ESAB Aristo® Mig 4500i, Mig U4500i Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur
Ce manuel convient également à

Valid for serial no. 620--xxx--xxxx0459 376 187 060523
Mig 4500i
Mig U4500i
Aristot
These INSTRUCTIONS are for experienced operators. If you are not fully familiar with the principles of operation and safe practices
for arc welding equipment, we urge you to read our booklet, “Precations and Safe Practices for Arc, Cutting and Gouging, “Form
52--529. Do NOT permit untrained persons to install, operate, or maintain this equipment. Do NOT attempt to install or operate this
equipment until you have read and fully understand these instructions. If you do not fully understand these instructions, contact your
supplier for further information. Be sure to read the Safety Precautions before installing or operating this equipment.
CAUTION
Be sure this information reaches the operator.
You can get extra copies through your supplier .
US
Instruction manual

-- 2 --
TOCa
Sous réserve de modifications sans avis préalable.
Rights reserved to alter specifications without notice.
1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS 3............................................
2 USER RESPONSIBILITY 6............................................
3SAFETY 6...........................................................
4 INTRODUCTION 7...................................................
4.1 Equipment 7................................................................
4.2 Settings 7..................................................................
5 TECHNICAL DATA 8.................................................
6 INSTALLATION 9....................................................
6.1 Lifting instructions 9.........................................................
6.2 Placing 9...................................................................
6.3 Installation 10................................................................
6.4 Primary input 11.............................................................
6.5 Electrical installation 12.......................................................
6.6 Terminating resistor 13........................................................
7 OPERATION 13.......................................................
7.1 Connections and control devices 14............................................
7.2 Connection of several wire feed units 15.........................................
7.3 Overheating protection 15.....................................................
7.4 W ater flow guard 15..........................................................
7.5 Remote control unit 15........................................................
8 MAINTENANCE 16....................................................
8.1 Topping up the coolant 16.....................................................
8.2 Inspection and cleaning 16....................................................
9 TROUBLE SHOOTING 16..............................................
10 REPLACEMENT AND REPAIR PARTS 17................................
10.1 Ordering 17.................................................................
2 RESPONSABILITÉ DE L’UTILISATEUR 22...............................
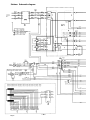
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM 34................................................
ORDERING NUMBER 36.................................................
ACCESSORIES 37.......................................................

-- 3 --
safetyaa
1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: These Safety Precautions are for your protection. They summarize precautionary information from the references
listed in Additional Safety Information section. Before performing any installation or operating procedures, be sure to read and follow the
safety precautions listed below as well as all other manuals, material safety data sheets, labels, etc. Failure to observe Safety
Precautions can result in injury or death.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS
Some welding, cutting and gouging precesses are noisy and require ear protection. The arc, like the sun,
emits ultraviolet (UV) and other radiation and can injure skin and eyes. Hot metal can cause burns. T raining
in the proper use of the processes and equipment is essential to prevent accidents. Therefore:
1. Always wear safety glasses with side shields in any work area, even if welding helmets face shields and goggles are also
required.
2. Use a face shield fitted with the correct filter and cover plates to protect your eyes, face, neck and ears from sparks and rays of
the arc when operating or observing operations. Warn bystanders not to watch the arc and not to expose themselves to the rays
of the electric--arc or hot metal.
3. Wear flameproof gauntlet type gloves, heavy long--sleeve shirt, cuffless trousers, high--topped shoes and a welding helmet or cap
for protection, to protect against arc rays and hot sparks or hot metal. A flameproof apron may also be desirable as protection
against radiated heat and sparks.
4. Hot sparks or metal can lodge in rolled up sleeves, trouser cuffs, or pockets. Sleeves and collars should be kept buttoned and
open pockets eliminated from the front of clothing.
5. Protect other personnel from arc rays and hot sparks with a suitable nonflammable partition or curtains.
6. Use goggles over safety glasses when chipping slag or grinding. Chipped slag may be hot and can fly far. Bystanders should also
wear goggles over safety glasses.
FIRES AND EXPLOSIONS
Heat from flames and arcs can start fires. Hot slag or sparks can also cause fires and explosions.
Therefore:
1. Remove all combustible materials well away from the work area or cover the materials with a protective nonflammable covering.
Combusible materials include wood, clot, sawdust, liquid and gas fuels, solvents, pants and coatings papper , etc.
2. Hot sparks or hot metal can fall through cracks or crevices in floors or wall openings and cause a hidden smoldering fire or fires
on the floor below. Make certain that such openings are protected from hot sparks and metal.
3. Do not weld, cut or perform other hot work until the workpiece has been completely cleaned so that there are no substances on
the workpiece which might produce flammable or toxic vapors. Do not do hot work on closed containers. They may explode.
4. Have fire extinguishing equipment handy for instant use, such as a garden hose, water pail, sand bucket, or portable fire
extinguisher . Be sure you are trained in its use.
5. Do not use equipment beyond its ratings. For example, overloaded welding cable can overheat and create a fire hazard.
6. After completing operations, inspect the work area to make certain there are no hot sparks or hot metal which could cause a later
fire. Use fire watchers when necessary .
7. For additional information refer to NFPA Standard 51B, “Fire Prevention in Use of Cutting and Welding Processes”, available from
the National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
ELECTRICAL SHOCK
Contact with live electrical parts and ground can cause severe injury or death. DO NOT use AC welding
current in damp areas, if movement is confined, or if there is danger of falling. Therefore:
1. Be sure the power source frame (chassis) is connected to the ground system of the input power.
2. Connect the workpiece to a good electrical ground.
3. Connect the work cable to the workpiece. A poor or missing connection can expose you or others to a fatal shock.
4. Use well--maintained equipment. Replace worn or damaged cables.
5. Keep everything dry , including clothing, work area, cables, torch/electrode holder and power source.
6. Make sure that all parts of your bady are insulated from work and
from ground.
7. Do not stand directly on metal or the earth while working in tight quarters or a damp area; stand on dry boards or an insulating
platform and wear rubber--soled shoes.
8. Put on dry, hole--free gloves before turning on the power.
9. Turn off the power before removing your gloves.
10. Refer to ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 (listed on next page) for specific grounding recommendations. Do not mistake the work lead
for a ground cable.
US

-- 4 --
safetyaa
ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
May be dangerous. Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized Electric and Magnetic
Fields (EMF). Welding and cutting current creates EMF around welding cables and welding machines.
Therefore:
1. Welders having pacemakers should consult their physician before welding. EMF may interfere with some pacemakers.
2. Exposure to EMF may have other health effects which are unknown.
3. Welders should use the following procedures to minimize exposure to EMF:
a. Route the electrode and work cables together . Secure them with tape when possible.
b. Never coil the torch or work cable around your body.
c. Do not place your body between the torch and work cables. Route cables on the same side of your body.
d. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as possible to the area being welded.
e. Keep welding power source and cables as far away from your body as possible.
FUMES AND GASES
Fumes and gases, can cause discomfort or harm, particularly in confined spaces. Do not breathe fumes and
gases. Shielding gases can cause asphyxiation.
Therfore:
1. Always provide adequate ventilation in the work area by natural or mechanical means. Do not weld, cut or gouge on materials
such as galvanized steel, stainless steel, cooper, zinc, lead beryllium or cadmium unless positive mechanical ventilation is
provided. Do not breathe fumes from these materials.
2. Do not operate near degreasing and spraying operations. The heat or arc can react with chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors to form
phosgene, a highly toxic gas and other irritant gases.
3. If you develop momentary eye, nose or throat irritation while operating, this is an indication that ventilation is not adequate. Stop
work and take necessary steps to improve ventilation in the work area. Do not continue to operate if physical discomfort persists.
4. Refer to ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 (see listing below) for specific ventilation recommendations.
5. WARNING: This product when used for welding or cutting, produces fumes or gases which contain chemicals known to the State
of Californa to cause birth defects and in some cases cancer (California Health & Safety Code §25249.5 et seq.)
CYLINDER HANDLING
Cylinders, if mishandled, can rupture and violently release gas. Sudden rupture of cylinder valve or relief
device can injure or kill.
Therefore:
1. Use the proper gas for the process and use the proper pressure reducing regulator designed to operate from the compressed gas
cylinder . Do not use adaptors. Maintain hoses and fittings in good condition. Follow manufacturer’s operating instructions for
mounting regulator to a compressed gas cylinder.
2. Always secure cylinders in an upright position by chain or strap to suitable hand trucks, undercarriages, benches, wall, post or
racks. Never secure cylinders to work tables or fixtures where they may become part of an electrical circuit.
3. When not in use, keep cylinder valves closed. Have valve protection cap in place if regulator is not connected. Secure and move
cylinders by using suitable hand trucks.
4. Locate cylinders away from heat, sparks and flames. Never strike an arc on a cylinder.
5. For additional information, refer to CGA Standard P--1, “Precations for Safe Handling of Comporessed Gases in Cylinders”, which
is available from Compressed Gas Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE
Faulty or improperly maintained equipment can cause injury or death. Therefore:
1. Always have qualified personnel perform the installaion, troubleshooting and maintenance work. Do not perform any electrical
work unless you are qualified to perform such work.
2. Before performing any maintenance work inside a power source, disconnect the power source from the incoming electrical power.
3. Maintain cables, grounding wire, connections, power cord and power supply in safe working order. Do not operate any equipment
in faulty condition.
4. Do not abuse any equipment or accessories. Keep equipment away from heat sources such as furnaces, wet conditions such as
water puddles, oil or grease, corrosive atmospheres and inclement weather.
5. Keep all safety devices and cabinet covers in position and in good repair.
6. Use equipment only for its intended purpose. Do not modify it in any manner.
US

DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
-- 5 --
safetyaa
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION
For more information on safe practices for electric arc welding and cutting equipment, ask your supplier for a copy
of “Precautions and Safe Practices for Arc Welding, Cutting and Gouging”, Form 52--529.
The following publications, which are available from the American Welding Society , 550 N.W. LeJuene Road, Miami, FL 33126, are
recommended to you:
1. ANSI/ASC Z49.1 -- “Safety in Welding and Cutting”
2. AWS C5.1 . “Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc Welding”
3. AWS C5.2 -- “Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc Cutting“
4. AWS C5.3 -- “Recommended Practices for Air Carbon, Arc Gouging and Cutting”
5. AWS C5.5 -- “Recommended Practices for Gas Tungsten Arc Welding”
6. AWS C5.6 -- “Recommended Practices for Gas Metal Arc welding”
7. AWS SP -- “Safe practices” -- Reprint, Welding Handbook
8. ANSI/AWS F4.1 -- “Recommended Safe Practices for Welding and Cutting of Containers That Have Held Hazardous Substances”
MEANING OF SYMBOLS
As used throughout this manual: Means Attention! Be Alert!
Means immediate hazards which, if not avoided, will result in immediate, serious personal injury
or loss of life.
Means potential hazards which could result in personal injury or loss of life.
Means hazards which could result in minor personal injury.
US

-- 6 --
bu18d1tua
2 USER RESPONSIBILITY
This equipment will perform in conformity with the description thereof contained in this manual and
accompanying labels and/or insert when installed, operated, maintained and repaired in accordance with
the instruction provided. This equipment must be checked periodically. Defective equipment should not be
used. Parts that are broken, missing, worn, distorted or contaminated should be replaced immediately.
Should such repair or replacement become necessary, the manufacturer recommends that a telephone or
written request for service advice be made to the Authorized Distributor from whom it was purchased.
This equipment or any of its parts should not be altered without the prior written approval of the
manufacturer. The user of this equipment shall have the sole responsibility for any malfunction which
results from improper use, faulty maintenance, damage improper repair or alteration by anyone other than
the manufacturer or a service facility designated by the manufacturer.
3SAFETY
Before the Mig 4500i / Mig U4500i power sources are put into operation, the safety precautions on page 3
and safety on page 6 should be read completely. This will help avoid possible injury due to misuse or
improper installation.
Users of ESAB welding equipment have the ultimate responsibility for ensuring that anyone who
works on or near the equipment observes all the relevant safety precautions. Safety precautions
must meet the requirements that apply to this type of welding equipment. The following recommen-
dations should be observed in addition to the standard regulations that apply to the workplace.
All work must be carried out by trained personnel well--acquainted with the operation of the welding
equipment. Incorrect operation of the equipment may lead to hazardous situations which can result
in injury to the operator and damage to the equipment.
1. Anyone who uses the welding equipment must be familiar with:
S its operation
S location of emergency stops
S its function
S relevant safety precautions
S welding
2. The operator must ensure that:
S no unauthorized person is stationed within the working area of the equipment when it is
started up.
S no--one is unprotected when the arc is struck
3. The workplace must:
S be suitable for the purpose
S be free from drafts
4. Personal safety equipment
S Always wear recommended personal safety equipment, such as safety glasses, flame--proof
clothing, safety gloves.
S Do not wear loose--fitting items, such as scarves, bracelets, rings, etc., which could become
trapped or cause burns.
5. General precautions
S Make sure the ground cable is connected securely.
S Work on high voltage equipment may only be carried out by a qualified electrician.
S Appropriate fire extinquishing equipment must be clearly marked and close at hand.
S Lubrication and maintenance must not be carried out on the equipment during operation.
ESAB can p rovide you with all necessary welding protection and accessories.
US

-- 7 --
bu18d1tua
WARNING!
Read and understand the instruction manual before installing
or operating.
Do not use the power source for thawing frozen pipes.
WARNING!
This product is solely intended for arc welding.
4 INTRODUCTION
The Mig 4500i and Mig U4500i power sources are intended for MMA (welding with
coated electrodes), MIG/MAG welding, TIG welding and carbon--arc gouging.
Mig is used together with the control unit U8 and/or wire feed unit Feed 3004 or Feed
4804.
ESAB’s accessories for the product can be found on page 37.
4.1 Equipment
Mig is supplied with terminating resistor, mains cable, guide pin, gas cylinder shelf, return
cable and instruction manual.
4.2 Settings
All settings are made using the control panel
U8 or wire feed unit with MMC.
Operation -- see separate instruction manuals.
US

-- 8 --
bu18d1tua
5 TECHNICAL DATA
Mig 4500i / MigU4500i
Mains voltage 230/400/500 V 3~50 Hz
208/230/460/475/575 V 3~60 Hz
Permittedloadat
100 % duty cycle
360 A / 34.4 V
60 % duty cycle 425 A / 37 V
45 % duty cycle 450 A / 38 V
Setting range
MIG/MAG
30 A / 15 V (8 V)--450 A / 36.5 V
MMA 10 A / 20 V -- 450 A / 38 V
TIG 10 A / 10 V -- 450 A / 28 V
Open circuit voltage
MIG/MAG
65 -- 80 V
MMA 50 -- 60 V
TIG 50 -- 60 V
Open circuit output
with cooling unit
140 W
310 W
Efficiency at maximum current
MIG/MAG
MMA
TIG
82 %
83 %
83 %
Power factor a t maximum current
MIG/MAG
MMA
TIG
0.92
0.92
0.90
Enclosure class IP 23
Weight
with cooling unit
315.2 lbs (143 kg)
346.1 lbs (157 kg)
Dimensions,lxwxh 35.9 x 25.3 x 32.9 inches
910 x 642 x 835 mm
Application class
Maximum number of water--cooled welding guns/torches that may be connected: two MIG welding guns
or one TIG torch and one MIG welding gun
Duty cycle
The duty cycle refers to the time as a percentage of a ten--minute period that you can weld at a cer-
tain load without overloading.
Enclosure class
The IP code indicates the enclosure class, i. e. the degree of protection against penetration by solid
objects or water. Equipment marked IP 23 is designed for indoor and outdoor use.
Application class
The symbol indicates that the power source is designed for use in areas with increased
electrical hazard.
US

-- 9 --
bu18d1tua
6 INSTALLATION
The installation must be done by a professional.
WARNING!
This product is intended for industrial use. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference. It is the user’ s responsibility to take adequate precautions.
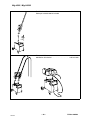
6.1 Lifting instructions
The power supply should be lifted by means of its lifting eye.
The handle is only intended for pulling it along the ground.
Lifting instructions
6.2 Placing
WARNING -- TIPPING RISK!
Fasten the equipment -- particularly if the
ground is uneven or sloping.
IMPORTANT! Place the equipment in an appropriate position and ensure that the
power source is not covered or placed so that cooling is obstructed.
US

-- 1 0 --
bu18d1tua
6.3 Installation
US

-- 1 1 --
bu18d1tua
6.4 Primary input
ELECTRIC SCHOCK CAN KILL! Precautionary measures should be taken to provide maximum
protection against electrical shock.
Be sure that all power is OFF by opening the line (wall) disconnect switch when primary
electrical connections are made to the power source.
Be sure to check your input leads with a voltmeter to make sure all power is OFF.
Check that the power source is connected to the
correct mains voltage and has the correct fuse
protection.
Earth according to applicable regulations.
Rating plate with connection data.
Recommended fuse protection and minimum cab le cross section
Mig 4500i 3~50 Hz 3~50 Hz 3~50 Hz 3~60 Hz 3~60 Hz 3~60 Hz 3~60 Hz 3~60 Hz
Mains voltage V
230 400 500 208 230 460 475 575
Current A 100 % 40 24.5 18.5 45 41 20 19.5 16.2
60 % 51 30.5 23 57.5 51.5 25 24.5 20.4
45 % 55.5 34 25 62 56.5 27.5 26.5 22.2
Mains cable cross
section
4G10 4G4 4G4 4G10 4G10 4G4 4G4 4G4
Fuse anti--surge A 50 20 20 50 50 20 20 20
NB! Sizes per National Electric Code for 90˚C rated cooper conductors @30˚C ambient. Not more than
three conductors in raceway or cable. Local codes should be followed if they specify larger sizes other
than those listed above.
US

-- 1 2 --
bu18d1tua
6.5 Electrical installation
US

-- 1 3 --
bu18d1tua
6.6 Terminating resistor
In order to avoid communication interference, the ends of the CAN bus must be fitted
with terminat ing resistors.
One end of the CAN bus is at the control unit or wire feed unit MMC, which has an
integral terminating resistor. The other end must be fitted with the terminating resistor,
as shown in the figure.
Depending on the connection in question the resistor is connected as follows:
1. Control panel connected to the wire feed unit.
THE TERMINATING RESISTOR IS CONNECTED AT
THE REAR OF THE POWER SOURCE.
(CONNECTED LIKE THIS ON DELIVERY)
.
2. Control unit connected to the power source.
THE TERMINATING RESISTOR IS
CONNECTED TO THE FRONT OF
THEWIREFEEDUNIT.
7 OPERATION
General safety regulations for the handling of the equipment can be found on
page 6. Read through before you start using the equipment!
NOTE!
When pulsing ensure the connection cable (max 8 m) between the power source,
feeding unit and return cable (max 8 m) are not rolled up.
US

-- 1 4 --
bu18d1tua
7.1 Connections and control devices
TIG Central connection
TIG, OKC connection
MMA, MIG/MAG
1 Cooling water filling 11 OKC connection TIG--torch.
2 Orange indicator lamp, overheating 12 Gas connection to TIG--torch
3 White indicator lamp, mains voltage 13 Connection for start signal from TIG--torch
4 Mains voltage switch 1 / 0 14 Gas hose connection
5 Cooling unit switch 15 Connection for welding current cable (+) to
wire feed unit.
6 Connection for cooling water from
TIG--torch RED
16 MCB 42V to wire feed unit.
7 Connection for cooling water to TIG--torch
BLUE
17/18 Connection for U8 control unit, for control
cable to the wire feed unit, for terminating
resistor or for the remote control adapter.
9 Connection (--) for the return cable with
MMA and MIG/MAG or for the welding
current cable with TIG welding
19 Connection for cooling water from the wire
feed unit RED
10 Connection (+) for the welding current
cable with MMA welding or for the return
cable with TIG welding
20 Connection for cooling water to the wire feed
unit BLUE
US

-- 1 5 --
bu18d1tua
7.2 Connection of several wire feed units
The wire feed unit Feed 3004 or Feed 4804 with control panel (M0) and control unit U8
should be used when connecting several wire feed units.
Contact authorised ESAB service personnel when connecting several wire feed units.
7.3 Overheating protection
The power source is cooled by forced air and is equipped with a thermal overload that
trips when the temperature is too high, this prevents overheating. Resetting takes place
automatically once the power source has cooled.
When this occurs the welding current is interrupted and the orange indicator lamp on
the front of the power source comes on.
7.4 Water flow guard
The water flow guard b locks the power source if the cooling water stops. When this
occurs the welding current is interrupted and an alarm is shown on the control unit.
The water flow guard is an a ccessory.
7.5 Remote control unit
The program version in U8 should be 1.20 or higher. Machines with intergral control
panels should have program version 1.21 or higher, in order for the remote control to
function correctly.
When the remote control unit is connected, the power source and wire feed unit are in
remote control mode; the buttons and knobs are blocked. T he functions can only be
adjusted via the remote unit.
If the remote control unit is not to be used, the r emote control unit must be disconnected
from the power source / wire feed unit, as otherwise it will remain in remote control
mode.
When a rem ote control unit is used to set the voltage, the function will be changed to
the setting of current during MMA welding.
For more information about the operation of the remote control unit, see the operating
instructions for the control unit/MMC.
US

-- 1 6 --
bu18d1tua
8 MAINTENANCE
Regular maintenance is important for safe, reliable operation.
Maintenance must be done by a professional.
Only those persons who have appropriate electrical knowledge (authorized personnel)
may remove the safety plates.
Note!
Supplier warranty is void if customer attempts any work on product during the warranty
period.
8.1 Topping up the coolant
We recommend a 50/50 % mixture of
water and ethylene glycol for the
coolant.
8.2 Inspection and cleaning
Check regularly that the power source is not dirty.
Methods and how often cleaning should be done depend on: the weld process, arc
times, placement, and the surrounding environment. It is normally sufficient to blow
down the power source with compressed air (reduced pressure) once a year.
9 TROUBLE SHOOTING
Try these recommended checks and inspections before sending for an authorised
service technician.
Type of fault Action
The power source does not produce an arc. S Check that the mains power supply switch is
turned on.
S Check that the welding current supply and return
cables are correctly connected.
S Check that the correct current value is set.
S Check to see whether the MCB has tripped.
Welding current is interrupted during welding. S Check whether the thermal overload has tripped
(indicated by the orange lamp on the front panel).
S Check the main power supply fuses.
US

-- 1 7 --
bu18d1tua
Type of fault Action
The thermal overload trips frequently. S Make sure the rated data for the power source is
not exceeded (overloading the power source).
Poor welding result. S Check that the welding current supply and return
cables are connected correctly.
S Check that the correct current value is set.
S Check that defective electrodes are not being
used.
S Check the main power supply fuses.
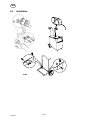
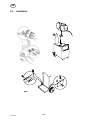
10 REPLACEMENT AND REPAIR PARTS
Repair and electrical work should be performed by an authorized ESAB service
personnel. Use only ESAB original replacement and wear parts.
When ordering replacement parts, order by part number and part name , as illustrated
on the figure. Always provide the series or serial number on the unit on which the parts
will be used. The serial number is stamped on the rating plate.
10.1 Ordering
To assure proper operation, it is recommended that only genuine ES
A
B parts and
products be used with this equipment.
Replacement parts may be ordered from your ESAB distibutor or from:
ESAB Welding & Cuttin Products
Attn: Customer Service Dept.
P.O. Box 100545, 411 S. Ebenezer Road
Florence, SC 29501--0545
To order parts by phone, contact ESAB at 1--843--664--5540. Orders may also be faxed
to 1--800--634--7548. Be sure to indicate any special shipping instructions when
ordering r eplacement parts.
Refer to the Communication Guide located on the last page of this manal for a list of
customer service phone numbers.
US

-- 1 8 --
TOCf
1 MESURES DE SECURITE 19...........................................
3 SÉCURITÉ 22.........................................................
4 INTRODUCTION 23...................................................
4.1 Équipement 23...............................................................
4.2 Paramètres 23...............................................................
5 CARACTÉRISTIQUES TECHNIQUES 24.................................
6 INSTALLATION 25....................................................
6.1 Instructions de levage 25......................................................
6.2 Emplacement 25.............................................................
6.3 Installation 26................................................................
6.4 Alimentation secteur 27.......................................................
6.5 Installation électrique 28.......................................................
6.6 Résistance d’extrémité 29.....................................................
7 UTILISATION 29......................................................
7.1 Appareils de contrôle et connexion 30...........................................
7.2 Connexion de plusieurs dévidoirs 31............................................
7.3 Protection contre la surchauffe 31..............................................
7.4 Capteur de débit d’eau 31.....................................................
7.5 Commande à distance 31.....................................................
8 ENTRETIEN 32.......................................................
8.1 Liquide de refroidissement 32..................................................
8.2 Inspection et nettoyage 32.....................................................
9 DÉPANNAGE 32......................................................
10 COMMANDE DE PIÈCES DE RECHANGE 33............................
10.1 Commande 33...............................................................
SCHÉMA 34.............................................................
NUMÉRO DE RÉFÉRENCE 36............................................
ACCESSOIRES 37.......................................................

-- 1 9 --
safetyaf
1 MESURES DE SECURITE
ATTENTION : ces règles de sécurité ont pour objet d’assurer votre protection. Elles constituent une synthèse des mesures de
sécurité contenues dans les ouvrages de référence repris au chapitre Informations complémentaires relatives à la Sécurité. Avant toute
installation ou utilisation du matériel, veillez à lire et à respecter les règles de sécurité énoncées ci--dessous ainsi que dans les divers
manuels, fiches de sécurité du matériel, étiquettes, etc. Le non--respect de ces précautions risque d’entraîner des blessures graves ou
mortelles.
PROTECTION INDIVIDUELLE ET DE L’ENTOURAGE
Certains procédés de soudage, découpage et gougeage sont bruyants et requièrent le port de protections
auditives. L’arc, tout comme le soleil, émet des ultraviolets (UV) et d’autres rayonnements susceptibles de
provoquer des lésions oculaires et dermatologiques. Le métal chaud peut être à l’origine de brûlures. Une
formation à l’utilisation correcte des procédés et équipements est essentielle pour prévenir les accidents.
En conséquence :
1. Porter impérativement des lunettes avec écrans latéraux dans les zones de travail, même lorsque le port du casque de soudage,
de l’écran facial et des lunettes de protection est obligatoire
2. Tant pour exécuter les travaux que pour y assister, porter un écran facial muni de plaques protectrices et de verres filtrants
appropriés pour protéger les yeux, le visage, le cou et les oreilles des étincelles et du rayonnement de l’arc. Avertir les personnes
se trouvant à proximité qu’elles ne doivent pas regarder l’arc, ni s’exposer à son rayonnement ou à celui du métal incandescent.
3. Porter des gants ignifuges à crispins, une tunique épaisse à longues manches, des pantalons sans rebord, des chaussures à
embout d’acier et un casque de soudage ou une casquette pour se protéger du rayonnement de l’arc, des étincelles et du métal
incandescent. Le port d’un tablier ininflammable est également recommandé afin de se protéger des étincelles et du rayonnement
thermique.
4. Les étincelles ou projections de métal en fusion risquent de se loger dans les manches retroussées, les bords relevés de
pantalons ou dans les poches. Il convient donc de boutonner complètement les manches et le col, et de porter des vêtements
sans poches à l’avant.
5. Protéger du rayonnement de l’arc et des étincelles les personnes se trouvant à proximité à l’aide d’un écran ou d’un rideau
ininflammable approprié.
6. Porter des oculaires et des lunettes de protection pendant le meulage du laitier. Les particules meulées, souvent brûlantes,
peuvent être projetées à des distances importantes, de sorte que les personnes se trouvant à proximité doivent également porter
des lunettes de protection.
INCENDIES ET EXPLOSIONS
La chaleur dégagée par les flammes et les arcs peuvent être à l’origine d’incendies. Le laitier incandescent
et les étincelles peuvent également provoquer incendies et explosions. En conséquence :
1. Éloigner suffisamment tous les matériaux combustibles de la zone de travail ou les recouvrir complètement d’une bâche ignifuge.
Ce type de matériaux comprend le bois, les vêtements, la sciure, les carburants sous forme liquide et gazeuse, les peintures, les
enduits, le papier, etc.
2. Les étincelles ou projections de métal en fusion peuvent tomber dans les fissures du sol ou des murs et déclencher une
combustion lente dans les planchers ou à l’étage inférieur. V eiller à protéger ces ouvertures pour que les étincelles et projections
n’y pénètrent pas.
3. Ne pas procéder à des travaux de soudage, de découpage et autres travaux à chaud tant que la surface n’est pas complètement
nettoyée et débarrassée des substances susceptibles de produire des vapeurs inflammables ou toxiques. Ne pas effectuer de
travaux à chaud sur des conteneurs fermés pour éviter tout risque d’explosion.
4. Conserver à portée de main un équipement d’extinction – tuyau d’arrosage, seau d’eau ou de sable, extincteur portatif, etc. et
s’assurer d’en connaître l’utilisation.
5. Ne pas utiliser l’équipement au--delà de ses spécifications. Par exemple, un câble de soudage surchargé est susceptible de
surchauffer et d’être à l’origine d’un incendie.
6. Une fois le travail terminé, inspecter la zone de travail pour s’assurer qu’aucune étincelle ou projection de métal ne risque de
déclencher un incendie. Le cas échéant, utiliser des systèmes de détection d’incendie.
7. Pour toute information supplémentaire, voir la norme NFPA 51B relative à la prévention des incendies lors de travaux de
découpage et de soudage, disponible auprès de la National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269 –
USA.
FR

-- 2 0 --
safetyaf
CHOC ELECTRIQUE
Tout contact avec des éléments sous tension et la masse peut provoquer des blessures graves ou
mortelles. NE PAS utiliser de courant de soudage CA dans des zones humides, des lieux exigus ou lorsqu’il
existe un risque de chute. En conséquence :
1. Vérifier que le châssis du générateur est bien relié au dispositif de mise à la masse de l’alimentation.
2. Assurer une mise à la masse correcte de la pièce à souder .
3. Connecter le câble de soudage à la pièce à souder. Un raccordement médiocre ou inexistant constitue un risque mortel pour
l’utilisateur et son entourage.
4. Utiliser du matériel correctement entretenu. Remplacer les câbles usés ou endommagés.
5. Empêcher l’apparition de toute humidité, notamment sur les vêtements, dans la zone de travail, sur les câbles, la torche de
soudage, le porte--électrode et le générateur.
6. S’assurer que le corps est totalement isolé de la pièce à souder et de la masse.
7. Éviter tout contact direct avec du métal ou la masse lors de travaux dans des endroits exigus et en zone humide ; se tenir sur des
panneaux ou sur une plate--forme isolante et porter des chaussures à semelles en caoutchouc.
8. Enfiler des gants secs et sans trous avant de mettre l’équipement sous tension.
9. Mettre l’équipement hors tension avant de retirer les gants.
10. V oir la norme ANSI/ASC Z49.1 (voir page suivante) pour les recommandations de mise à la masse. Ne pas confondre le câble de
soudage et le câble de masse.
CHAMPS ELECTRIQUES ET MAGNETIQUES
Danger. Le courant électrique parcourant les conducteurs génère localement des champs électriques et
magnétiques (EMF). Le courant de soudage et de découpe crée des EMF autour des câbles de soudage et
des postes à souder.
En conséquence :
1. Les porteurs de stimulateurs cardiaques consulteront leur médecin avant d’effectuer des travaux de soudage. Les EMF peuvent
en effet provoquer des interférences.
2. L’exposition aux EMF peut également avoir des effets méconnus sur la santé.
3. Les soudeurs respecteront les procédures suivantes pour réduire l’exposition aux EMF :
a. Rassembler en faisceau les câbles de soudage et d’électrode. Si possible, les attacher avec du ruban adhésif.
b. Ne jamais enrouler le câble de la torche ou le câble de soudage autour du corps.
c. L ’utilisateur ne doit jamais se trouver entre le câble de la torche et le câble de soudage. Faire passer tous les câbles du
même côté du corps.
d. Connecter le câble de soudage à la pièce à souder, au plus près de l’endroit du soudage.
e. S’éloigner au maximum du générateur et des câbles.
FUMEES ET GAZ
L’inhalation des fumées et gaz peut provoquer des malaises et des dommages corporels, surtout lors de
travaux dans les espaces confinés. Ne pas les respirer. Les gaz inertes peuvent causer l’asphyxie.
En conséquence :
1. Assurer une aération adéquate de la zone de travail par une ventilation naturelle ou mécanique. Ne pas effectuer de travaux de
soudage, découpage ou gougeage sur des matériaux tels que l’acier galvanisé, le cuivre, le zinc, le plomb, le béryllium et le
cadmium en l’absence d’une ventilation mécanique adéquate. Ne pas inhaler les fumées dégagées par ces matériaux.
2. Ne pas travailler à proximité d’opérations de dégraissage et de pulvérisation étant donné que la chaleur dégagée et l’arc peut
réagir avec les hydrocarbures chlorés pour former du phosgène – un gaz particulièrement toxique – et d’autres gaz irritants.
3. Une irritation momentanée des yeux, du nez ou de la gorge provoquée par les travaux est le signe d’une ventilation inappropriée.
Dans ce cas, il convient d’arrêter le travail et de prendre les mesures nécessaires pour améliorer l’aération. Ne pas poursuivre le
travail si le malaise persiste.
4. Voir la norme ANSI/ASC Z49.1 (voir ci--dessous) pour les recommandations de ventilation.
5. ATTENTION : utilisé dans des opérations de soudage et de découpage, ce produit dégage des fumées et gaz qui contiennent
des substances chimiques reconnues par l’État de Californie comme pouvant être à l’origine de malformations congénitales et de
cancers (California Health & Safety Code §25249.5 et seq.).
FR
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
ESAB Aristo® Mig 4500i, Mig U4500i Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur
- Ce manuel convient également à
dans d''autres langues
Documents connexes
-
ESAB Mig U4500i Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Mig U5000i Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Mig U5000i Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Mig U5000i Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Mig U5000i Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Mig U5000i Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Aristo®Mig U500 Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Mig 5000i Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Mig 5000i Manuel utilisateur
-
ESAB Mig 5000i Manuel utilisateur











































