Lincoln Electric Handy MIG Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur

HANDY MIG
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
IM756-A
August, 2005
Safety Depends on You
Lincoln arc welding and cutting
equipment is designed and built
with safety in mind. However, your
overall safety can be increased by
proper installation ... and thought-
ful operation on your part. DO
NOT INSTALL, OPERATE OR
REPAIR THIS EQUIPMENT
WITHOUT READING THIS
MANUAL AND THE SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS CONTAINED
THROUGHOUT. And, most
importantly, think before you act
and be careful.
For use with machine Code Number:10919, 11205
• Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide •
Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. TEL: 216.481.8100 FAX: 216.486.1751 WEB SITE: www.lincolnelectric.com
• World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products •
ISO 9001
CERTIFICATE NUMBER: 30273
Designed and Manufactured Under a
Quality Program Certified by
ABS Quality Evaluations, Inc.
to ISO 9001 Requirements.
QMS
ANSI RAB
Copyright © 2005 Lincoln Global Inc.

FOR ENGINE
powered equipment.
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting and maintenance
work unless the maintenance work requires it to be running.
____________________________________________________
1.b.Operate engines in open, well-ventilated
areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes
outdoors.
____________________________________________________
1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame
welding arc or when the engine is running.
Stop the engine and allow it to cool before
refueling to prevent spilled fuel from vaporiz-
ing on contact with hot engine parts and
igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling tank. If
fuel is spilled, wipe it up and do not start
engine until fumes have been eliminated.
____________________________________________________
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, coversand devices in posi-
tion and in good repair.Keep hands, hair, clothing and tools
away from V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving parts
when starting, operating or repairing equipment.
____________________________________________________
1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety
guards to perform required maintenance. Remove
guards only when necessary and replace them when the
maintenance requiring their removal is complete.
Always use the greatest care when working near moving
parts.
___________________________________________________
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan.
Do not attempt to override the governor or
idler by pushing on the throttle control rods
while the engine is running.
___________________________________________________
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while
turning the engine or welding generator during maintenance
work, disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or
magneto wire as appropriate.
i
SAFETY
i
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH.
KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD CONSULT WITH THEIR DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
Read and understand the following safety highlights. For additional safety information, it is strongly recommended that you
purchase a copy of “Safety in Welding & Cutting - ANSI Standard Z49.1” from the American Welding Society, P.O. Box
351040, Miami, Florida 33135 or CSA Standard W117.2-1974. A Free copy of “Arc Welding Safety” booklet E205 is available
from the Lincoln Electric Company, 22801 St. Clair Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44117-1199.
BE SURE THAT ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION, MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ARE
PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS.
WARNING
Mar ‘95
ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS
may be dangerous
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor causes
localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding
current creates EMF fields around welding cables and
welding machines
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and
welders having a pacemaker should consult their physician
before welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health
effects which are now not known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1.
Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil the electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between the electrode and
work cables. If the electrode cable is on your right
side, the work cable should also be on your right side.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as
possible to the area being welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the
radiator pressure cap when the engine is
hot.
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents
are known to the State of California to cause can-
cer, birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
The engine exhaust from this product contains
chemicals known to the State of California to cause
cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65 WARNINGS
The Above For Diesel Engines
The Above For Gasoline Engines

ii
SAFETY
ii
ARC RAYS can burn.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover
plates to protect your eyes from sparks and
the rays of the arc when welding or observing
open arc welding. Headshield and filter lens
should conform to ANSI Z87. I standards.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant
material to protect your skin and that of your helpers from
the arc rays.
4.c. Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable
screening and/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose
themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can
kill.
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits
are electrically “hot” when the welder is on.
Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare
skin or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free
gloves to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation.
Make certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full
area of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if welding
must be performed under electrically hazardous
conditions (in damp locations or while wearing wet
clothing; on metal structures such as floors, gratings or
scaffolds; when in cramped positions such as sitting,
kneeling or lying, if there is a high risk of unavoidable or
accidental contact with the workpiece or ground) use
the following equipment:
• Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder.
• DC Manual (Stick) Welder.
• AC Welder with Reduced Voltage Control.
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode,
electrode reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic
welding gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical
connection with the metal being welded. The connection
should be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical
(earth) ground.
3.f.
Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and
welding machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace
damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of
electrode holders connected to two welders because voltage
between the two can be the total of the open circuit voltage
of both welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect
yourself from a fall should you get a shock.
3.j. Also see Items 6.c. and 8.
FUMES AND GASES
can be dangerous.
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases
hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these
fumes and gases.When welding, keep
your head out of the fume. Use enough
ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep
fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When
welding with electrodes which require special
ventilation such as stainless or hard facing (see
instructions on container or MSDS) or on lead or
cadmium plated steel and other metals or coatings
which produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as
low as possible and below Threshold Limit Values (TLV)
using local exhaust or mechanical ventilation. In
confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a
respirator may be required. Additional precautions are
also required when welding on galvanized steel.
5.b.
Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon
vapors
coming from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations.
The heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors
to
form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating
products.
5.c. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and
cause injury or death. Always use enough ventilation,
especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
5.d. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) and follow your
employer’s safety practices. MSDS forms are available from
your welding distributor or from the manufacturer.
5.e. Also see item 1.b.
Mar ‘95

FOR ELECTRICALLY
powered equipment.
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect
switch at the fuse box before working on
the equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code, all local codes and the manufacturer’s
recommendations.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the U.S. National
Electrical Code and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
CYLINDER may explode
if damaged.
7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders
containing the correct shielding gas for the
process used and properly operating
regulators designed for the gas and
pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be suitable for
the application and maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely
chained to an undercarriage or fixed support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
• Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to
physical damage.
• A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and
any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other
electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet
when opening the cylinder valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand
tight except when the cylinder is in use or connected for
use.
7.g. Read and follow the instructions on compressed gas
cylinders, associated equipment, and CGA publication P-l,
“Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,” available from the Compressed Gas Association
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
iii
SAFETY
iii
Mar ‘95
WELDING SPARKS can
cause fire or explosion.
6.a.
Remove fire hazards from the welding area.
If this is not possible, cover them to prevent
the welding sparks from starting a fire.
Remember that welding sparks and hot
materials from welding can easily go through small cracks
and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near
hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site,
special precautions should be used to prevent hazardous
situations. Refer to “Safety in Welding and Cutting” (ANSI
Standard Z49.1) and the operating information for the
equipment being used.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode
circuit is touching the work or ground. Accidental contact
can cause overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the
proper steps have been taken to insure that such procedures
will not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances
inside. They can cause an explosion even
though
they have
been “cleaned”. For information, purchase “Recommended
Safe Practices for the
Preparation
for Welding and Cutting of
Containers and Piping That Have Held Hazardous
Substances”, AWS F4.1 from the American Welding Society
(see address above).
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or
welding. They may explode.
6.f.
Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil
free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt,
cuffless trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear
ear plugs when welding out of position or in confined places.
Always wear safety glasses with side shields when in a
welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding
area as practical. Work cables connected to the building
framework or other locations away from the welding area
increase the possibility of the welding current passing
through lifting chains, crane cables or other alternate cir-
cuits. This can create fire hazards or overheat lifting chains
or cables until they fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.

iv
SAFETY
iv
PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ
Pour votre propre protection lire et observer toutes les instruc-
tions et les précautions de sûreté specifiques qui parraissent
dans ce manuel aussi bien que les précautions de sûreté
générales suivantes:
Sûreté Pour Soudage A L’Arc
1. Protegez-vous contre la secousse électrique:
a. Les circuits à l’électrode et à la piéce sont sous tension
quand la machine à souder est en marche. Eviter toujours
tout contact entre les parties sous tension et la peau nue
ou les vétements mouillés. Porter des gants secs et sans
trous pour isoler les mains.
b. Faire trés attention de bien s’isoler de la masse quand on
soude dans des endroits humides, ou sur un plancher
metallique ou des grilles metalliques, principalement dans
les positions assis ou couché pour lesquelles une
grande partie du corps peut être en contact avec la
masse.
c. Maintenir le porte-électrode, la pince de masse, le câble
de soudage et la machine à souder en bon et sûr état
defonctionnement.
d.Ne jamais plonger le porte-électrode dans l’eau pour le
refroidir.
e. Ne jamais toucher simultanément les parties sous tension
des porte-électrodes connectés à deux machines à soud-
er parce que la tension entre les deux pinces peut être le
total de la tension à vide des deux machines.
f. Si on utilise la machine à souder comme une source de
courant pour soudage semi-automatique, ces precautions
pour le porte-électrode s’applicuent aussi au pistolet de
soudage.
2. Dans le cas de travail au dessus du niveau du sol, se pro-
téger contre les chutes dans le cas ou on recoit un choc. Ne
jamais enrouler le câble-électrode autour de n’importe quelle
partie du corps.
3. Un coup d’arc peut être plus sévère qu’un coup de soliel,
donc:
a. Utiliser un bon masque avec un verre filtrant approprié
ainsi qu’un verre blanc afin de se protéger les yeux du
rayonnement de l’arc et des projections quand on soude
ou quand on regarde l’arc.
b. Porter des vêtements convenables afin de protéger la
peau de soudeur et des aides contre le rayonnement de
l‘arc.
c. Protéger l’autre personnel travaillant à proximité au
soudage à l’aide d’écrans appropriés et non-inflamma-
bles.
4. Des gouttes de laitier en fusion sont émises de l’arc de
soudage. Se protéger avec des vêtements de protection
libres de l’huile, tels que les gants en cuir, chemise épaisse,
pantalons sans revers, et chaussures montantes.
5. Toujours porter des lunettes de sécurité dans la zone de
soudage. Utiliser des lunettes avec écrans lateraux dans les
zones où l’on pique le laitier.
6. Eloigner les matériaux inflammables ou les recouvrir afin de
prévenir tout risque d’incendie dû aux étincelles.
7. Quand on ne soude pas, poser la pince à une endroit isolé de
la masse. Un court-circuit accidental peut provoquer un
échauffement et un risque d’incendie.
8. S’assurer que la masse est connectée le plus prés possible
de la zone de travail qu’il est pratique de le faire. Si on place
la masse sur la charpente de la construction ou d’autres
endroits éloignés de la zone de travail, on augmente le risque
de voir passer le courant de soudage par les chaines de lev-
age, câbles de grue, ou autres circuits. Cela peut provoquer
des risques d’incendie ou d’echauffement des chaines et des
câbles jusqu’à ce qu’ils se rompent.
9. Assurer une ventilation suffisante dans la zone de soudage.
Ceci est particuliérement important pour le soudage de tôles
galvanisées plombées, ou cadmiées ou tout autre métal qui
produit des fumeés toxiques.
10. Ne pas souder en présence de vapeurs de chlore provenant
d’opérations de dégraissage, nettoyage ou pistolage. La
chaleur ou les rayons de l’arc peuvent réagir avec les
vapeurs du solvant pour produire du phosgéne (gas forte-
ment toxique) ou autres produits irritants.
11. Pour obtenir de plus amples renseignements sur la sûreté,
voir le code “Code for safety in welding and cutting” CSA
Standard W 117.2-1974.
PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÛRETÉ POUR
LES MACHINES À SOUDER À
TRANSFORMATEUR ET À
REDRESSEUR
1. Relier à la terre le chassis du poste conformement au code
de l’électricité et aux recommendations du fabricant. Le dis-
positif de montage ou la piece à souder doit être branché à
une bonne mise à la terre.
2. Autant que possible, I’installation et l’entretien du poste
seront effectués par un électricien qualifié.
3. Avant de faires des travaux à l’interieur de poste, la
debrancher à l’interrupteur à la boite de fusibles.
4. Garder tous les couvercles et dispositifs de sûreté à leur
place.
Mar. ‘93

vv
Thank You
for selecting a QUALITY product by Lincoln Electric. We want you
to take pride in operating this Lincoln Electric Company product
••• as much pride as we have in bringing this product to you!
Read this Operators Manual completely before attempting to use this equipment. Save this manual and keep it
handy for quick reference. Pay particular attention to the safety instructions we have provided for your protection.
The level of seriousness to be applied to each is explained below:
WARNING
This statement appears where the information must be followed exactly to avoid serious personal injury or
loss of life.
This statement appears where the information must be followed to avoid minor personal injury or damage to
this equipment.
CAUTION
Please Examine Carton and Equipment For Damage Immediately
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon receipt by the carrier. Consequently, Claims
for material damaged in shipment must be made by the purchaser against the transportation company at the
time the shipment is received.
Please record your equipment identification information below for future reference. This information can be
found on your machine nameplate.
Product _________________________________________________________________________________
Model Number ___________________________________________________________________________
Code Number or Date Code_________________________________________________________________
Serial Number____________________________________________________________________________
Date Purchased___________________________________________________________________________
Where Purchased_________________________________________________________________________
Whenever you request replacement parts or information on this equipment, always supply the information you
have recorded above. The code number is especially important when identifying the correct replacement parts.
On-Line Product Registration
- Register your machine with Lincoln Electric either via fax or over the Internet.
• For faxing: Complete the form on the back of the warranty statement included in the literature packet
accompanying this machine and fax the form per the instructions printed on it.
• For On-Line Registration: Go to our
WEB SITE at www.lincolnelectric.com. Choose “Quick Links” and then
“Product Registration”. Please complete the form and submit your registration.

vi
vi
MASTER TABLE OF CONTENTS FOR ALL SECTIONS
Page
Installation .......................................................................................................Section A
Technical Specifications ........................................................................................A-1
Identify and Locate Components...........................................................................A-2
Select Suitable Location ........................................................................................A-3
Stacking.................................................................................................................A-3
Changing Polarity ..................................................................................................A-3
Gun Installation......................................................................................................A-3
Input Connections..................................................................................................A-3
Gas Connections ...................................................................................................A-3
Shielding Gas Connections ...................................................................................A-4
Code Requirements ..............................................................................................A-4
________________________________________________________________________
Operation .........................................................................................................Section B
Safety Precautions ................................................................................................B-1
General Description...............................................................................................B-1
Recommended Processes.....................................................................................B-1
Operation Features and Controls .........................................................................B-1
Design Features ....................................................................................................B-1
Welding Capability.................................................................................................B-2
Limitations..............................................................................................................B-2
Controls and Settings ............................................................................................B-2
Welding Operations ...............................................................................................B-2
Shielding Gas ........................................................................................................B-3
Making a Weld and Process Table........................................................................B-4
Cleaning Tip and Gas Nozzle................................................................................B-5
Changing Machine over to Feed Other Wire Sizes,Overload Protection...............B-5
________________________________________________________________________
Accessories.....................................................................................................Section C
Accessories ...........................................................................................................C-1
Replacement Parts................................................................................................C-1
________________________________________________________________________
Maintenance ....................................................................................................Section D
Safety Precautions ................................................................................................D-1
Items Requiring No Maintenance ..........................................................................D-1
Routine Maintenance.............................................................................................D-1
Cleaning the Gun Liner..........................................................................................D-2
Cleaning Components as Required.......................................................................D-2
Component Replacement Procedures ..................................................................D-2
Changing Contact Tip............................................................................................D-2
Changing the Drive Roll.........................................................................................D-2
Gun Assembly Removal........................................................................................D-3
Work Cable Installation..........................................................................................D-3
________________________________________________________________________
Troubleshooting..............................................................................................Section E
Safety Precautions.................................................................................................E-1
How to Use Troubleshooting Guide.......................................................................E-1
Troubleshooting Guide.........................................................................E-2 THRU E-4
________________________________________________________________________
Wiring Diagrams..............................................................................................Section F
Wiring Diagram .....................................................................................................F-1
________________________________________________________________________
Parts Lists ....................................................................................................P437 Series

A-1
HANDY MIG
A-1
Fuse or
Output Mode Input Voltage Breaker Size
1
Input Amps Power Cord Extension Cord
AT
RATED 120V/60Hz 20 Amp 20 15 Amp, 125V, Three Conductor
OUTPUT Three Prong Plug #12 AWG
(NEMA Type 5-15P) (3.3 mm
2
) or Larger
Up to 50 Ft. (15.2 mm)
INSTALLATION
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS – HANDY MIG
INPUT – SINGLE PHASE ONLY
RATED OUTPUT
OUTPUT RANGE
RECOMMENDED INPUT CABLE AND FUSE SIZES
Height Width Depth Weight
12.8 in 8.8 in 18 in 46 Ibs
325 mm 224 mm 457 mm 20.9 kg
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
Standard Voltage/Frequency Input Current
120V/60Hz 20 Amps - Rated Output
Duty
Cycle Amps Volts at Rated Amperes
20% Duty Cycle 70 17
Welding Current Range Maximum-Open Circuit Voltage No Load 0 - 450 in/min
DC OUTPUT: 35-88 Amps 29V (0 - 17.7m/min)
While welding 0-300 in/min.
(0-11.8 m/min.)
1
If connected to a circuit protected by fuses use Time Delay Fuse marked “D”.

A-2
INSTALLATION
HANDY MIG
A-2
Read entire installation section before starting
installation.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
IDENTIFY AND LOCATE
COMPONENTS
If you have not already done so, unpack the machine
from its carton and remove all packing material
around the machine. The following items are shipped
loose. (see Figure A.1):
1. HANDY MIG with work clamp, Gun and cable
assembly attached.
2. This operating manual
3. Two contact tips for .035(0.9mm) diameter wire.
4. Three contact tips for .025(0.6mm) diameter wire.
5. Gas Nozzle.
6. Chipping hammer and brush.
7. Starter spool of .035” (0.9mm) NR211-MP flux
cored wire.
8. Starter spool of .025” (0.6mm) solid mig wire.
9. Gas regulator and hose with hose clamps.
10. Handshield with filter plate and lens.
For available options and accessories refer to the
Accessories Section of this manual.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Only qualified personnel should perform
this installation.
• Only personnel that have read and under-
stood the Machine Operating Manual
should install and operate this equipment.
• Machine must be plugged into a receptacle
which is grounded per any national, local
or other applicable electrical codes.
• The Machine power switch is to be in the
OFF (“O”) position when installing work
cable and gun and when connecting power
cord to input power.
WARNING
FIGURE A.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
9
10
8
1
.
0
-
.
0
4
0
A
L
1
.
0
-
.
0
4
0
A
L
1
.
0
-
.
0
4
0
A
L
1
.
0
-
.
0
4
0
A
L
1
.
0
-
.
0
4
0
A
L
Handy Mig 101
IM000
October 1998
For use with machines having Code Numbers:
00000
Safety Depends on You
Lincoln arc welding and cutting
equipment is designed and built
withsafety in mind. However,your
overallsafety can be increased by
properinstallation...and thoughtful
operation on your part. DO NOT
INSTALL,OPERATE OR REPAIR
THIS EQUIPMENT WITHOUT
READINGTHIS MANUALAND THE
SAFETT PRECAUTIONS
CONTAINEDTHROUGHOUT. And,
most importantly,think before you
act and be careful.
World's Leader in Welding and Cutting Products Premier Manufacturer of Industrial Motors
Sales and Service through Subsidiaries and Distributors Worldwide
22801 St. Clair Ave. Cleveland, ohio 44117-1199 U.S.A. Tel. (216) 481-8100
1

INPUT CONNECTIONS
(FIGURE A.4)
Refer to Figure A.4.
The machine has two input connections, the power
input cable and the gas inlet fitting. The power input
cable and gas inlet fitting are located on the rear.
GAS CONNECTION
When using the MIG process, a cylinder of shielding
gas (appropriate for the metal being welded) must be
obtained.
CYLINDER may explode if damaged.
Keep cylinder upright and chained to
support.
• Keep cylinder away from areas where it
may be damaged.
• Never lift welder with cylinder attached.
• Never allow welding electrode to touch cylinder.
• Keep cylinder away from welding or other live
electrical circuits.
BUILDUP OF SHIELDING GAS may harm
health or kill.
• Shut off shielding gas supply when not
in use.
• SEE AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Z-49.1,
“SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING” PUB-
LISHED BY THE AMERICAN WELDING SOCIETY.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
GAS INLET FITTING
POWER INPUT CABLE
A-3
INSTALLATION
HANDY MIG
A-3
SELECT SUITABLE LOCATION
Place the machine on a secure, level surface or rec-
ommended undercarriage. The machine may topple
over if this procedure is not followed. To minimize over
heating, locate the welder in a dry location where there
is free circulation of clean air. Do not place on com-
bustible surfaces.
STACKING
Machines cannot be stacked.
CHANGING POLARITY
1. For Negative Polarity Welding (DC-): Refer to
Figure A.2. As delivered, the machine is wired for
Negative polarity with the gun cable connected to
the Negative (-) output terminal and the work cable
to the Positive (+) output terminal. Make sure that
both thumbscrews are tight. This is the typical con-
figuration for Flux Cored Welding (FCAW).
2.For Positive Polarity Welding (DC+): Refer to
Figure A.3. To wire for Positive polarity, connect
the gun cable to the Positive (+) output terminal and
the work cable to the Negative (-) terminal. This is
the typical configuration for the Metal Inert Gas
(MIG) process. Make sure that both thumbscrews
are tight.
WARNING
WORK CABLE
WORK CABLE
WORK CABLE
WORK CABLE
GUN CABLE
GUN CABLE
GUN CABLE
GUN CABLE
(FIGURE A.3)
WORK CABLE
WORK CABLE
WORK CABLE
WORK CABLE
GUN CABLE
GUN CABLE
GUN CABLE
GUN CABLE
FIGURE A.2

A-4
INSTALLATION
HANDY MIG
A-4
SHIELDING GAS CONNECTION
(FIGURE A.5)
Refer to Figure A.5.
1. Chain the cylinder to a wall or other stationary sup-
port to prevent the cylinder from falling over.
Insulate the cylinder from the work circuit work
ground.
2. With the cylinder securely installed, remove the
cylinder cap. Stand to one side away from the out-
let and open the cylinder valve very slightly for an
instant. This blows away any dust or dirt which may
have accumulated in the valve outlet.
BE SURE TO KEEP YOUR FACE AWAY FROM
THE VALVE OUTLET WHEN “CRACKING” THE
VALVE. Never stand directly in front of or behind
the flow regulator when opening the cylinder
valve. Always stand to one side.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
3. Attach one end of the inlet gas hose to the outlet fit-
ting of the gas cylinder secure with hose clamp.
Connect the other end to the Gas Inlet Fitting on
the machine and secure with hose clamp. Make
certain the gas inlet hose is not kinked or twisted.
4. The machine is supplied with a regulator suitable
for a mixed shielding gas CO
2 Argon. For welding
with 100% CO2 a suitable regulator or adapter must
be purchased separately from a welding gas suppli-
er. To prevent leakage, if welding with 100% CO2
shielding gas the regulator for carbon dioxide must
have a plastic adapter washer seated in the fitting
that attaches to the cylinder. This adapter is avail-
able from your local gas supplier.
WARNING
CYLINDER VALVE
GAS CYLINDER
REGULATOR
HOSE
CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR ELECTRI-
CAL INPUT CONNECTIONS
This welding machine must be connected to a
power source in accordance with applicable elec-
trical codes.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
The United States National Electrical Code (Article
630-B, 1990 Edition) provides standards for amperage
handling capability of supply conductors based on
duty cycle of the welding source.
If there is any question about the installation meeting
applicable electrical code requirements, consult a
qualified electrician.
Do not connect the machine to an input power
supply with a rated voltage that is greater than 125
volts.
Do not remove the power cord ground prong.
REQUIREMENTS FOR MAXIMUM OUTPUT
A line cord with a 15 amp, 125 volt, three-prong plug
(NEMA Type 5-15P) is factory installed on the
machine Connect this plug to a mating grounded
receptacle which is connected to a 20 amp branch cir-
cuit with a nominal voltage rating of 115 volts to 125
volts, 60 hertz, AC only. If connected to a circuit pro-
tected by fuses, use a time delay fuse marked “D”.
With this installation, the machine can be used at an
output of 70 amps, 17 volts, 20% duty cycle (2 min-
utes of every 10 minutes used for welding).
EXTENSION CORD USAGE
If an extension cord is required, use one that is rated
for the application and is 3 conductor #14 AWG (2.1
mm
2
) or larger. The recommended maximum lengths
are 25 ft (7.5 m) if #14 AWG (2.1 mm
2
) is used and 50
ft (15 m) if #12 AWG (3.3 mm
2
) is used.
WARNING
CAUTION

B-1
OPERATION
B-1
HANDY MIG
Read entire operation section before
operating the machine.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch electrically live
parts or electrode with skin or
wet clothing. Insulate yourself
from work and ground.
• Always wear dry insulating
gloves.
FUMES AND GASES can be
dangerous.
• Keep your head out of fumes.
• Use ventilation or exhaust to
remove fumes from breathing
zone.
WELDING SPARKS can
cause fire or explosion.
• Keep flammable material away.
• Do not weld on closed contain-
ers.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes
and skin.
• Wear eye, ear and body protec-
tion.
Observe all safety information throughout
this manual.
WARNING
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The machine is a semiautomatic constant voltage DC
arc welder. The machine uses a single phase con-
stant voltage transformer, solid state rectifier and a
DC permanent magnet motor for feeding and welding
solid steel electrode and flux-cored electrode.
The machine is ideally suited for individuals having
access to 115 volt AC input power and wanting the
ease of use, quality and dependability of both metal
inert gas (MIG) welding and the Innershield electrode
process (self-shielded flux-cored welding). The
machine will handle reels of wire up to 2 lbs(1 kg).
RECOMMENDED PROCESSES
The machine can be used for welding carbon and low-
alloy steel with CO
2
or argon/CO
2
mixture shielding
gas. The welder can also be used without gas for the
self-shielded, Innershield electrode process. The
machine is configured for the Flux Cored Arc Welding
process as delivered from the factory.
OPERATIONAL FEATURES AND CONTROLS
The machine has the following controls as standard:
• Power ON/OFF Switch
• Heat Range Switch
• 1 – 2 Fine Heat Adjustment Switch
• Wire Speed Control
DESIGN FEATURES AND ADVANTAGES
• Operates on 115 volt input - no special wiring
required.
• Solid state output control.
• Overload protection - incorporates a thermostat to
protect the welder from overheating caused by mal-
functions or overly heavy use.
• Permanent magnet wire drive motor.
• Easy-to-set controls for arc voltage and wire speed.
• Thumbscrew release idle roll pressure arm is easily
adjusted.
• Reversible, dual groove drive roll will feed .023-
.035” (0.6- 0.9 mm) diameter wire.
• Accommodates spools of wire up to 2 lbs(1 kg) in
weight.
• No external shielding gas is required when used
with Lincoln Innershield .035” (0.9 mm) NR®-211-
MP electrode.
• Easy to change polarity.

B-2
OPERATION
B-2
TABLE B.1 – MIG WELDING MATERIAL/GAS COMBINATIONS
Material Gas
Carbon Steel CO2 or Argon/CO2
Low Alloy Steel CO2 or Argon/CO2
FLUX-CORED (INNERSHIELD) WELDING
The recommended electrode for the flux-cored, self-
shielded process is 0.035” (0.9 mm) diameter Lincoln
Innershield NR-211-MP on 2 lbs. (.9 kg) spools.
SEQUENCE OF OPERATIONS
WIRE LOADING AND THREADING
Refer to Figure B.2.
Turn machine power switch to the OFF (“0”) position
before working inside the wire feed enclosure.
Make sure that the wire feed drive roll and the contact
tip of the gun match the diameter and type of wire
used.
1. Push the spool onto the spindle so that the wire
feeds off the bottom of the spool, toward the drive
roll.
2. Push the spool spacer onto the spindle, against the
spool.
3. Slide the spring onto the spool, then press on the
spool lock, turning it clockwise to lock the spool
assembly onto the spindle.
WELDING CAPABILITY
The machine is rated at 70 amps, 17 volts, at 20%
duty cycle on a ten minute basis. It is capable of high-
er output currents at lower duty cycles.
LIMITATIONS
The machine is recommended for welding on mild
steel up to 1/8” thick.
CONTROLS AND SETTINGS
Refer to Figure B.1.
1. Power ON/OFF Switch -When the power is ON
the welding output and wire feeder are ON (“hot”)
when the gun trigger is pressed.
2. Low / High Heat Range Switch. -A rocker switch
control that gives low or high coarse range adjust-
ment of the power source output voltage.
3. 1 – 2 Fine Heat Adjustment Switch. -Allows fine
adjustment of the voltage within the selected Low
or High output range.
4. Wire Speed Control. -Controls the wire feed
speed. Wire speed is not affected when changes
are made in the voltage control.
WELDING OPERATIONS
PROCESS GUIDELINES
MIG WELDING
Table B.1 shows the recommended material/gas
combinations for MIG welding with solid electrodes.
HANDY MIG
1
4
2
3
FIGURE B.1
SPINDLE
SPRING
SPOOL
LOCK
SPOOL
SPACER
SPOOL
FIGURE B.2

B-3
OPERATION
B-3
FIGURE B.3 – WIRE THREADING DETAILS
Refer to Figure B.3.
4. Release the spring loaded thumbscrew and lift up
the idle roll arm away from the wire feed drive roll.
Ensure that the visible, stenciled size on the drive
roll side facing you matches the wire size being
used.
5. Carefully detach the end of the wire from the spool
maintain tension on the wire. To prevent the spool
from unwinding and do not release the wire until
after step 8.
6. Cut the bent portion of wire off and straighten the
first 4” (100 mm).
7. Thread the wire through the ingoing guide tube,
over the drive roll, and into the gun liner.
8. Close the idle roll arm and turn down the thumb-
screw until the idle roller presses down firmly on the
wire. (Now you may release the welding wire).
Make sure the wire is positioned in the groove of
the lower drive roll.
9. The spring loaded thumbscrew on the idle roll arm
adjusts the pressure on the wire. Adjust pressure
by turning the thumbscrew to prevent spool over-
run, but still allow smooth and easy wire feeding.
Start with the pressure set to an intermediate value.
Readjust, if necessary. Slightly less pressure may
be required when using 0.023 - 0.025” (0.6 mm)
wire. If the drive roll slips while feeding wire, the
pressure should be increased until the wire feeds
properly.
• When feeding the welding wire
through the gun, the drive roll, the
gun connector block and the gun
contact tip are always energized rela-
tive to work and ground.
FIGURE B.4 – WIRE STICKOUT
10. Remove the gas nozzle and contact tip from the
gun.
11. Turn the machine ON (“I”).
12. Straighten the gun cable assembly.
13.Depress the gun trigger switch and feed welding
wire through the gun and cable. (Point the gun
away from yourself and others while feeding wire.)
Release the gun trigger after wire appears at the
end of the gun.
14.Turn off the machine.
15.Replace the contact tip. Refer to Figure B-4. Cut
the wire off so that 3/8” to 5/8” (10 - 15 mm) pro-
trudes from the end of the tip.
16.Turn on the machine. The machine is now ready
to weld.
SHIELDING GAS
When using the MIG process, you will need a cylinder
of carbon dioxide (CO
2
) or argon-carbon dioxide
mixed shielding gas.
The preset regulator supplied with the machine is
designed for use with argon blend gas. An adapter
and plastic washer are needed for using 100% CO
2
gas. This adapter is available from your local gas sup-
plier.
1. Open the cylinder valve slowly a fraction of a turn.
When the cylinder pressure gauge pointer stops
moving, open the valve fully.
2. Keep the cylinder valve closed, except when weld-
ing. When finished welding:
• Close the cylinder valve to stop gas flow.
• Depress the gun trigger briefly to release the
pressure in the gas hose.
• Turn off the machine.
HANDY MIG
Spring Loaded Thumb Screw
Ingoing Guide Tube
Wire
Wire Feed
Lower Drive Roll
Upper
Idler Roll Arm
CONTACT
TIP
WIRE
ELECTRODE
3/8"
Contact Tip To Work
Distance (CTWD)
WARNING

B-4
OPERATION
B-4
MAKING A WELD
FIGURE B.5 – WELDING SETUP
READ the LEARNING TO WELD (LTW1) manual
prior to making your first weld. Also, refer to Table
B.1 and the Procedure Decal located on the inside of
the wire drive compartment door of your machine for
process selection, consumables, and quick tips for
welding.
1. Select the right welding process based on the type
and condition of the pieces to be welded; the envi-
ronment in which welding is to be done; and the
desired finished appearance of the weld.
2. Select and install the welding wire to match the
process. Use Genuine Lincoln Electric Brand wire.
Wire quality is essential for successful welding.
3. Install the drive roll, contact tip, and nozzle appro-
priate for the weld process.
HANDY MIG
WORKPIECE
GUN CABLE
ARC
WORK CLAMP
4. Check that the polarity is correct for the welding wire
being used and that the gas supply, if required, is
turned on.
5. Refer to Figure B.5. Connect the work clamp to the
metal to be welded. The work clamp must make
good electrical contact to the work piece. The work
piece must also be grounded as stated in Arc
Welding Safety Precautions in the beginning of this
manual.
6. Based on the welding process type and material
thickness of the work piece, use the chart below (or
on the procedure decal located on the wire drive
door) to set the correct wire feed speed and heat
range setting.
7. Based on the weld joint type and orientation of the
weld joint, position the gun into the joint at the cor-
rect angle. Refer to the LEARNING TO
WELD(LTW1) manual.
8. To begin welding, raise your hand shield to protect
your eyes and pull the trigger.
9. While welding, travel at a constant speed and main-
tain an electrode stickout of 3/8". Follow the correct
direction of travel for the process and joint type and
orientation as detailed in the LEARNING TO WELD
(LTW1) manual.
10. To stop welding, release the gun trigger.
11. When no more welding is to be done, close the
valve on the gas cylinder (if used), momentarily
operate the gun trigger to release gas pressure,
and turn off the machine.
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 8
7
7
8 8
TABLE B.1

B-5
OPERATION
B-5
HANDY MIG
CLEANING TIP AND GAS NOZZLE
Clean the contact tip and gas nozzle to avoid arc
bridging between them. Bridging can result in a short-
ed nozzle, poor welds and an overheated gun. Hint:
Anti-stick spray or gel, available from a welding supply
distributor, may reduce buildup and aid in spatter
removal.
CHANGING MACHINE OVER TO FEED
OTHER WIRE SIZES
The machine is shipped from the factory ready to feed
0.035” (0.9 mm) diameter wire. To operate the
machine with other sizes of wire, it is necessary to
change the contact tip and change the drive roll to
other sizes. Refer to Changing the Contact Tip and
Changing the Drive Roll in the MAINTENANCE sec-
tion for specific information on these procedures.
OVERLOAD PROTECTION
THERMAL PROTECTION
The machine has a maximum output duty cycle of
20%. If the duty cycle is exceeded, a thermal protector
will shut off the output until the machine cools to a
normal operating temperature. This is an automatic
function of the machine and does not require user
intervention.

C-1
ACCESSORIES
C-1
ACCESSORIES
INNERSHIELD WELDING WIRE
NR-211-MP Innershield welding wire - .035” (0.9 mm)
diameter flux-cored electrode.
MIG WELDING WIRE
Lincoln L56- .025” (0.6mm) diameter solid steel elec-
trode)
CONSUMABLE PARTS
The following items are commonly consumed over the
life of the welder and may need to be ordered. See
the complete parts list at the end of this manual for
machine replacement parts.
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO.
1 Chipping Hammer/Brush S24355-12
2 Face Shield G3364
3
Filter Lens/Clear Cover Lens
G3364-C & -D
4 Drive Roll - “.023-.035”
(0.6-0.9 mm) KP2315-1
5 Contact Tip “.023-.025”
(0.6 mm) KH710
6 Contact Tip “.035”(0.9 mm) KH712
7 Flux Nozzle (Gasless) KH726
8 Gas Nozzle KH725
9 Gas Hose T10642-120
10 Gas Diffuser S25351-1
11 Liner S25351-50
HANDY MIG

MAINTENANCE
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Disconnect input power by removing
plug from receptacle before working
inside machine. Use only grounded
receptacle. Do not touch electrically
“hot” parts inside machine
• Have qualified personnel do the mainte-
nance and trouble shooting work.
ITEMS REQUIRING
NO MAINTENANCE
• Drive Motor and Gearbox – Lifetime lubrication
• Wire Reel Spindle – Do NOT lubricate shaft
ROUTINE AND PERIODIC
MAINTENANCE
BEFORE EACH USE
• Check over machine and accessories for any obvious condi-
tion that may prevent safe performance or operation. Repair
or replace items as necessary to correct any abnormal con-
dition.
AFTER 5 MINUTES OF WELDING
or when spatter accumulates in the gas nozzle:
• Clean the contact tip and gas nozzle to avoid bridging
between the nozzle and contact tip. Bridging results in a
shorted nozzle, poor welds and overheated gun. Hint: Anti-
stick spray or gel available from a welding supply distributor
may reduce buildup and aid in spatter removal.
D-1
MAINTENANCE
D-1
HANDY MIG
WARNING

D-2
MAINTENANCE
D-2
HANDY MIG
CLEANING THE GUN LINER
• Unplug the machine or turn the power switch to the
OFF - “0” position.
• Remove the gas nozzle and contact tip from the
gun.
• Clean the inside diameter with a short piece of wire.
• Clean the cable liner when rough and erratic wire
feeding occur:
Lay the cable out straight. Blow out gently with dry
compressed air (max 145 psi) through the wire guide
tube and check the condition of the tube. Bend the
cable back and forth, then blow the tube out again.
Repeat until clean.
Excessive pressure at start may cause the dirt to
form a plug.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
CLEANING COMPONENTS AS REQUIRED
• Unplug the machine or turn the power switch to the
OFF - “0” position.
• Blow dirt out of the welder with low pressure air to
eliminate excessive dirt and dust buildup that could
cause the welder to run hot.
• Vacuum accumulated dirt from the gear-box and
wire feed section.
• Inspect the incoming guide tube and clean the
inside diameter if necessary. Replace when exces-
sively worn.
• Replace Contact Tip - when the hole is enlarged or
elongated. (Refer to Changing The Contact Tip, in
this section.)
• Check the condition of the wire feed rollers.
Remove any metallic dust deposited in the feed
area (rollers and entrance and outlet wire guide).
• Check the gas hose and fittings for tightness.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
PROCEDURES
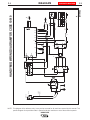
FIGURE D.1 – CONTACT TIP REPLACEMENT
CHANGING THE CONTACT TIP
1. Refer to Figure D.1. Remove the gas nozzle from
the gun by unscrewing it counter-clockwise.
2. Remove the existing contact tip from the gun by
unscrewing it counter-clockwise.
3. Insert and tighten the desired contact tip. Do not
overtighten.
4. Replace the gas nozzle.
CHANGING THE DRIVE ROLL
FIGURE D.2 – DRIVE ROLL REPLACEMENT
The machine Wire Feed Drive Roll has two grooves;
one for 0.023” - 0.025” (0.6 mm) solid steel electrode
and the other for 0.030” (0.8 mm) solid and 0.035”
(0.9 mm) flux-cored steel electrode. See Figure D.2.
Use the appropriate sized groove for the wire used (as
indicated by the stenciling on the side of the drive roll).
Reverse the drive roll as follows.
Refer to Figure D.2.
1. Make certain the machine power switch is OFF -
“0”.
2. Open the spring loaded pressure arm. Lift up the
idle roll arm.
CAUTION
NOZZL
E
CONTACT
TIP
EN50078
1
.
0
-
.
0
4
0
A
L
HHANDLE SCREW
UPPER
IDLER ROLLARM
WIRE FEED
LOWER DRIVE ROLL
AND THUMB SCREW
INCOMING GUIDE TUBE
WIRE
SPRING LOADED

D-3
MAINTENANCE
D-3
HANDY MIG
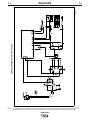
3. Remove the Thumbscrew holding the drive roll.
4. Replace the drive roll so that the desired size, sten-
ciled on the side of the drive roll, is toward the
inside and visible.
5. Replace the Thumbscrew and tighten.
GUN ASSEMBLY REMOVAL
1. Unplug machine and disconnect gas supply.
2. Remove wire drive door and left case side.
3. Remove trigger leads. the trigger leads are routed
through the center panel and connected to the P.C.
board (3/1,3/2). Use care in removal as not to dam-
age the P.C. board or adjoining leads.
4. Remove gas line connections.
5. Remove gun connections from output studs.
6. Disconnect the gun liner from the wire drive.
Remove nut and spacer and slide liner back and
out.
7. Installation is the reverse of removal. (7 thru 1)
WORK CABLE INSTALLATION
The work cable and clamp comes already installed. If
you should ever need to replace or reinstall the cable,
do the following. Refer to Figure D.3.
1. Remove the case sides.
2. Pass the end of the work cable with the terminal lug
through the Work Cable Access Hole in the case
front.
3. Route the cable as detailed in the picture. The work
cable should be routed between the metal divider
panel and the wire feed gear box and gun assem-
bly.
WORK CABLE AND GROMMET
FIGURE D.3
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
Lincoln Electric Handy MIG Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur
dans d''autres langues
Documents connexes
-
Lincoln Electric SP125 Plus Mode d'emploi
-
Lincoln Electric EASY-MIG 180 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Lincoln Electric Pro-MIG 135 Manuel utilisateur
-
Lincoln Electric Pro-MIG 180 Mode d'emploi
-
Lincoln Electric SP130-T Mode d'emploi
-
Lincoln Electric SP130-T Mode d'emploi
-
Lincoln Electric Weldmark 135 Plus Mode d'emploi
-
Lincoln Electric 215 Manuel utilisateur
-
Lincoln Electric 215 Manuel utilisateur
-
Lincoln Electric Eagle 10,000 Mode d'emploi































