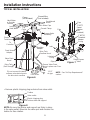
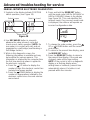
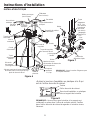
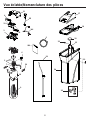
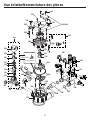
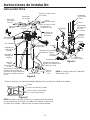
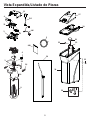
Ci-dessous, vous trouverez de brèves informations pour GXSH40V, GXSH45V. Il s'agit d'un système d'adoucissement de l'eau qui utilise un processus d'échange d'ions pour éliminer les minéraux durs de l'eau. Le système est doté d'un bouton de recharge qui permet de lancer manuellement une recharge. Le système dispose d'une fonction de diagnostic automatique qui surveille les composants et les circuits électroniques pour un fonctionnement correct. Le système a une capacité d'efficacité nominale de 4 000 grains d'échange de dureté totale par livre de sel. Le système doit être installé conformément aux codes de la plomberie locaux et doit être protégé des éléments si installé à l'extérieur.
Ci-dessous, vous trouverez de brèves informations pour GXSH40V, GXSH45V. Il s'agit d'un système d'adoucissement de l'eau qui utilise un processus d'échange d'ions pour éliminer les minéraux durs de l'eau. Le système est doté d'un bouton de recharge qui permet de lancer manuellement une recharge. Le système dispose d'une fonction de diagnostic automatique qui surveille les composants et les circuits électroniques pour un fonctionnement correct. Le système a une capacité d'efficacité nominale de 4 000 grains d'échange de dureté totale par livre de sel. Le système doit être installé conformément aux codes de la plomberie locaux et doit être protégé des éléments si installé à l'extérieur.




















-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
Ci-dessous, vous trouverez de brèves informations pour GXSH40V, GXSH45V. Il s'agit d'un système d'adoucissement de l'eau qui utilise un processus d'échange d'ions pour éliminer les minéraux durs de l'eau. Le système est doté d'un bouton de recharge qui permet de lancer manuellement une recharge. Le système dispose d'une fonction de diagnostic automatique qui surveille les composants et les circuits électroniques pour un fonctionnement correct. Le système a une capacité d'efficacité nominale de 4 000 grains d'échange de dureté totale par livre de sel. Le système doit être installé conformément aux codes de la plomberie locaux et doit être protégé des éléments si installé à l'extérieur.
dans d''autres langues
- English: GE GXSH40V Owner's manual
- español: GE GXSH40V El manual del propietario
Documents connexes
Autres documents
-
Pentair OMNIFILTER OM26K Le manuel du propriétaire
-
OmniFilter OM34K/OM40K Le manuel du propriétaire
-
 Kinetico 4040s with Overdrive Le manuel du propriétaire
Kinetico 4040s with Overdrive Le manuel du propriétaire
-
OmniFilter OM26KCS Installation Instructions Manual
-
 Kenmore Elite 625385200 Guide d'installation
Kenmore Elite 625385200 Guide d'installation
-
Castorama Integral Manuel utilisateur
-
vitapur VWS296GR Manuel utilisateur

























































































































