D Turn face away from valve outlet when opening cylinder valve.
D Keep protective cap in place over valve except when cylinder is in
use or connected for use.
D Read and follow instructions on compressed gas cylinders,
associated equipment, and CGA publication P-1 listed in Safety
Standards.

OM-210 540 Page 3
Return To Table Of Contents
1-3. Additional Symbols For Installation, Operation, And Maintenance
FIRE OR EXPLOSION hazard.
D Do not install or place unit on, over, or near
combustible surfaces.
D Do not install unit near flammables.
D Do not overload building wiring − be sure power supply system is
properly sized, rated, and protected to handle this unit.
FALLING UNIT can cause injury.
D Use lifting eye to lift unit only, NOT running
gear, gas cylinders, or any other accessories.
D Use equipment of adequate capacity to lift and
support unit.
D If using lift forks to move unit, be sure forks are
long enough to extend beyond opposite side of
unit.
OVERUSE can cause OVERHEATING
D Allow cooling period; follow rated duty cycle.
D Reduce current or reduce duty cycle before
starting to weld again.
D Do not block or filter airflow to unit.
STATIC (ESD) can damage PC boards.
D Put on grounded wrist strap BEFORE handling
boards or parts.
D Use proper static-proof bags and boxes to
store, move, or ship PC boards.
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
D Keep away from moving parts.
D Keep away from pinch points such as drive
rolls.
WELDING WIRE can cause injury.
D Do not press gun trigger until instructed to do
so.
D Do not point gun toward any part of the body,
other people, or any metal when threading
welding wire.
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
D Keep away from moving parts such as fans.
D Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards
closed and securely in place.
H.F. RADIATION can cause interference.
D High-frequency (H.F.) can interfere with radio
navigation, safety services, computers, and
communications equipment.
D Have only qualified persons familiar with
electronic equipment perform this installation.
D The user is responsible for having a qualified electrician prompt-
ly correct any interference problem resulting from the installa-
tion.
D If notified by the FCC about interference, stop using the
equipment at once.
D Have the installation regularly checked and maintained.
D Keep high-frequency source doors and panels tightly shut, keep
spark gaps at correct setting, and use grounding and shielding to
minimize the possibility of interference.
ARC WELDING can cause interference.
D Electromagnetic energy can interfere with
sensitive electronic equipment such as
computers and computer-driven equipment
such as robots.
D Be sure all equipment in the welding area is
electromagnetically compatible.
D To reduce possible interference, keep weld cables as short as
possible, close together, and down low, such as on the floor.
D Locate welding operation 100 meters from any sensitive elec-
tronic equipment.
D Be sure this welding machine is installed and grounded
according to this manual.
D If interference still occurs, the user must take extra measures
such as moving the welding machine, using shielded cables,
using line filters, or shielding the work area.
1-4. California Proposition 65 Warnings
Y Welding or cutting equipment produces fumes or gases which
contain chemicals known to the State of California to cause
birth defects and, in some cases, cancer. (California Health &
Safety Code Section 25249.5 et seq.)
Y Battery posts, terminals and related accessories contain lead
and lead compounds, chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer and birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
For Gasoline Engines:
Y Engine exhaust contains chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive
harm.
For Diesel Engines:
Y Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known
to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and
other reproductive harm.

OM-210 540 Page 4
Return To Table Of Contents
1-5. Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
from American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd, Miami FL 33126
(phone: 305-443-9353, website: www.aws.org).
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cut-
ting of Containers and Piping, American Welding Society Standard
AWS F4.1, from American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd, Mi-
ami, FL 33126 (phone: 305-443-9353, website: www.aws.org).
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protec-
tion Association, P.O. Box 9101, 1 Battery March Park, Quincy, MA
02269−9101 (phone: 617−770−3000, website: www.nfpa.org and www.
sparky.org).
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1,
from Compressed Gas Association, 1735 Jefferson Davis Highway,
Suite 1004, Arlington, VA 22202−4102 (phone: 703−412−0900, web-
site: www.cganet.com).
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, CSA Standard W117.2, from
Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale
Boulevard, Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3 (phone:
800−463−6727 or in Toronto 416−747−4044, website: www.csa−in-
ternational.org).
Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protection,
ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute, 11
West 42nd Street, New York, NY 10036−8002 (phone: 212−642−4900,
website: www.ansi.org).
Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot
Work, NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire Protection Association,
P.O. Box 9101, 1 Battery March Park, Quincy, MA 02269−9101 (phone:
617−770−3000, website: www.nfpa.org and www. sparky.org).
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Standards for General Indus-
try, Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1910, Subpart Q,
and Part 1926, Subpart J, from U.S. Government Printing Office, Super-
intendent of Documents, P.O. Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250 (there
are 10 Regional Offices−−phone for Region 5, Chicago, is
312−353−2220, website: www.osha.gov).
1-6. EMF Information
Considerations About Welding And The Effects Of Low Frequency
Electric And Magnetic Fields
Welding current, as it flows through welding cables, will cause electro-
magnetic fields. There has been and still is some concern about such
fields. However, after examining more than 500 studies spanning 17
years of research, a special blue ribbon committee of the National
Research Council concluded that: “The body of evidence, in the
committee’s judgment, has not demonstrated that exposure to power-
frequency electric and magnetic fields is a human-health hazard.”
However, studies are still going forth and evidence continues to be
examined. Until the final conclusions of the research are reached, you
may wish to minimize your exposure to electromagnetic fields when
welding or cutting.
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the following
procedures:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them.
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cables around your body.
4. Keep welding power source and cables as far away from opera-
tor as practical.
5. Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as possi-
ble.
About Pacemakers:
Pacemaker wearers consult your doctor first. If cleared by your doctor,
then following the above procedures is recommended.

OM-210 540 Page 5
Revenez à la table des matières
SECTION 2 − CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ − À LIRE AVANT
UTILISATION
som_fre 8/03
2-1. Signification des symboles
Signifie « Mise en garde. Faire preuve de vigilance. »
Cette procédure présente des risques identifiés par les
symboles adjacents aux directives.
Y Identifie un message de sécurité particulier.
. Signifie « NOTA » ; n’est pas relatif à la sécurité.
Ce groupe de symboles signifie « Mise en garde. Faire preuve de vigi-
lance. » Il y a des dangers liés aux CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES, aux
PIÈCES EN MOUVEMENT et aux PIÈCES CHAUDES. Se reporter
aux symboles et aux directives ci-dessous afin de connaître les me-
sures à prendre pour éviter tout danger.
2-2. Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc
Y Les symboles ci-après sont utilisés tout au long du présent
manuel pour attirer l’attention sur les dangers potentiels et les
identifier. Lorsqu’on voit un symbole, faire preuve de vigilance et
suivre les directives mentionnées afin d’éviter tout danger. Les
consignes de sécurité énoncées ci-après ne font que résumer le
contenu des normes de sécurité mentionnées à la section 2-4.
Lire et respecter toutes ces normes.
Y L’installation, l’utilisation, l’entretien et les réparations ne doi-
vent être confiés qu’à des personnes qualifiées.
Y Pendant l’utilisation de l’appareil, tenir à l’écart toute personne,
en particulier les enfants.
LES DÉCHARGES ÉLECTRIQUES
peuvent être mortelles.
Un simple contact avec des pièces sous tension peut
causer une électrocution ou des blessures graves.
L’électrode et le circuit de soudage sont sous tension
dès que l’appareil est en fonctionnement. Le circuit
d’entrée et les circuits internes de l’appareil sont également sous tension.
En soudage semi−automatique ou automatique, le fil, le dévidoir, le
logement des galets d’entraînement et les pièces métalliques en contact
avec le fil de soudage sont sous tension. Tout matériel mal installé ou mal
mis à la terre présente un danger.
D Ne jamais toucher aux pièces électriques sous tension.
D Porter des gants et des vêtements de protection secs et exempts de
trous.
D S’isoler de la pièce et de la terre au moyen de tapis ou autres disposi-
tifs isolants suffisamment grands pour empêcher tout contact
physique avec la pièce ou la terre.
D Ne pas se servir d’une source de courant alternatif dans les zones humi-
des, les endroits confinés ou là où on risque de tomber.
D Ne se servir d’une source de courant alternatif QUE si le procédé de souda-
ge l’exige.
D Si l’utilisation d’une source de courant alternatif s’avère nécessaire, se ser-
vir de la fonction de télécommande si l’appareil en est équipé.
D Couper l’alimentation ou arrêter le moteur avant de procéder à l’instal-
lation, à la réparation ou à l’entretien de l’appareil. Couper/étiqueter
l’alimentation selon la norme OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 (voir les nor-
mes de sécurité).
D Installer et mettre à la terre correctement l’appareil conformément à
son manuel d’utilisation et aux codes nationaux, provinciaux et
municipaux.
D Toujours vérifier la terre du cordon d’alimentation − Vérifier et s’assu-
rer que le fil de terre du cordon d’alimentation est bien raccordé à la
borne de terre du sectionneur ou que la fiche du cordon est raccordée
à une prise correctement mise à la terre.
D Pour exécuter les branchements d’entrée, fixer d’abord le conducteur
de mise à la terre adéquat et contre−vérifier les connexions.
D Vérifier fréquemment le cordon d’alimentation et s’assurer qu’il n’est
ni endommagé ni dénudé ; le remplacer immédiatement s’il est en-
dommagé − tout câble dénudé peut causer une électrocution.
D Mettre l’appareil hors tension quand on ne l’utilise pas.
D Ne pas utiliser de câbles usés, endommagés, de calibre insuffisant ou
mal épissés.
D Ne pas s’enrouler les câbles autour du corps.
D Si la pièce soudée doit être mise à la terre, le faire directement avec un
câble distinct.
D Ne pas toucher l’électrode quand on est en contact avec la pièce, la
terre ou une électrode d’une autre machine.
D N’utiliser que du matériel en bon état. Réparer ou remplacer sur−le−
champ les pièces endommagées. Entretenir l’appareil conformément
au présent manuel.
D Porter un harnais de sécurité quand on travaille en hauteur.
D Maintenir solidement en place tous les panneaux et capots.
D Fixer le câble de retour de façon à obtenir un bon contact métal sur
métal avec la pièce à souder ou la table de travail, le plus près possible
de la soudure.
D Ne pas connecter plus d’une électrode ou plus d’un câble de masse à un
même terminal de sortie.
Il subsiste un COURANT CONTINU IMPORTANT
dans les convertisseurs après la suppression de
l’alimentation électrique.
D Arrêter les convertisseurs, débrancher le courant électrique et dé-
charger les condensateurs d’alimentation selon les instructions
énoncées à la section Entretien avant de toucher les pièces.
Le soudage génère des fumées et des gaz dont
l’inhalation peut être dangereuse pour la santé.
LES FUMÉES ET LES GAZ peuvent
être dangereux.
D Se tenir à distance des fumées et ne pas les inhaler.
D À l’intérieur, ventiler la zone et/ou utiliser un dispositif d’aspiration au
niveau de l’arc pour l’évacuation des fumées et des gaz de soudage.
D Si la ventilation est insuffisante, utiliser un respirateur à adduction
d’air agréé.
D Lire les fiches techniques de santé−sécurité (FTSS) et les instruc-
tions du fabricant concernant les métaux, les consommables, les
revêtements, les nettoyants et les dégraisseurs.
D Ne travailler dans un espace clos que s’il est bien ventilé ou porter un
respirateur à adduction d’air. Demander toujours à un surveillant dû-
ment formé de se tenir à proximité. Des fumées et des gaz de soudage
peuvent se substituer à l’air, abaisser la teneur en oxygène et causer
des lésions ou des accidents mortels. S’assurer que l’air est respira-
ble.
D Ne pas souder à proximité d’opérations de dégraissage, de nettoyage
ou de pulvérisation. La chaleur et les rayons de l’arc peuvent réagir en
présence de vapeurs et former des gaz hautement toxiques et irri-
tants.
D Ne pas souder de métaux munis d’un revêtement, tels que la tôle
d’acier galvanisée, plombée ou cadmiée, à moins que le revêtement
n’ait été enlevé dans la zone de soudage, que l’endroit soit bien venti-
lé, et si nécessaire, porter un respirateur à adduction d’air. Les
revêtements et tous les métaux renfermant ces éléments peuvent dé-
gager des fumées toxiques lorsqu’on les soude.

OM-210 540 Page 6
Revenez à la table des matières
Le rayonnement de l’arc génère des rayons visibles et
invisibles intenses (ultraviolets et infrarouges) suscep-
tibles de causer des brûlures oculaires et cutanées.
Des étincelles sont projetées pendant le soudage.
LES RAYONS DE L’ARC peuvent cau-
ser des brûlures oculaires et cuta-
nées.
D Porter un masque de soudage muni d’un filtre de la nuance adéquate
pour se protéger le visage et les yeux pendant le soudage ou pour re-
garder (voir les normes de sécurité ANSI Z49.1 et Z87.1).
D Porter des lunettes de sécurité à écrans latéraux sous le masque.
D Utiliser des écrans ou des barrières pour protéger les tiers de l’éclat
éblouissant ou aveuglant de l’arc ; leur demander de ne pas regarder
l’arc.
D Porter des vêtements de protection en matière durable et ignifuge
(cuir ou laine) et des chaussures de sécurité.
Le soudage effectué sur des récipients fermés tels que
des réservoirs, des fûts ou des conduites peut causer
leur éclatement. Des étincelles peuvent être projetées
de l’arc de soudure. La projection d’étincelles, les
pièces chaudes et les équipements chauds peuvent causer des
incendies et des brûlures. Le contact accidentel de l’électrode avec tout
objet métallique peut causer des étincelles, une explosion, un surchauf-
fement ou un incendie. Avant de commencer le soudage, vérifier et
s’assurer que l’endroit ne présente pas de danger.
LE SOUDAGE peut causer un incen-
die ou une explosion.
D Se protéger et protéger les tiers de la projection d’étincelles et de mé-
tal chaud.
D Ne pas souder à un endroit où des étincelles peuvent tomber sur des
substances inflammables.
D Placer toutes les substances inflammables à une distance de 10,7 m
de l’arc de soudage. En cas d’impossibilité, les recouvrir soigneuse-
ment avec des protections agréées.
D Des étincelles et des matières en fusion peuvent facilement passer
même par des fissures et des ouvertures de petites dimensions.
D Surveiller tout déclenchement d’incendie et tenir un extincteur à proxi-
mité.
D Le soudage effectué sur un plafond, un plancher, une paroi ou une
cloison peut déclencher un incendie de l’autre côté.
D Ne pas souder des récipients fermés tels que des réservoirs, des fûts
ou des conduites, à moins qu’ils n’aient été préparés conformément à
l’AWS F4.1 (voir les normes de sécurité).
D Brancher le câble sur la pièce le plus près possible de la zone de sou-
dage pour éviter que le courant ne circule sur une longue distance, par
des chemins inconnus, et ne cause des risques d’électrocution et d’in-
cendie.
D Ne pas utiliser le poste de soudage pour dégeler des conduites ge-
lées.
D En cas de non utilisation, enlever la baguette d’électrode du porte−
électrode ou couper le fil au raz du tube−contact.
D Porter des vêtements de protection exempts d’huile tels que des
gants en cuir, une chemise en tissu épais, des pantalons sans revers,
des chaussures montantes et un masque.
D Avant de souder, retirer tout produit combustible de ses poches, tel
qu’un briquet au butane ou des allumettes.
LES PARTICULES PROJETÉES peu-
vent blesser les yeux.
D Le soudage, le burinage, le passage de la pièce à
la brosse métallique et le meulage provoquent
l’émission d’étincelles et de particules métalli-
ques. Pendant leur refroidissement, les soudures risquent de projeter du
laitier.
D Porter des lunettes de sécurité à écrans latéraux agréés, même sous le
masque de soudage.
LES ACCUMULATIONS DE GAZ peu-
vent causer des blessures ou même
la mort.
D Couper l’alimentation en gaz protecteur en cas de
non utilisation.
D Veiller toujours à bien ventiler les espaces confinés ou porter un respira-
teur à adduction d’air agréé.
LES PIÈCES CHAUDES peuvent cau-
ser des brûlures graves.
D Ne pas toucher les pièces chaudes à main nue.
D Prévoir une période de refroidissement avant
d’utiliser le pistolet ou la torche.
LES CHAMPS MAGNÉTIQUES peuvent
perturber le fonctionnement des stimu-
lateurs cardiaques.
D Les personnes qui portent un stimulateur cardiaque
doivent se tenir à distance.
D Ils doivent consulter leur médecin avant de s’appro-
cher d’un lieu où on exécute des opérations de sou-
dage à l’arc, de gougeage ou de soudage par points.
LE BRUIT peut affecter l’ouïe.
Le bruit de certains processus et équipements peut
affecter l’ouïe.
D Porter des protecteurs d’oreille agréés si le niveau
sonore est trop élevé.
Les bouteilles de gaz protecteur contiennent du gaz
sous haute pression. Toute bouteille endommagée
peut exploser. Comme les bouteilles de gaz font
normalement partie du procédé de soudage, les
manipuler avec précaution.
Les BOUTEILLES endommagées
peuvent exploser.
D Protéger les bouteilles de gaz comprimé de la chaleur excessive, des
chocs mécaniques, du laitier, des flammes nues, des étincelles et des
arcs.
D Placer les bouteilles debout en les fixant dans un support stationnaire
ou dans un porte−bouteilles pour les empêcher de tomber ou de se
renverser.
D Tenir les bouteilles éloignées des circuits de soudage ou autres cir-
cuits électriques.
D Ne jamais poser une torche de soudage sur une bouteille de gaz.
D Ne jamais mettre une électrode de soudage en contact avec une bou-
teille de gaz.
D Ne jamais souder une bouteille contenant du gaz sous pression − elle
risquerait d’exploser.
D N’utiliser que les bouteilles de gaz protecteur, régulateurs, tuyaux et
raccords adéquats pour l’application envisagée ; les maintenir en bon
état, ainsi que les pièces connexes.
D Détourner la tête lorsqu’on ouvre la soupape d’une bouteille.
D Laisser le capuchon protecteur sur la soupape, sauf en cas d’utilisa-
tion ou de branchement de la bouteille
D Lire et suivre les instructions concernant les bouteilles de gaz compri-
mé, les équipements associés et les publications P−1 de la CGA,
mentionnées dans les normes de sécurité.

OM-210 540 Page 7
Revenez à la table des matières
2-3. Autres symboles relatifs à l’installation, au fonctionnement et à l’entretien de
l’appareil.
Risque D’INCENDIE OU D’EXPLO-
SION
D Ne pas placer l’appareil sur une surface inflam-
mable, ni au−dessus ou à proximité d’elle.
D Ne pas installer l’appareil à proximité de produits inflammables.
D Ne pas surcharger l’installation électrique − s’assurer que l’alimen-
tation est correctement dimensionnée et protégée avant de mettre
l’appareil en service.
LA CHUTE DE L’APPAREIL peut
blesser.
D N’utiliser que l’anneau de levage pour lever l’ap-
pareil. NE PAS utiliser le chariot, les bouteilles de
gaz ou tout autre accessoire.
D Utiliser un engin de capacité adéquate pour lever
l’appareil.
D Si on utilise un chariot élévateur pour déplacer l’unité, s’assurer que
les fourches sont suffisamment longues pour dépasser du côté op-
posé de l’appareil.
L’EMPLOI EXCESSIF peut FAIRE
SURCHAUFFER L’ÉQUIPEMENT.
D Prévoir une période de refroidissement ; respec-
ter le cycle opératoire nominal.
D Réduire le courant ou le cycle opératoire avant de
reprendre le soudage.
D Ne pas obstruer les orifices ou filtrer l’alimentation en air du poste.
LES CHARGES ÉLECTROSTATI-
QUES peuvent endommager les cir-
cuits imprimés.
D Mettre un bracelet antistatique AVANT de mani-
puler des cartes ou des pièces.
D Utiliser des pochettes et des boîtes antistatiques
pour stocker, déplacer ou expédier des cartes de
circuits imprimés.
LES PIÈCES MOBILES peuvent cau-
ser des blessures.
D Se tenir à l’écart des pièces mobiles.
D Se tenir à l’écart des points de coincement tels
que les dévidoirs.
LES FILS DE SOUDAGE peuvent cau-
ser des blessures.
D Ne pas appuyer sur la gâchette avant d’en avoir
reçu l’instruction.
D Ne pas diriger le pistolet vers soi, vers d’autres
personnes ou vers toute pièce mécanique en en-
gageant le fil de soudage.
LES ORGANES MOBILES peuvent
causer des blessures.
D Se tenir à l’écart des organes mobiles comme les
ventilateurs.
D Maintenir fermés et bien fixés les portes,
panneaux, recouvrements et dispositifs de
protection.
LE RAYONNEMENT HAUTE FRÉ-
QUENCE (H. F.) risque de causer des
interférences.
D Le rayonnement haute fréquence peut causer
des interférences avec les équipements de radio-
navigation et de communication, les services de
sécurité et les ordinateurs.
D Ne demander qu’à des personnes qualifiées familiarisées avec les
équipements électroniques de faire fonctionner l’installation.
D L’utilisateur est tenu de faire corriger rapidement par un électricien
qualifié les interférences causées par l’installation.
D Si la Federal Communications Commission signale des interféren-
ces, arrêter immédiatement l’appareil.
D Faire régulièrement contrôler et entretenir l’installation.
D Maintenir soigneusement fermés les panneaux et les portes des sour-
ces de haute fréquence, maintenir le jeu d’éclatement au réglage
adéquat et utiliser une terre et un blindage pour réduire les interféren-
ces éventuelles.
LE SOUDAGE À L’ARC peut causer
des interférences.
D L’énergie électromagnétique peut causer des
interférences avec l’équipement électronique
sensible tel que les ordinateurs et l’équipement
commandé par ordinateur tel que les robots.
D Veiller à ce que tout l’équipement de la zone de soudage soit compati-
ble au point de vue électromagnétique.
D Pour réduire la possibilité d’interférence, maintenir les câbles de sou-
dage aussi courts que possible, les grouper, et les poser aussi bas
que possible (par ex. : à terre).
D Veiller à souder à une distance de 100 mètres de tout équipement
électronique sensible.
D Veiller à ce que le poste de soudage soit posé et mis à la terre confor-
mément au présent manuel.
D En cas d’interférences après exécution des directives précédentes, il
incombe à l’utilisateur de prendre des mesures supplémentaires tel-
les que le déplacement du poste, l’utilisation de câbles blindés,
l’utilisation de filtres de ligne ou la pose de protecteurs dans la zone de
travail.
LES CHAMPS MAGNÉTIQUES peuvent
affecter les stimulateurs cardiaques.
D Porteurs de stimulateur cardiaque, restez à dis-
tance.
D Les porteurs d’un stimulateur cardiaque doivent
d’abord consulter leur médecin avant de s’appro-
cher des opérations de soudage à l’arc, de gou-
geage ou de soudage par points.

OM-210 540 Page 8
Revenez à la table des matières
2-4. Principales normes de sécurité
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, norme ANSI Z49.1,
de l’American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd, Miami FL 33126
(téléphone : (305) 443−9353, site Web : www.aws.org).
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cut-
ting of Containers and Piping, norme American Welding Society AWS
F4.1, de l’American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd, Miami, FL
33126 (téléphone : (305) 443−9353, site Web : www.aws.org).
National Electrical Code, norme NFPA 70, de la National Fire Protection
Association, P.O. Box 9101, 1 Battery March Park, Quincy, MA
02269−9101 (téléphone : (617) 770−3000, sites Web : www.nfpa.org et
www.sparky.org).
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, brochure CGA P−1,
de la Compressed Gas Association, 1735 Jefferson Davis Highway,
Suite 1004, Arlington, VA 22202−4102 (téléphone : (703) 412−0900,
site Web : www.cganet.com).
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, norme CSA W117.2, de la Ca-
nadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 178 boulevard
Rexdale, Rexdale (Ontario) Canada M9W 1R3 (téléphone : (800)
463−6727 ou à Toronto : (416) 747−4044, site Web : www.csa−interna-
tional.org).
Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protection,
norme ANSI Z87.1, de l’American National Standards Institute, 11 West
42nd Street, New York, NY 10036−8002 (téléphone : (212) 642−4900,
site Web : www.ansi.org).
Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot
Work, norme NFPA 51B, de la National Fire Protection Association,
P.O. Box 9101, 1 Battery March Park, Quincy, MA 02269−9101 (télé-
phone : (617) 770−3000, site Web : www.nfpa.org et www.sparky.org).
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Standards for General Indus-
try, Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1910, Subpart Q,
and Part 1926, Subpart J, de l’U.S. Government Printing Office, Super-
intendent of Documents, P.O. Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250 (il y a
10 bureaux régionaux − Téléphone pour la Région 5, Chicago : (312)
353−2220, site Web : www.osha.gov).
2-5. Information sur les champs électromagnétiques
Données sur le soudage électrique et les effets des champs magnéti-
ques basse fréquence sur l’organisme
En parcourant les câbles de soudage, le courant crée des champs élec-
tromagnétiques. Les effets potentiels de tels champs restent
préoccupants. Cependant, après avoir examiné plus de 500 études qui
ont été faites pendant une période de recherche de 17 ans, un comité
de spécialistes du National Research Council a conclu : « L’accumula-
tion de preuves n’a pas démontré que l’exposition aux champs
magnétiques et aux champs électriques à haute fréquence constitue un
risque pour la santé humaine ». Toutefois, les études et l’examen des
preuves se poursuivent. En attendant les conclusions finales de la re-
cherche, il serait souhaitable de réduire l’exposition aux champs
électromagnétiques pendant le soudage ou le coupage.
Afin de réduire les champs électromagnétiques en milieu de travail, res-
pecter les consignes suivantes :
1. Garder les câbles ensemble en les torsadant ou en les fixant avec du
ruban adhésif.
2. Mettre tous les câbles du côté opposé à l’opérateur.
3. Ne pas s’enrouler les câbles autour du corps.
4. Garder le poste de soudage et les câbles le plus loin possible de soi.
5. Placer la pince de masse le plus près possible de la zone de soudage.
Consignes relatives aux stimulateurs cardiaques :
Les personnes qui portent un stimulateur cardiaque doivent avant tout
consulter leur médecin. Si ce dernier les déclare aptes, il leur est recom-
mandé de respecter les consignes ci-dessus.

OM-210 540 Page 9
Return To Table Of Contents
SECTION 3 − INSTALLATION
Appearance of actual unit may vary from unit shown in manual.
NOTE
3-1. Specifications
Input
Power
Rated
Welding
Output
Voltag
e
Range
Amper-
age
Range In
CC Mode
Wire Feed
Speed
Range**
Wire
Diameter
Range
Max
Open
Circuit
Voltage
Amperes Input At Rated Load Out-
put 60 Hz,
Three-Phase
Inpu
t
kVA
Inpu
t
KW
Power
Output
Range
Range In
CC Mode
Range**
Range
Voltage
DC
208 V 230 V 460 V 575 V
kVA
KW
Three
Phase
230 V in-
put: 450 A
@
44 V DC,
100%
Duty
Cycle;
460 V in-
put: 450 A
@
44 V DC,
100%
Duty
Cycle
10-44 5-600 A Standard:
50-1400
ipm
(1.3-35.6
mpm)
.030-.062 in
(0.8-1.6
mm)
80 67.0
(0-1A*)
59.0
(0-1A*)
29.0
(0-1A*)
23.0
(0-1A*)
23.8
(0.8*)
22.9
(0.17*
)
*While idling; Input amperage fluctuates while idling and is always less than one Ampere. Use one Ampere for power efficiency calculations.
**Wire feed speed ranges are for GMAW welding. While pulse welding, wire feed speed ranges may be more limited.
3-2. Dimensions And Weight
Hole Layout Dimensions
A
E
22 in
(559 mm)
A 15-1/8 in (384 mm)
A
22 in
(559 mm)
B 16 in (406 mm)
C 19-3/32 in (485 mm)
28 in
(711 mm)
D 13-5/8 in (346 mm)
B
C
E 11/32 in (9 mm)
Weight
15-1/2 in
(394 mm)
135 lb (61 kg)
D
803 244-A
(394 mm)

OM-210 540 Page 10
Return To Table Of Contents
3-3. Duty Cycle And Overheating
Duty Cycle is percentage of 10 min-
utes that unit can weld at rated load
without overheating.
If unit overheats, thermostat(s)
opens, output stops, and cooling
fan runs. Wait fifteen minutes for
unit to cool. Reduce amperage or
duty cycle before welding.
Y Exceeding duty cycle can
damage unit and void war-
ranty.
Overheating
0
15
A/V
OR
Reduce Duty Cycle
Minutes
duty1 4/95 − 181 560
Continuous Welding
100% Duty Cycle At 450 Amperes 60% Duty Cycle At 580 Amperes
6 Minutes Welding 4 Minutes Resting
3-4. Volt-Ampere Curves
va_curve1 4/95
Volt-ampere curves show minimum
and maximum voltage and amper-
age output capabilities of unit.
Curves of other settings fall be-
tween curves shown.
. This volt-ampere curve repre-
sents the dynamic output of the
unit with a static load.
CV MODE
0.0
10.0
20.0
30.0
40.0
50.0
60.0
70.0
80.0
0.0 100.0 200.0 300.0 400.0 500.0 600.0 700.0 800.0 900.0
AMPERAGE
VOLTAGE

OM-210 540 Page 11
Return To Table Of Contents
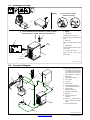
3-5. Selecting A Location
loc_2 3/96 -803 244-A
Y Do not stack units. Beware of
tipping.
1 Lifting Forks
Use lifting forks to move unit.
Extend forks beyond opposite side
of unit.
2 Hand Cart
Use cart or similar device to move
unit.
3 Rating Label
Use rating label to determine input
power needs.
4 Line Disconnect Device
Locate unit near correct input
power supply.
Movement
2
Location
4
18 in
(460 mm)
18 in
(460 mm)
3
Y Do not move or operate
unit where it could tip.
Tipping
1
OR
Y Special installation may be required where gasoline or volatile
liquids are present − see NEC Article 511 or CEC Section 20.
803 244-A / Ref. 801 915-A
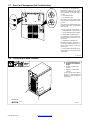
. The proper interface kit must
be installed in the welding pow-
er source/interface unit to allow
it to be connected to the robot.
1 Robot (Will Vary According To
Application)
2 Motor/Drive Assembly
3 Gas Cylinder
4 Gas Hose
5 Robot Control
6 Robot Input/Output Cable
7 Gas And Motor Control Cable
8 Welding Power
Source/Interface Unit
9 Negative (−) Weld Cable
10 Workpiece
11 Voltage Sensing Lead
(Optional)
. Positive (+) voltage sensing
lead is contained in the motor
cable.
12 Positive (+) Weld Cable
1
2 3
4
5
7
6
8
9
10
11
12
3-6. Connection Diagram

OM-210 540 Page 12
Return To Table Of Contents
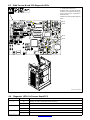
Ref. 803 245-B
1 115 V 10 A AC Receptacle RC2
Receptacle supplies 60 Hz single-
phase power. Maximum output from
RC2 is limited by circuit breaker CB2 to
10 amps.
2 Circuit Breaker CB1
3 Circuit Breaker CB2
CB1 protects 115 volt receptacle RC2
from overload. If CB1 opens, RC2 does
not work.
CB2 protects the wirefeed motor from
overload. If CB2 opens, the wirefeeder
does not work.
. Press button to reset breaker. If
breaker continue to open, contact a
Factory Authorized Service Agent.
4 Wirefeed/Gas Receptacle RC8
Use receptacle to connect gas and mo-
tor control cable to power source (see
Section 3-6).
5 Peripheral Receptacle RC25
Receptacle provides connection to
touch sensor, water flow switch, jog +/−,
and n/o relay contacts circuitry (see
Section 3-10).
6 Robot Interface Receptacle RC72
Use receptacle to connect robot input/
output cable.
2
3
3-7. Rear Panel Receptacles And Circuit Breakers
1
6
4
5
3-8. Connecting To Weld Terminals
Y Turn off power before con-
necting to weld output ter-
minals.
1 Positive (+) Weld Output
Terminal
2 Negative (−) Weld Output
Terminal
Connect positive weld cable to
Positive (+) weld terminal and
negative (−) cable to Negative
weld terminal.
Tools Needed:
803 244-A
1
2
3/4 in

OM-210 540 Page 13
Return To Table Of Contents
3-9. Selecting Weld Cable Sizes*
Weld Cable Size** and Total Cable (Copper) Length in Weld Circuit
Not Exceeding***
100 ft (30 m) or Less
150 ft
(45 m)
200 ft
(60 m)
250 ft
(70 m)
300 ft
(90 m)
350 ft
(105 m)
400 ft
(120 m)
Y Turn off power before
connecting to weld out-
put terminals.
Y Do not use worn, dam-
aged, undersized, or
poorly spliced cables.
Welding
Amperes
10 − 60%
Duty
Cycle
60 − 100%
Duty
Cycle
10 − 100% Duty Cycle
100 4 (20) 4 (20) 4 (20) 3 (30) 2 (35) 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 1/0 (60)
150 3 (30) 3 (30) 2 (35) 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 3/0 (95)
200 3 (30) 2 (35) 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120) 4/0 (120)
250 2 (35) 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
300 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
350 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
400 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
500 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
600 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
3 ea. 4/0
(3x120)
3 ea. 4/0
(3x120)
700 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
3 ea. 4/0
(3x120)
3 ea. 4/0
(3x120)
4 ea. 4/0
(4x120)
800 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 4/0
(3x120)
3 ea. 4/0
(3x120)
4 ea. 4/0
(4x120)
4 ea. 4/0
(4x120)
900
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
1000
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
1250
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
4 ea. 3/0
(4x95)
* This chart is a general guideline and may not suit all applications. If cable overheating occurs (normally you can smell it), use next size larger
cable.
**Weld cable size (AWG) is based on either a 4 volts or less drop or a current density of at least 300 circular mils per ampere.
( ) = mm
2
for metric use S-0007-E
***For distances longer than those shown in this guide, call a factory applications representative at 920-735-4505.

OM-210 540 Page 14
Return To Table Of Contents
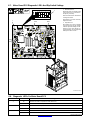
3-10. Peripheral Receptacle Functions
Function Socket Socket Information
K
M
J
L
H
E
F
Programmable
Output Relay Con-
A Contact closure to B dependent upon state of
programmed output.
A
B
M
C
L
D
E
Output Relay Con-
tacts
B Contact closure to A dependent upon state of
programmed output.
B
C
C* Circuit common.
Purge
D Contact closure to C completes 24 volts dc
solenoid circuit to purge shielding gas line.
Coolant Flow
Switch Input
Signal
E Contact closure to F indicates coolant flow switch is
closed and recirculating coolant system is
operational.
Signal
F* Circuit common.
Jog + H** Contact closure to circuit common advances
welding wire at wire drive assembly.
Jog − J** Contact closure to circuit common retracts welding
wire at wire drive assembly.
K Contact closure to L energizes Touch Sensor
circuitry.
Touch Sensor ON
And Output Signa
l
L* Circuit common.
Ref. 803 245-B
And Output Signal
M Part touched +24 volts dc output signal referenced
to circuit common.
*Circuit common is same electrical reference point.
**Speed of Jog + and Jog − is at setup value for Jog IPM parameter.
Note: A customer supplied matching amphenol plug (Part No. MS3106A20-33P and strain relief clamp AN3057-12) is required to use peripheral
receptacle.
3-11. Electrical Service Guide
60 Hz
Input Voltage 208 230 460 575
Input Amperes At Rated Output 67 59 29 23
Max Recommended Standard Fuse Rating In Amperes
1
Time-Delay
2
80 70 35 25
Normal Operating 3 100 90 45 35
Min Input Conductor Size In AWG/Kcmil 4 6 10 10
Max Recommended Input Conductor Length In Feet (Meters)
173
(53)
136
(42)
228
(69)
356
(108)
Min Grounding Conductor Size In AWG/Kcmil 8 8 10 10
Reference: 1999 National Electrical Code (NEC)
1 Consult factory for circuit breaker applications.
2 “Time-Delay” fuses are UL class “RK5” .
3 “Normal Operating” (general purpose - no intentional delay) fuses are UL class “K5” (up to and including 60 amp), and UL class “H” ( 65 amp and
above).

OM-210 540 Page 15
Return To Table Of Contents
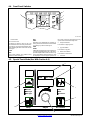
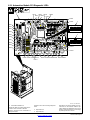
3-12. Connecting Input Power
801 535-B / 803 245-B / 802 777 / 213 848-A
Y Turn Off welding power source,
and check voltage on input ca-
pacitors according to Section
6-4 before proceeding.
Y Incorrect connections will
cause electric shock and dam-
age to the machine.
Y Have only qualified persons
perform these connections ac-
cording to all applicable codes
and safety practices.
Y Disconnect input power before
opening door for voltage con-
nections.
1 Clamp
Install clamp of proper size for unit and
input conductors.
2 Input And Grounding Conductors
Select size and length using Section
3-11.
Connect input conductors as shown in
illustration.
Connect grounding conductor first,
then line input conductors. Always
connect green wire to supply ground-
ing terminal, never to a line terminal.
Connect black, white, and red wires
(L1, L2, L3) to line terminals.
Double-check grounding conductor,
inside voltage connections, and input
voltage before applying power.
3 Line Disconnect Device
See Section 3-11.
Close door before operating unit.
Tools Needed:
5/16 in
= GND/PE
Y Always connect grounding
conductor first.
L1
3
L2
L3
1
2
Route ground conductor through
current transducer to ground terminal.
213 848−A
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill;
SIGNIFICANT DC VOLTAGE
exists after removal of
input power .
Always wait 60 seconds after power
is turned off before working on unit.
Check input capacitor voltage, and
be sure it is near 0 before touching
any parts.
Read Owner s Manual.
L1
L2
L3
Three−Phase Input Connection
GND/PE GND/PE
Route input power cable
through tubing inside unit.
3-13. Touch Sensor Operation
The touch sensor feature allows the robot to locate a weldment using the wire feed system and welding power source.
The weld output terminals provide a path for touch sensor voltage when this feature is turned on at the peripheral
receptacle. Turning on touch sensor causes a dc voltage to be present on the welding wire. When welding wire
touches the weldment, the voltage sensing circuit closes, and a +24 volts dc output signal is sent to the robot control
indicating weldment detection. Touch sensor dc voltage on the welding wire is 80 volts DC. As soon as touch sensor
turns on, WIRE LIVE appears on the front panel display.

OM-210 540 Page 16
Return To Table Of Contents
SECTION 4 − OPERATION
4-1. Operational Terms
The following is a list of terms and their definitions as they apply to this interface unit:
General Terms:
Adaptive Pulse Welding When the “adaptive pulse” welding process is selected, the unit will attempt to automatically regulate
pulse frequency in order to maintain a constant arc length, regardless of change in welding wire stick-
out.
Abk (Background Amperage) Abk is the low weld current. Background current preheats welding wire and maintains the arc. When
background current is too low, the arc is unstable and hard to maintain.
Apk (Peak Amperage) Apk is the high pulse of welding current. Peak current melts the welding wire and forms a droplet. The
droplet is forced into the weld puddle.
Vpk (Peak Voltage) Arc voltage during peak current phase of the pulse waveform. This determines arc length during
adaptive pulse welding.
Inductance In short circuit GMAW welding, an increase in inductance will decrease the number of short circuit
metal transfers per second (provided no other changes are made) and increase the arc-on time. The
increased arc-on time makes the pool more fluid.
PPS (Pulses Per Second) PPS, pulse rate, and frequency (Hz) are used interchangeably. A PPS or pulse rate of 60 Hz means
60 pulses of current are produced each second.
PWms (Pulse Width in Milliseconds) PWms is the time spent at peak current (1.2 ms is .0012 seconds). This time must be long enough to
form a droplet of welding wire. The stiffness or fluidity of the molten weld puddle is controlled by
PWms.
Synergic Synergic refers to the unit’s ability to use preprogrammed pulse parameters to determine the actual
pulse settings of Peak Amperage, Background Amperage, Pulse Frequency and Pulse Width at any
specific wire feed speed setting.
Trim Term used to represent arc length adjustments in pulse programs. Increasing trim increases the ac-
tual arc length. Likewise, decreasing trim shortens arc length. Trim is replaced by volts in MIG pro-
grams.
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
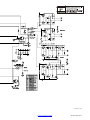 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
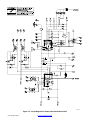 54
54
-
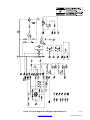 55
55
-
 56
56
-
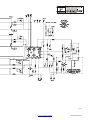 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
Miller LC499801 Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire
- Ce manuel convient également à
dans d''autres langues
- English: Miller LC499801 Owner's manual
Documents connexes
-
Miller LC499793 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller LH280008G Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller PIPEPRO 450 RFC Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller LG031658 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller LF310618 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller PIPEPRO 450 RFC CE Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller PIPEPRO 450 RFC CE Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller LG031658G Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller LF310618 Le manuel du propriétaire







































































