

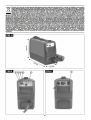
pilota viene trasferito tra l'elettrodo ed il pezzo stesso Figura (A) disegno ingombro macchina
instaurando un arco plasma detto anche arco di taglio.
Il tempo di mantenimento dell'arco pilota è di 2s ; se il SICUREZZA DEL SISTEMA PER TAGLIO PLASMA.
trasferimento non è effettuato entro questo tempo il ciclo Solo il modello di torcia previsto ed il relativo abbinamento
viene automaticamente bloccato salvo il mantenimento con la sorgente di corrente come indicato sui "DATI
dell'aria di raffreddamento. TECNICI" garantisce che le sicurezze previste dal
Per iniziare di nuovo il ciclo è necessario rilasciare il costruttore siano efficaci (sistema di interblocco).
pulsante torcia e ripremerlo. NON UTILIZZARE torce e relative parti di consumo di
diversa origine.
COMPOSIZIONE IMPIANTO. NON TENTARE DI ACCOPPIARE ALLA SORGENTE DI
Il sistema di taglio plasma comprende: CORRENTE torce costruite per procedimenti di taglio o
SORGENTE DI CORRENTE SALDATURA non previsti in queste istruzioni.
completa di: IL MANCATO RISPETTO DI QUESTE REGOLE può
Cavo di alimentazione dare luogo a GRAVI pericoli per la sicurezza fisica
Cavo di massa con pinza dell'utente e danneggiare l'apparecchiatura.
Torcia per taglio plasma INSTALLAZIONE
SORGENTE DI CORRENTE PER TAGLIO PLASMA
Protezione elettrica : Classe I ALLACCIAMENTO ALLA LINEA ELETTRICA
Grado protezione involucro : IP 23 La macchina deve essere collegata a un sistema Linea
Classe termica isolamento : H Neutro con conduttore di terra di protezione "PE".
Dimensioni (mm) : 475 x 170 x 340 Verificare che l'apposito terminale della presa sia
effettivamente collegato alla terra di distribuzione.
INPUT TAB.1
COLLEGAMENTO DEL CAVO DI MASSA.
Collegare il morsetto a pinza del cavo di massa al pezzo da
tagliare od al banco metallico di sostegno osservando le
seguenti precauzioni:
VERIFICARE CHE VENGA STABILITO UN BUON
CONTATTO ELETTRICO IN PARTICOLARE SE
VENGONO TAGLIATE LAMIERE CON RIVESTIMENTI
ISOLANTI, OSSIDATE, ETC.
ESEGUIRE IL COLLEGAMENTO DI MASSA IL PIU'
VICINO POSSIBILE ALLA ZONA DI TAGLIO.
L'UTILIZZAZIONE DI STRUTTURE METALLICHE NON
FACENTI PARTE DEL PEZZO IN LAVORAZIONE,
COME CONDUTTORE DI RITORNO DELLA
CORRENTE DI TAGLIO, PUO' ESSERE PERICOLOSO
PER LA SICUREZZA E DARE RISULTATI
INSUFFICIENTI NEL TAGLIO.
NON ESEGUIRE IL COLLEGAMENTO DI MASSA
OUTPUT SULLA PARTE DEL PEZZO CHE DEV'ESSERE
ASPORTATA.
UBICAZIONE E MOVIMENTAZIONE DELLA SORGENTE
DI CORRENTE.
Scegliere il luogo di ubicazione verificando che vi sia una
buona circolazione d'aria esente da polveri, fumi o gas
conduttivi o aggressivi.
Assicurarsi che eventuali ostacoli non impediscano il
flusso d'aria di raffreddamento dalle aperture anteriori e
posteriori della macchina.
Prevedere un piano di appoggio orrizzontale con uno
spazio libero non inferiore a 500 mm attorno alla
macchina.
Dovendo effettuare spostamenti della macchina staccare
MASSA DELLA MACCHINA (Tabella 1) sempre la spina dalla presa di alimentazione e
raccogliere cavi e tubazioni per evitare che possano
TORCIA MANUALE PER TAGLIO PLASMA essere danneggiati transitando sopra di essi.
(in dotazione) Controllare il corretto posizionamento della cinghia per il
Gas utilizzato: Aria compressa secca sollevamento della macchina (Fig. L).
Pressione aria compressa: 2,5 bar
Portata aria totale (per Plasma e raffred.): 30 L / min
Sistema d'innesco: a contatto elettrodo mobile ugello
Corrente di taglio: 7 ÷ 25 A
Massa ( Kg ): 1 Kg
2

5 Tensione di alimentazione (U ).
1
DISPOSITIVI DI CONTROLLO, 6 Corrente RMS massima assorbita I e corrente
1max
SEGNALAZIONE E SICUREZZA RMS nominale assorbita I .
1eff
c Generali
SORGENTE DI CORRENTE 7 Grado di protezione involucro.
Vedere disegno pannello anteriore e posteriore 8 Simbolo di apparecchiatura idonea ad ambienti a
(Fig B C) rischio accresciuto di shock elettrico.
1 INTERRUTTORE GENERALE O I .(Fig.C 1) 9 Simbolo del tipo di processo.
In posizione I (ON) macchina pronta per il funzionamento, 10 Schema di conversione di energia.
segnale luminoso verde dell'interruttore e led verde 11 Normativa di riferimento.
(Fig.B 6) di indicazione presenza rete accesi. I circuiti di 12 Identificazione dell' apparecchiatura.
controllo e servizio sono alimentati, ma non è presente 13 Nome del costruttore.
tensione alla torcia (STAND BY). 14 Gamma della corrente di taglio (min/max) e della
In posizione O (OFF) è inibito qualunque funzionamento; i corrispondente tensione convenzionale d’arco.
dispositivi di controllo sono disattivati, segnali luminosi 15 Numero di matricola fabbricazione.
spenti. 16 Valore dei fusibili ad azionamento ritardato da
prevedere per la protezione della linea.
2 POTENZIOMETRO DI CORRENTE DI TAGLIO(Fig B D) 17 Simboli riferiti a norme di sicurezza.
Permette di predisporre l'intensità di corrente di taglio
fornita dalla macchina da adottare in funzione
dell'applicazione (spessore del materiale/velocità). Rifarsi TORCIA
ai DATI TECNICI per il corretto rapporto d'intermittenza Il pulsante torcia è l'unico organo di controllo da cui può
lavoro pausa da adottare in funzione della corrente essere comandato l'inizio e l'arresto delle operazioni di
selezionata (periodo = 10 min.). taglio.
In TAB.2 è riportata la velocità di taglio in funzione dello Al cessare dell'azione sul pulsante il ciclo viene interrotto
spessore per i materiali alluminio, ferro e acciaio alla istantaneamente in qualunque fase salvo il mantenimento
corrente di 25A. dell'aria di raffreddamento (post aria).
3 TORCIA ENERGIZZATA (LED GIALLO di presenza Manovre accidentali: per dare il consenso di inizio ciclo,
tensione in torcia). (Fig.B 3) l'azione sul pulsante dev'essere esercitata per un tempo di
Quando acceso indica che il circuito di taglio è almeno 500 ms (millisecondi).
attivato: Arco Pilota o Arco di Taglio "ON".
E' normalmente spenta (circuito di taglio disattivato) con
pulsante torcia NON azionato (condizione di stand by). OPERAZIONI DI TAGLIO
E' spenta, con pulsante torcia azionato, nelle seguenti
condizioni: PRELIMINARI.
Durante la fase di POSTARIA (>20s). Verificare e rendere operative le condizioni previste
Se l'arco pilota non viene trasferito al pezzo entro il nei paragrafi (1) SICUREZZA e (3) INSTALLAZIONE di
tempo massimo di 2 secondi. queste istruzioni.
Se l'arco di taglio s'interrompe per eccessiva distanza IMPORTANTE!
torcia pezzo, eccessiva usura dell'elettrodo o Prima di iniziare le operazioni di taglio, verificare il corretto
allontanamento forzato della torcia dal pezzo. montaggio delle parti di consumo ispezionando la testa
Se è intervenuto un sistema di SICUREZZA. della torcia come indicato nel paragrafo
"MANUTENZIONE TORCIA".
4 SICUREZZA TERMICA E ANOMALIA DI TENSIONE DI Chiudere (portare in posizione I ), in sequenza
RETE (Led GIALLO di allarme generale) (Fig.B 4) l'interruttore automatico di linea e l'interruttore generale in
Quando acceso indica sovrariscaldamento di qualche macchina.
componente del circuito di potenza, o anomalia della Scegliere, agendo sul potenziometro di corrente di taglio,
tensione di alimentazione di ingresso (sotto o la corrente più adatta al lavoro da eseguire.
sovratensione) Premere e rilasciare il pulsante torcia dando luogo
Durante questa fase è inibito il funzionamento della all'efflusso aria (≥20 secondi post aria).
macchina. Lasciare terminare spontaneamente l'efflusso aria per
Il ripristino è automatico (spegnimento del led giallo) facilitare la rimozione di eventuale condensa
dopo che una delle anomalie tra quelle sopra indicate accumulatasi nella torcia.
rientra nel limite ammesso. TAGLIO
5 SICUREZZA TERMICA COMPRESSORE (LED rosso Modalità di taglio:
di allarme, Fig. B 5) Con la TORCIA si deve lavorare con UGELLO A
Quando acceso indica sovrariscaldamento degli CONTATTO
avvolgimenti del motore elettrico a bordo del compressore ATTENZIONE!
d’aria. L'esecuzione del taglio a contatto, ove non previsto, causa
una rapida usura dell'ugello torcia. Avvicinare l'ugello
6 TARGA DATI CARATTERISTICI (Fig. I) della torcia al bordo del pezzo (= 3 mm.), premere il
a Dati di utilizzazione (circuito di taglio). pulsante torcia; dopo circa 0.5 secondi (pre aria) si
1 Tensione a vuoto (U ).
0ottiene l'innesco dell'arco pilota (durata max 2 secondi).
2 Corrente tensione di taglio (I /U )
22 Se la distanza è adeguata l'arco pilota si trasferisce
3 Rapporto d'intermittenza (X) d'utilizzazione. immediatamente al pezzo dando luogo all'arco di taglio.
b Dati di linea (alimentazione). Spostare la torcia sulla superficie del pezzo lungo la linea
4 Numero fasi e frequenza di alimentazione 50/60 Hz. 3

ideale di taglio con avanzamento regolare. Adeguare la TORCIA
velocità di taglio in base allo spessore ed alla corrente Periodicamente, in funzione dell'intensità d'impiego o nella
selezionata, verificando che l'arco uscente dalla evenienza di difetti di taglio (vedi Paragrafo 5) verificare lo
superficie inferiore del pezzo assuma un'inclinazione di 5 stato d'usura delle parti della torcia interessate dall'arco
10° sulla verticale in senso opposto alla direzione plasma:
dell'avanzamento. 1 PORTAUGELLO (Fig. G 1)
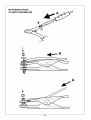
Figura (E) disegno torcia posizione sul pezzo Svitare manualmente dalla testa della torcia.
avanzamento, inclinazione arco Eseguire un'accurata pulizia o sostituirlo se danneggiato
Il distanziamento della torcia dal pezzo o l'assenza del (bruciature, deformazioni o incrinature).
materiale (fine taglio) causa l'immediata interruzione Verificare l'integrità del settore metallico superiore
dell'arco. (attuatore sicurezza torcia).
L'interruzione dell'arco (di taglio o pilota) è ottenuta 2 UGELLO (Fig. G 2)
sempre al rilascio del pulsante torcia. Controllare l'usura del foro di passaggio dell'arco plasma e
Foratura: dovendo eseguire questa operazione od delle superfici interne ed esterne.
effettuare partenze in centro pezzo, innescare con la Se il foro risulta allargato rispetto il diametro originale o
torcia inclinata e portarla con movimento progressivo in deformato sostituire l'ugello.
posizione verticale. Se le superfici risultano particolarmente ossidate pulirle con
carta abrasiva finissima.
Figura (F) disegno partenza con torcia inclinata 3 ANELLO DISTRIBUTORE ARIA (Fig. G 3)
Questa procedura evita che ritorni d'arco o di particelle Verificare che non siano presenti bruciature o incrinature
fuse rovinino il foro dell'ugello riducendone rapidamente oppure che non siano ostruiti i fori di passaggio aria.
la funzionalità. Se danneggiato sostituire immediatamente.
Forature di pezzi di spessore inferiore al 25% del massimo 4 ELETTRODO (Fig. G 4)
previsto nella gamma d'utilizzo possono essere eseguite Sostituire l'elettrodo quando la profondità del cratere che si
direttamente. forma sulla superficie emettitrice è di circa 1,5 mm
DIFETTI DI TAGLIO PIU' COMUNI Figura (G) disegno esploso torcia
Durante le operazioni di taglio possono presentarsi dei
difetti di esecuzione che non sono normalmente da Figura (H) disegno elettrodo con cratere
attribuire ad anomalie di funzionamento dell'impianto ma ad
altri aspetti operativi quali: ATTENZIONE!
a Penetrazione insufficiente o eccessiva formazione di Prima di eseguire qualsiasi intervento sulla torcia
scoria: lasciarla raffreddare almeno per tutto il tempo di
velocità di taglio troppo elevata, "postaria”
torcia troppo inclinata, Salvo casi particolari, è consigliabile sostituire elettrodo e
spessore pezzo eccessivo, ugello CONTEMPORANEAMENTE.
elettrodo ed ugello torcia usurati. Rispettare l'ordine di montaggio dei componenti della
b Interruzione dell'arco di taglio: torcia (inverso rispetto lo smontaggio), Fig.G.
velocità di taglio troppo bassa, Porre attenzione che l'anello distributore venga montato
distanza torcia pezzo eccessiva, correttamente.
elettrodo consumato, Rimontare il portaugello avvitandolo a fondo
intervento di una protezione manualmente con leggera forzatura.
c Taglio inclinato (non perpendicolare): In nessun caso montare il portaugello senza avere
posizione torcia con corretta, preventivamente montato elettrodo, anello distributore ed
usura asimmetrica del foro ugello e/o montaggio non ugello.
corretto componenti torcia. La tempestività e la corretta procedura dei controlli
d Usura eccessiva di ugello ed elettrodo: sulle parti di consumo della torcia sono vitali per la
pressione aria troppo bassa, sicurezza e la funzionalità del sistema di taglio.
aria contaminata (umidità),
portaugello danneggiato, CORPO TORCIA, IMPUGNATURA E CAVO.
eccesso d'inneschi d'arco pilota in aria. Normalmente questi componenti non necessitano di
manutenzione particolare salvo un'ispezione periodica ed
MANUTENZIONE una pulizia accurata da eseguire SENZA UTILIZZARE
ATTENZIONE! SOLVENTI DI QUALSIASI NATURA.
IN NESSUN CASO ACCEDERE ALL'INTERNO DELLA Se si riscontrano danni all'isolamento quali fratture,
SORGENTE DI CORRENTE (RIMOZIONE DEI incrinature e bruciature oppure allentamento delle
PANNELLI) O ESEGUIRE INTERVENTI SULLA TORCIA condutture elettriche, la torcia NON PUO' ESSERE
(SMONTAGGIO) SENZA CHE SIA STATA IN ULTERIORMENTE UTILIZZATA POICHE' LE CONDIZIONI
PRECEDENZA SCOLLEGATA LA SPINA DALLA PRESA DI SICUREZZA NON SONO SODDISFATTE.
DI ALIMENTAZIONE. IN QUESTO CASO LA RIPARAZIONE (MANUTENZIONE
CONTROLLI ESEGUITI SOTTO TENSIONE STRAORDINARIA) NON PUO' ESSERE EFFETTUATA
ALL'INTERNO DELLA MACCHINA O DELLA TORCIA SUL LUOGO MA DELEGATA AD UN CENTRO DI
POSSONO CAUSARE SHOCK ELETTRICO GRAVE ASSISTENZA AUTORIZZATO, IN GRADO DI
ORIGINATO DA CONTATTO DIRETTO CON PARTI IN EFFETTUARE LE PROVE SPECIALI DI COLLAUDO
TENSIONE. DOPO LA RIPARAZIONE.
Per mantenere in efficenza torcia e cavo è necessario
4


unique alimentation autant pour le gaz plasma que pour
le gaz de refroidissement et de protection.
Le départ du cycle est déterminé par un arc, appelé arc
pilote, qui s'instaure entre l'électrode mobile ( polarité )
et la tuyère de la torche ( polarité + ) sous l'effet du (forni)
courant de court circuit entre ces deux éléments. Gaz utilisé : Air comprimé sec
En mettant la torche en contact direct avec le morceau à Pression air comprimé : 2,5 bar
couper ( branché à la polarité + de la source de courant ) Débit d'air total (pour Plasma et refroidissement): 30 L / min.
l'arc pilote est transféré entre l'électrode et le morceau lui Système d'enclenchement :par cont act élec trode
même, instaurant ainsi un arc de plasma aussi appelé arc mobile tuyère
de coupe. Courant de coupe : 7 ÷ 25 A
Le temps de maintien de l'arc pilote programmé en usine Poids ( Kg ) : 1 Kg
est de 2s ; si le transfert n'est pas effectué dans cette
limite de temps, le cycle est automatiquement bloqué mis
à part le maintien de l'air de refroidissement.
Pour commencer un nouveau cycle il faut relâcher le
bouton poussoir de la torche et l'enclencher à nouveau.
BRANCHEMENT A LA LIGNE ELECTRIQUE
La machine doit être branchée à un système Ligne Neutre
avec conducteur de terre de protection "PE".
Vérifier que le terminal de la prise prévu à cet effet soit
bien branché à la terre de distribution.
TORCHE MANUELLE POUR COUPE PLASMA
Figure (A) Dessin dimensions de la machine
ATTENTION!
SÉCURITÉ DU SYSTEME POUR COUPE PLASMA.
Seul le modèle de torche prévu et son raccord avec le
COMPOSITION DE L’INSTALLATION générateur de courant (comme il est indiqué au paragraphe
Le système de coupe au plasma comprend: “DONNÉES TECHNIQUES”) garantit l’efficacité des
GÉNÉRATEUR DE COURANT sécurités prévues par le constructeur (système interbloc).
avec: NE PAS UTILISER de torches et d’électrodes d’origines
Câble d’alimentation différentes.
Kit de raccords pour air comprimé NE PAS ESSAYER DE BRANCHER AU GÉNÉRATEUR
Câble de masse avec pince DE COURANT des torches construites pour des
Torche pour coupe au plasma procédés de coupe ou de SOUDURE non prévues dans
ces instructions.
GÉNÉRATEUR DE COURANT POUR COUPE PLASMA LE NON RESPECT DE CES REGLES peut donner lieu à
Protection électrique : Classe I de GRAVES dangers pour la sécurité physique de
Degré protection enveloppe : IP 23 l’utilisateur, et endommager l’appareil.
Classe thermique isolation : H
Dimensions (mm) : 475x170x340 INSTALLATION
INPUT:
TAB.1
BRANCHEMENT DU CABLE DE MASSE
Brancher la borne à pince du câble de masse à la pièce à
couper ou à l’établi métallique de soutien en observant les
précautions suivantes:
VÉRIFIER QU’UN BON CONTACT ÉLECTRIQUE
S’ÉTABLISSE, EN PARTICULIER SI L’ON COUPE DES
TOLES AVEC DES REVETEMENTS ISOLANTS,
OXYDÉES, ETC.
EFFECTUER LE BRANCHEMENT DE MASSE LE PLUS
PRES POSSIBLE DE LA ZONE DE COUPE.
OUTPUT: L’UTILISATION DE STRUCTURES MÉTALLIQUES NE
FAISANT PAS PARTIE DE LA PIECE, COMME
CONDUCTEUR DE RETOUR DU COURANT DE
COUPE, PEUT ETRE DANGEREUSE POUR LA
SÉCURITÉ ET DONNER DES RÉSULTATS
INSUFFISANTS LORS DE LA COUPE.
NE PAS EFFECTUER LE BRANCHEMENT DE MASSE
SUR LA PARTIE DE LA PIECE DEVANT ETRE
ENLEVÉE.
BRANCHEMENT DE LA TORCHE POUR LA COUPE
PLASMA
IMPORTANT!
Avant de commencer les opérations de coupe, vérifier que
le montage des parties sujette à usure soit correct en
inspectant la tête de la torche comme il est indiqué au
MASSE DE LA SOUDEUSE (Tableau 1)
6

paragraphe “ENTRETIEN TORCHE”. 4. SÉCURITÉ THERMIQUE ET ANOMALIE TENSION
RESEAU (Fig.B 4) (Voyant lumineux JAUNE d’alarme
SITUATION ET DÉPLACEMENT DE LA SOURCE DE générale).
COURANT Quand il est allumé il indique une surchauffe de quelques
Choisir l’emplacement en vérifiant qu’il y ait une bonne composants du circuit de puissance, ou anomalies de la
circulation d’air exempte de poussières, fumées ou tension d’alimentation en entrée (sous ou surtension).
gaz conducteurs ou agressifs. Pendant cette phase le fonctionnement de la machine
S’assurer qu’aucun obstacle n’empêche le passage d’air est inhibé.
de refroidissement par les ouvertures avant et arrière de
la machine.
Prévoir un espace libre d’au moins
500mm autour de la machine.
En cas de nécessité de déplacement de la machine,
débrancher la prise du secteur et recueillir câbles et
tuyaux pour éviter qu’ils ne soient abîmés ou piétinés.
Contrôler le positionnement correct de la courroie pour le
soulPvement de la machine (Fig. L). 6. SÉCURITÉ PRESSION AIR. (voyant lumineux JAUNE
IMPORTANT! couplé au voyant lumineux ROUGE de l’alarme
L’air contenant une quantité considérable d’humidité générale). (Fig.C 7)
ou d’huile, peut causer une usure excessive des parties
y étant sujettes ou endommager la torche.
DISPOSITIFS DE CONTROLE,
SIGNALISATION ET SÉCURITÉ SOURCE
DE COURANT
Figure (C) Voir dessin panneaux antérieur et postérieur.
1. INTERRUPTEUR GÉNÉRAL O - I. (Fig.B C)
Sur I (ON), machine prête pour le fonctionnement,Voyant
lumineux (vert) de l’interrupteur avec en plus un voyant
lumineux de couleur verte (Fig.B 6) d’indication de
branchement au réseau.
Les circuits de contrôle et de service sont alimentés, mais il
n’y a pas de tension à la torche (STAND BY).
Sur O (OFF) tout fonctionnement est inhibé; les dispositifs
de contrôle sont désactivés, signal lumineux éteint.
2. POTENTIOMETRE COURANT DE COUPE. (Fig. B D)
Permet de régler l’intensité du courant de coupe fourni par la
machine, qui doit être adoptée en fonction de l’application
(épaisseur du matériau/vitesse).Se référer aux DONNÉES
TECHNIQUES pour un rapport d’intermittence travail
pause correct à adopter en fonction de la gamme
sélectionnée (période = 10 min). TORCHE
Le bouton torche est le seul organe de contrôle duquel peut
être commandé le départ et l’arrêt des opérations de coupe.
Quand on cesse d’appuyer sur le bouton, le cycle
s’interrompt instantanément pendant n’importe quelle
3. TORCHE “ON” (Voyant lumineux jaune indiquant la phase excepté le maintient de l’air de refroidissement (post
mise sous tension de la torche). (Fig.B 3) air).
Quand ce dernier est allumé cela signifie que le circuit Manoeuvres accidentelles: Pour donner le départ du
de coupe est activé: Arc Pilote et Arc de Coupe “ON”. cycle, appuyer sur le bouton pendant au moins 500ms
Elle est normalement éteinte (circuit de coupe désactivé) (millisecondes).
avec bouton torche NON actionné (condition de stand by).
Elle est éteinte, avec bouton torche actionné, dans les OPÉRATIONS DE COUPE
conditions suivantes:
Durant la phase de POST AIR (>20s). PRÉLIMINAIRES
Si l’arc pilote n’est pas transféré à la pièce dans le temps Vérifier et appliquer les conditions prévues aux
maximum de 2 secondes. paragraphes (1) SÉCURITÉ et INSTALLATION de ces
Si l’arc pilote s’interrompt à cause de la distance instructions.
excessive torche pièce, de l’usure excessive de Fermer (mettre en position I), l’un après l’autre
l’électrode ou allentamento forcé de la torche de la pièce. l’interrupteur automatique de ligne et l’interrupteur
Si un système de SÉCURITÉ est intervenu. général de la machine.
Choisir, en agissant sur le potentiomètre du courant de
La remise en fonction est automatique (extinction de la led
jaune) 4s après la correction d'une des anomalies
un plan horizontal, indiquées ci dessus la limite admise.
5 SÉCURITÉ THERMIQUE COMPRESSEUR (DEL rouge
d'alarme, Fig. B 5)
Le DEL allumé indique une surchauffe des enroulements
du moteur électrique du compresseur à air.
a Données d'utilisation (circuit de coupe).
1 Tension à vide (U).
0
2 Courant tension de coupe (I /U )
22
3 Rapport d'intermittence (X) d'utilisation.
b Données de ligne (alimentation).
4 Nombre de phases et fréquence d'alimentation 50/60
Hz.
5 Tension d'alimentation (U ).
1
6 Courant RMS maximal absorbé I1max et courant RMS
nominal absorbé I .
1eff
c Généralités
7 Degré de protection étui
8 Symbole d'appareil adéquat pour milieux à risque accru
de choc électrique
9 Symbole du type de processus
10 Schéma de conversion d'énergie
11 Norme de référence
12 Identification de l'appareil
13 Nom du constructeur
14 Gamme du courant de coupe (min/max) et de la tension
d'arc conventionnelle correspondante.
15 Numéro de matricule fabrication
16 Valeur des fusibles à commande retardée à prévoir pour
la protection de la ligne.
17 Symboles se référant aux normes de sécurité.
La Tab. 2 représente la vitesse de coupe en fonction de
l'épaisseur pour les matériaux en aluminium, fer et acier
avec un courant maximal de 25A.
7

coupe la position la plus adéquate au travail à effectuer. incorrect des composants de la torche.
Presser et relâcher le poussoir torche pour libérer le flux dUsure excessive de la buse et de l’électrode:
pression trop basse de l’air,
d'air (≥20 secondes post air). air contaminé (humidité, huile),
Laisser terminer spontanément le débit d’air pour faciliter porte buse endommagé,
l’évacuation de buée éventuelle qui aurait pu s’accumuler excès d’amorçages d’arc pilote en l’air.
dans la torche.
ENTRETIEN
ATTENTION!
N’ACCÉDER EN AUCUN CAS A L’INTÉRIEUR DU
GÉNÉRATEUR DE COURANT (RETRAIT DES
PANNEAUX) ET NE PAS EFFECTUER NON PLUS
D’INTERVENTIONS SUR LA TORCHE (DÉMONTAGE)
SANS QU’ELLE AIT ÉTÉ DÉBRANCHÉE AU PRÉALABLE
DE LA PRISE DE SECTEUR.
DES CONTROLES EFFECTUÉS SOUS TENSION A
L’INTÉRIEUR DE LA MACHINE PEUVENT CAUSER UN
CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE GRAVE AYANT POUR ORIGINE UN
CONTACT DIRECT AVEC DES PARTIES SOUS
TENSION.
TORCHE
Périodiquement, en fonction de l’intensité d’utilisation ou en
cas de défauts de coupe (voir paragraphe 5), vérifier l’état
d’usure des parties de la torche intéressées par l’arc
plasma:
1. PORTE BUSE (Fig.G 1)
Figure (E) Dessin torche, position sur la pièce, Dévisser manuellement la tête de la torche
avancement, inclinaison arc En effectuer soigneusement le nettoyage et le remplacer
L'éloignement de la torche de la piPce et l'absence de s’il est endommagé (brûlures, déformations ou criques).
matériau (fin de coupe) entraîne l'interruption immédiate Vérifier l’integrité du secteur métallique supérieur (sécurité
de l'arc. de la torche).
L’interruption de l’arc (de coupe ou pilote) s’obtient 2. BUSE (Fig.G 2)
toujours en relâchant le bouton torche. Contrôler l’usure de l’orifice de passage de l’arc plasma et
Perçage: Si vous devez effectuer cette opération ou des surfaces intérieures et extérieures.
commencer au milieu de la pièce, amorcer avec la torche Si l’orifice est élargi ou déformé par rapport au diamètre
inclinée et l’amener par un mouvement progressif en originel, remplacer la buse.
position verticale. Si les surfaces résultent particulièrement oxydées, les
Ce procédé évite que des retours d’arc ou des particules nettoyer avec du papier abrasif très fin.
fondues abîment l’orifice de la buse et en réduisent 3. BAGUE DE DISTRIBUTION D’AIR (Fig.G 3)
rapidement le bon fonctionnement. Vérifier qu’il n’y ait pas de brûlures ou de cr iques ou que les
orifices de passage de l’air ne soient pas bouchés.
Figure (F) Dessin départ avec torche inclinée La remplacer immédiatement si elle est endommagée.
Cette précaution évite que des retours d'arc ou de 4. ÉLECTRODE (Fig.G 4)
particules en fusion puisse endommager l'orifice de la Remplacer l’électrode quand la profondeur du cratère se
buse et en compromettre le fonctionnement. formant sur la surface émettrice est d’environ 1,5mm.
DÉFAUTS DE COUPE LES PLUS COMMUNS Figure (G) Dessin esplosé torche
Pendant les opérations de coupe il peut se présenter des
défauts d’exécution qui ne doivent normalement pas être Figure (H) Dessin électrode avec cratère
attribués à des anomalies de fonctionnement de
l’installation mais à d’autres aspects opérationnels tels que: ATTENTION!
aPénétration insuffisante ou formation excessive de Avant d’effectuer toute intervention sur la torche, la laisser
déchets: refroidir au moins pendant tout le temps de “post air”.
vitesse de coupe trop élevée, Sauf dans certains cas, il est conseillé de remplacer
torche trop inclinée, l’électrode et la buse EN MEME TEMPS.
épaisseur de la pièce excessive, Respecter l’ordre de montage des composants de la
électrode et buse de la torche usées. torche (inverse par rapport au démontage), .
bInterruption de l’arc de coupe: Faire attention à ce que la bague de distribution soit
vitesse de coupe trop basse, montée dans le bon sens.
distance torche pièce excessive, Remonter le porte buse en vissant manuellement à fond
électrode usée, en forçant légèrement.
intervention de la sécurité. Ne monter en aucun cas le porte buse sans avoir
cCoupe inclinée (non perpendiculaire): préalablement monté l’électrode, la bague de distribution
position incorrecte de la torche, et la buse.
usure asymétrique de l’orifice de la buse et/ou montage La régularité et le bon ordre des contrôles sur les
COUPE
Modalités de coupe:
AVEC TORCHE on doit travailler avec la TUYERE EN
CONTACT
ATTENTION!
L'exécution de la coupe par contact, là où elle n'est pas
prévue, cause une usure rapide de la tuyère de la torche.
Approcher la tuyère de la torche du bord du morceau (= 3
mm.), appuyer sur le bouton poussoir de la torche; après
environ 0.5 secondes (pré air) on obtient
l'enclenchement de l'arc pilote (durée max. 2 secondes).
Si la distance est bonne l'arc pilote se transfère
immédiatement au morceau donnant lieu à l'arc de coupe.
Déplacer la torche sur la surface du morceau le long de la
ligne idéale de coupe avec une progression régulière.
Adapter la vitesse de coupe à l'épaisseur et au courant
sélectionné en vérifiant que l'arc qui sort de la surface
inférieure du morceau ait une inclinaison de 5 10° par
rapport à la verticale dans le sens opposé à la direction de
progression.
Fig.G
8


Ensure that appropriate fire fighting equipment is
accessible in the cutting area.
Plasma is a gas that is heated to an extremely high
temperature and ionised so that it becomes a conductor of
electricity.
This cutting procedure utilises the plasma to transfer the
electric arc to the metal workpiece, which is melted by the
heat and then separated.
The torch uses compressed air from a single source, for
both the plasma and cooling and protective gas.
The start of the cycle is determined by an arc, called the
pilot arc, which is struck between the mobile electrode (
ve polarity) and the torch nozzle ( +ve polarity ) due to the
short circuit between these two elements. MANUAL TORCH FOR PLASMA CUTTING
When the torch is brought into direct contact with the (supplied as standard)
workpiece to be cut (connected to the +ve polarity of the Gas used : dry compressed air
power source) the pilot arc is transferred between the Compressed air pressure : 2.5 bar
electrode and the workpiece itself thus striking a plasma Total air flow rate (for Plasma and cooling): 30 litres / min
arc, also called cutting arc. Arc striking system : contact between mobile
The duration of the pilot arc is set in the factory at 2 sec; if electrode and nozzle
the transfer has not been made within this time, the cycle Cutting current : 7 ÷ 25 A
is automatically stopped except for the cooling air which is Weight (kg ) : 1kg
kept on.
To recommence the cycle, the torch button must be
released and pressed again.
POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
The machine must be connected to a Line Neutral system
with a "PE" protected grounding wire.
Check that the relevant socket terminal is actually
connected to the distribution system grounding.
TAB.1
OUTPUT
GENERAL INFORMATION
PLASMA ARC AND BASIC PRINCIPLES FOR THE
PERFORMANCE OF PLASMA CUTTING.
MASS OF MACHINE (Table 1)
WARNING !
SAFETY OF PLASMA CUTTING SYSTEM.
Only the type of torch and its relative connection to the
UNIT COMPOSITION. power source indicated in the “TECHNICAL DATA” ensure
The plasma cutting system includes: the efficacy of the safety measures adopted by the
POWER SOURCE PLASMA manufacturer (interblocking system).
complete with:
Mains cable DO NOT USE torches and relative consumables different
Kit of connectors for compressed air from original ones.
Earth cable with clamp DO NOT TRY TO FIT torches for cutting or welding
Plasma cutting torch procedures to this power source, if they are not described
in these instructions.
PLASMA CUTTING POWER SOURCE PLASMA IF THESE RULES ARE NOT OBSERVED serious
Electric protection : Class I dangers may occur both to the user and to the machine.
Case protection degree : IP 23
Insulation class : H INSTALLATION
Dimensions (mm) : 475x170x340
INPUT
CONNECTION TO GROUND CABLE
Connect the work cable clamp to the piece to be cut or to the
metallic workbench.Take following precautions:
VERIFY THAT THERE IS A GOOD ELECTRIC CONTACT
PARTICULARLY IF INSULATED OR OXIDATED COATED
SHEETS ARE CUT.
MAKE GROUND CONNECTION AS CLOSE AS
POSSIBLE TO CUTTING AREA.
THE USE OF METALLIC STRUCTURES WHICH ARE
NOT PART OF THE WORKPIECE, SUCH AS THE
RETURN CABLE OF THE CUTTING CURRENT, MAY
ENDANGER THE SAFETY SYSTEM AND GIVE POOR
CUTTING RESULT S.
DO NOT MAKE A GROUND CONNECTION ON THE
PIECE WHICH HAS TO BE REMOVED.
10

WARNING !
Before starting with cutting operations verify that the parts
are properly assembled by inspecting the head of the torch
as shown on paragraph “TORCH MAINTENANCE”.
LOCATION AND HANDLING OF POWER SOURCE
Choose location verifying that there is a good air flow and
no dust, smoke or gas is present. 5.COMPRESSOR THERMAL SAFETY (RED warning
Make sure that obstacles do not prevent the cooling air LED Fig. B 5)
flow out of front and rear openings of the machine. When lit, it signals overheating of electric motor wiring
Arrange an open space of at least 500 inside arc compressor
mm. around the machine.
In case the machine has to be moved always disconnect 6.
the plug from the outlet and gather the cables and pipes so
as not to damage them.
Check for the belt to be set in the correct position for lifting
the machine (Fig. L).
WARNING !
Air with considerable quantities of humidity or oil may
cause an excessive wear of the parts or even damage
the torch.
CONTROL, WARNING AND SAFETY
DEVICES.
POWER SOURCE
Figure (B C) See drawing of back and front panel
1. GENERAL SWITCH O I. (Fig.C 1)
In position I (ON) the machine is ready for functioning green
signal light and green led (Fig.B 6) indicating mains ON
are lit.
Control and duty circuits are fed but there is no voltage in
the torch (STAND BY).
In position 0 (OFF) any functioning is inhibited, control
devices and warnings light are off.
2. CUTTING CURRENT POTENTIOMETER (Fig. B D) TORCH
It allows to set the intensity of cutting current supplied by the The torch button is the only control device which can start
machine according to the use (thickness of material/speed). and stop cutting operations.
See TECHNICAL DATA for proper relation of intermittence When button is released the cycle is immediately and
on/stand by to be adopted according to selected range. always stopped with the exception of cooling air (post air).
(period = 10 min.). Accidental manoeuvres: in order to start cycle button
must be pushed at least 500 ms.
CUTTING OPERATIONS
3.ENERGIZED TORCH (YELLOW SIGNAL LIGHT). PRELIMINARIES.
(Fig.B 3) Check and follow instructions as foreseen in the
When lit it shows that cutting circuit has been paragraphs 1 SAFETY and 2 INSTALLATION of the
present instruction manual.
activated: Pilot arc or cutting arc “ON”.
It is usually off (disengaged cutting circuit) with non Close (bring to position I) automatic mains switch and
activated torch button (stand by). general machine switch in sequence.
Choose, by turning the cutting current potentiometer, the
It is off, with torch button pushed, under following most suitable position to the work to be performed.
conditions:
During POSTGAS (>30s) phases. Push and release torch button causing air outflow (≥20s
If the pilot arc is not moved to the part within max. 2 post air). .
seconds. Let air outflow terminate spontaneously to facilitate
If the cutting arc interrupts because it is too far from the removal of condense which settled on the torch.
torch part, or the electrode is worn out, or the torch has
been forced away from the part.
In presence of a SECURITY system.
(Fig.B 4)
on a level surface
supply (undervoltage or voltage surge)
During this phase machine operation is disabled.
Reset is automatic (the YELLOW led goes off) 4 sec after
the abnormal value (as described above) returns within
the permitted limits.
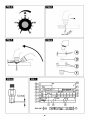
RATING PLATE (Fig. I)
a Utilisation data (cutting circuit).
1 No load voltage (U ).
0
2 Cutting current voltage (I /U )
22
3 Duty cycle (X) in use.
b Main power supply data.
4 Number of phases and mains frequency 50/60 Hz.
5 Mains voltage (U ).
1
6 Maximum RMS current absorbed I1max and nominal
RMS current absorbed I .
1eff
c General information
7 Level of protection for sheathing
8 Symbol for apparatus suitable for environments with
increased risk of electric shock
9 Symbol for type of process
10 Energy conversion chart
11 Standards of reference
12 Apparatus identification
13 Name of manufacturer
14 Range of cutting current (min/max) and corresponding
conventional arc voltage.
15 Manufacturer’s serial number
16 Value of delayed action fuses to be used to protect the
power line.
17 Symbols referring to safety standards
Tab.2 shows the cutting rate as a function of thickness for
materials in aluminium, iron and steel at a maximum current
of 25A.
CUTTING
Cutting mode:
WITH THE TORCH it is necessary to work with the
4. THERMAL CUTOUT AND ABNORMAL VOLTAGE NOZZLE IN CONTACT.
( YELLOW LED for general warning) WARNING!
When lit, it signals overheating of some component in the Making an unprepared contact cut will cause rapid wear of
power circuit, or abnormal input voltage of the power the torch nozzle. Bring the torch nozzle near the edge of the
11

workpiece (= 3 mm.), press the torch button; after approx.
0.5 seconds (pre air) the pilot arc is struck (max duration 2
seconds). If the distance is correct, the pilot arc immediately
transfers to the workpiece causing the cutting arc to be
struck.
Move the torch on the surface of the workpiece making
steady progress along the ideal cutting line. Adjust the
cutting speed according to the thickness and the selected
current, and check that the arc coming out of the lower
surface of the workpiece has an inclination of 5 10° to the
vertical in the opposite direction to the cutting direction.
DIRECT CONTACT WITH PARTS UNDER VOLTAGE:
TORCH
Periodically, according to its use or to cutting faults (see
Paragraph 5) verify wear of the par ts connected to plasma
arc:
1. NOZZLE HOLDER (Figure G 1)
Unscrew manually from head of the torch. Clean throughly
and replace if damaged (burns, distortions or cracks). Verify
integrity of superior metal sector (actuator torch safety).
2. NOZZLE (Figure G 2)
Check wear of plasma arc hole and of inner and outer
surfaces.
Figure (E) the drawing shows torch position on part If the hole is widened compared to its original width or if it is
moving forward, arc tilting damaged, replace nozzle. If surfaces are particularly
The removal of the torch from the piece or the absence of oxidated clean them with extra fine abrasive paper.
material (end cut) causes the immediate interruption of 3. AIR DISTRIBUTION RING (Figure G 3)
the arc. Verify there are no burns or cracks or that airflow holes are
Interruption of arc (cutting or pilot) is obtained by releasing not obstructed. If damaged, replace immediately.
torch button. 4. ELECTRODE (Figure G 4)
Piercing: If you have to make this operation or if you have Replace electrode when crater settling on emitting surface
to start from the center of the piece, ignite keeping the is about 1,5 mm.
torch tilted and bring it to an upright position with a smooth
movement. Figure (G) drawing shows exploded view of torch
This procedure avoids that returns of arc or melted parts
spoil the hole of the nozzle reducing its functionality. Figure (H) drawing shows electrode with crater
WARNING !
Figure (F) the drawing shows the starting with Before making any operation to the torch let it cool at least
tilted torch all along the”postgas” period.
This procedure prevents arc or melted particles to come Except for particular cases it is advisable to replace
back thus spoiling the nozzle hole and reducing its electrode and nozzle AT THE SAME TIME.
functionality quickly. Respect assembly order of torch parts (reserved
Piercing of parts with a thickness of 25 % of max. usuable compared to disassemblage) .
foreseen, may be carried out directly. Be careful that distributing is assembled properly.
Reassemble nozzle holder screwing tightly and manually.
COMMONEST CUTTING FAULTS Never assemble nozzle holder without having assembled
During cutting operations performance faults may arise electrode distributing ring and nozzle beforehand.
which are not caused by plant malfunctioning but by other Timely and appropriate control procedures on torch
operational faults such as: parts are essential for safety and functionality of the
a Insufficient penetration or excessive scoria settlement: cutting system.
too high cutting speed,
torch is too tilted, TORCH BODY, HANDLE AND CABLE.
piece is too thick, These parts usually need no particular maintenance with
electrode and nozzle are worn out. the exception of a periodic inspection and an accurate
bInterruption of cutting arc: cleaning to be made WITHOUT THE USE OF
cutting speed too low. SOLVENTS.
excessive distance between torch and piece, In case of damages to the insulation such as breaks,
electrode is worn out, cracks and burns or even a loosening of electric
intervention of the protections conductors, the torch CANNOT BE USED FURTHER
cTilted cutting (not perpendicular) SINCE SAFETY CONDITIONS HAVE NOT BEEN
torch position not correct RESPECTED.
asymmetric wear of nozzle hole and/or wrong IN THIS CASE, REPAIRING (EXTRAORDINARY
assemblage of torch parts. MAINTENANCE) CANNOT BE MADE ON SITE BUT
dExcessive wear of nozzle and electrode: NEEDS TO BE DELEGATED TO AN AUTHORIZED
air pressure too low, SERVICE CENTER TO MAKE SPECIAL TEST TRIALS
contaminated air (humidity oil), AFTER REPAIRING HAS BEEN EXECUTED.
nozzle holder damaged, In order to keep the torch and cable efficient it is
excessive pilot arc ignitions in the air. necessary to follow these precautions:
DO NOT touch torch and cable with warm or hot parts.
MAINTENANCE DO NOT strain the cable.
DO NOT move the cable on sharp edges or abrasive
WARNING ! surfaces.
NEVER ACCESS INSIDE THE MACHINE (PANEL Gather the cable in regular coils if it is too long.
REMOVAL) OR TOUCH THE TORCH (DISASSEMBLAGE) DO NOT step on the cable.
WITHOUT HAVING DISCONNECTED POWER PLUG.
ANY INSPECTION PERFORMED UNDER VOLTAGE
INSIDE THE MACHINE OR INSIDE THE TORCH MAY
CAUSE SEVERE ELECTRIC SHOCKS CAUSED BY
Fig.G
12


(Minuspol) und der Brennerdüse (Pluspol) bildet. Verwendetes Gas: Trockene Druckluft
Wenn man den Brenner in direkten Kontakt mit dem zu Luftdruck: 2,5 bar
schneidenden Werkstück bringt (das mit dem Pluspol der Gesamte Luftfördermenge
Stromquelle verbunden ist), wird die Pilotenflamme von (für Plasma und Kühlung): 30 L / min
der Elektrode auf das Werkstück übertragen und bildet Zündverfahren: Kontakt bewegliche Elektrode Düse
dadurch einen Plasmalichtbogen, auch Schneidestrom: 7 ÷ 25 A
Schneidelichtbogen genannt. Gewicht ( kg ): 1 kg
Die Aufrechterhaltungsdauer der Pilotenflamme wird
werkseitig auf 2 Sekunden eingestellt. Erfolgt die
Übertragung während dieser Zeit nicht, wird der Zyklus
automatisch unterbrochen und nur die Kühlluftzufuhr
aufrechterhalten.
Zum Start eines neuen Arbeitsganges den Brennerknopf
loslassen und erneut drücken.
ANSCHLUSS AN DIE STROMLEITUNG
Die Maschine muß an ein Leitungssystem mit Nulleiter und
"PE" Schutzleiter zur Erdung angeschlossen werden.
Prüfen Sie, ob der entsprechende Anschlußdraht der
Buchse tatsächlich mit der Verteilungserde verbunden
ist.
GEWICHT DER SCHWEISSMASCHINE (Tabelle 1)
im Lieferumfang enthalten)
Bild (A) Zeichnung des Gerätes
ACHTUNG!
SIHERHEIT
DES PLASMASCHNEIDESYSTEMS
Nur das Modell mit vorgesehenem Brenner und
vorgesehenem Stromanschluß, wie in den technischen
Daten angegeben, garantiert, daß die vom Erzeuger
ZUSAMMENSETZUNG DER ANLAGE erstellten Sicherheitsmaßnahmen greifen.
Das Plasmaschneidesystem enthält: (Blockiersystem)
STROMQUELLE PLASMA VERWENDEN SIE keine Brenner oder andere
komplett mit: Verbrauchsteile anderen Ursprungs.
Versorgungskabel VERSUCHEN SIE NIE Brenner, die für andere
Anschlußkit für Druckluft Schneideverfahren oder Schweißarbeiten erzeugt
Massekabel mit Klemme wurden, an die Stromquelle anzuschließen
Plasmaschneidbrenner MISSACHTUNG DIESER OBENGENANNTEN
PUNKTE kann zu großen Sicherheitseinschränkungen
STROMQUELLE FÜR PLASMASCHNEIDEN und zu Gefahren für den Betreibenden führen und das
Schutzklasse : Classe I Gärat beschädigen.
Schutzgrad der Hülle : IP 23
Wärmeisolierklasse : H INSTALLIERUNG
Dimensioni (mm) : 475x170x340
INPUT
TAB. 1
ANSCHLUSS DES MASSEKABELS
Schließen Sie die Zangenklemme des Massekabels an das
Schneidstück oder an die Metallbank an und beachten Sie
dabei folgende Vorsichtsmaßnahmen:
ACHTEN SIE DARAUF, DASS EIN GUTER
ELEKTRISCHER KONTAKT HERGESTELLT WIRD,
INSBESONDERE WENN BLECHE MIT
ISOLIERSCHICHT, OXIDATEN ETC. GESCHNITTEN
WERDEN.
SCHLIESSEN SIE DIE MASSE SO NAHE WIE
MÖGLICH AN DEM SCHNEIDEORT AN.
OUTPUT DIE VERWENDUNG VON METALLSTRUKTUREN, DIE
NICHT TEIL DES ARBEITSSTÜCKES SIND, WIE
STROMRÜCKLEITER DES SCHNEIDESTROMS,
KANN GEFÄHRLICH SEIN UND SCHLECHTE
SCHNEIDERESULTATE ERGEBEN.
SCHLIESSEN SIE DIE MASSE NICHT AN DEM TEIL
DES WERKSTÜCKES AN, DAS ENTFERNT WERDEN
SOLLT.
ANSCHLUSS DES PLASMASCHNEIDBRENNERS
WICHTIG !
Bevor Sie die Schneidearbeiten aufnehmen, überprüfen
Sie, ob der Anschluß der Abnützungsteile korrekt
durchgeführt wurde, indem Sie den Brennerkopf laut
Paragraph “Instandhaltung des Brenners” kontrollieren.
LAGE UND BEWEGUNG DER STROMQUELLE
Suchen Sie sich den Standort dort aus, wo eine gute
HANDBRENNER FÜR PLASMASCHNEIDEN Luftzirkulation besteht und kein Staub, Rauch oder
(
14

konduktive oder agressive Gase Zugang haben.
Sorgen Sie dafür, daß nicht etweige Gegenstände den
Kühlluftfluß aus den hinteren und vorderen Öffnungen
des Gerätes behindern
Sorgen Sie für einem
Freiraum rund um das Gerät von mindestens 500mm.
Wenn Sie das Gerät verstellen müssen, stecken Sie das
Gerät immer aus und sammeln Sie alle Kabel und Rohre
ein, um sie nicht zu beschädigen.
Kontrollieren Sie die richtige Position des Riemens zum
Anheben der Maschine (Abb. L).
WICHTIG !
Zu feuchte oder zu ölhältige Luft kann die Teile
überdurchschnittlich beanspruchen oder den Brenner
schädigen.
KONTROLL VORRICHTUNGEN,
SICHERHEITSLICHTER
Stromquelle
Bild (B C) Siehe Zeichnung vordere und hintere Tafel.
1 HAUPTSCHALTER O I , (Abb.C 1)
In Position I (ON) ist das Gerät betriebsbereit (Grünes
Lichtsignal des Schalters plus grünes Led (Abb.B 6) für
Netzanwesenheit).
Die Kontrollmechanismen werden mit Strom versorgt, aber
der Brenner ist Spannungsfrei (STAND BY).
In Position O (OFF) ist jede Funktion des Gerätes
unterbrochen, die Kontrolleeinrichtungen sind deaktiviert,
die Signale leuchten nicht auf.
2 POTENTIOMETER FUR SCHNEIDESTROM (Abb.B D)
Ermöglicht, daß Schneide Stromstärke des Gerätes an die
Anwendungsart angepaßt werden kann ( Dicke des
Material, Geschwindigkeit).
Siehen Sie in den technischen Daten nach, um das
korrekte Verhältnis zu wenden; Arbeit Pause je nach
Anwendungs modus zu finden. (periode 10min).
BRENNER
3 BRENNER IN FUNKTION (Gelbes Led bei Der Brenner ist der einzige Auslöser, von wo aus der Start
Anwesenheit von Spannung in dem Brenner ) und das anhalten der Schneidarbeit gesteuert werden
(Abb.B 3) kann.
Wenn das Licht aufleuchtet ist der Schneidekreislauf Wenn der Schalter augelassen wird, wird sofort der Zyklus
aktiviert. in jeder Phase unterbrochen. Nur die Luftkühlung läuft
Pilotbogen oder Schneidebogen “ON” Weiter (Nachluft)
Der Brenner ist abgeschaltet (Schneidekreislauf Zufällige Arbeit: um das Aufahren des Zyklus zu
unterbrochen) wenn der Brennerschalter nicht gedruckt ermöglichen, muß der Schalter mindestens 500ms
wird (Stand By) gedruckt werden.
Der Brenner ist unter folgenden Bedinungen deaktiviert,
obwohl der Brennerschalter eingeschaltet ist:
Während der Phase NACHLUFT (>20s). SCHNEIDEVERFAHREN
Wenn der Pilotbogen nicht auf das Werkstück innerhalb VORBEDINGUNGEN
von 2sek. übertragen wird. Überprüfen Sie die Vorkehrungen am Paragraph (1)
Wenn der Pilotbogen aufgrund zu großer Distanz SICHERHEIT und (3) INSTALLIERUNG
zwischen Brenner und Werkstück übermäßige abnützung Stellen Sie den automatischen Stromschalter und den
der Elektrode oder Nachlassen des Bogen unterbrochen Hauptschalter des Gerätes auf Pos. 1 ein.
wird. Suchen Sie, indem man auf das Potentiometer des
Wenn sich ein Sicherheitsmechanismus einschaltet. Schneide Stroms einwirkt, die für die gewünschte
Arbeitsart geeignete Einstellung.
(Abb.B 4)
Durch ihr Aufleuchten weist die Led darauf hin, daß
irgendeine Komponente des Leistungsschaltkreises
überhitzt oder die Versorgungsspannung am Eingang
gestört ist (Unter oder Überspannung).
eine waagerechte Fläche mit Während dieser Phase ist die Maschine nicht
betriebsbereit.
Die Wiederherstellung der Betriebsbereitschaft erfolgt
automatisch (Erlöschen der LED) 4 Sekunden, nachdem
eine der oben genannten Anomalien wieder innerhalb der
zugelassenen Grenzwerte liegt.
5 TERMISCHE SICHERHEIT DES KOMPRESSOR (ROT
LED ALARM) Durch ihr Aufleuchten weist die Led darauf
hin, dass die Wicklungen des elektrisches Motors des
Bogenkompressors ueberhitzt sind.
16 Werte der verzögert ansprechenden Sicherungen, die
zum Schutz der Leitung einzubauen sind.
17 Symbole beziehen sich auf Sicherheitsvorschriften.
4 THERMISCHE SICHERUNG UND STÖRUNGEN DER
NETZSPANNUNG (Led für Generalalarm)
6 TYPENSCHILD MIT DEN CHARAKTERISTISCHEN
DATEN (Abb. I)
a Betriebsdaten (Schneidezyklus).
1 Leerlaufspannung (U ).
0
2 Schneidestrom/ spannung (I /U )
22
3 Aussetzungsverhältnis (X) bei der Verwendung.
b Leiterdaten (Versorgung).
4 Phasenzahl und Versorgungsspannung 50/60 Hz.
5 Versorgungsspannung (U ).
1
6 Maximale Stromaufnahme RMS I1max
Nennstromaufnahme RMS I .
1eff
c Allgemeine Daten
7 Schutzart Umhüllung
8 Symbol für Apparate, die für Umgebungen mit erhöhter
Stromschlaggefahr geeignet sind
9 Symbol für den Prozeßtyp
10 Schema für die Energieumwandlung
11 Verweise auf Vorschriften
12 Identifikation des Apparates
13 Herstellername
14 Bereich des Schneidestroms (min/max) und der
entsprechenden konventionellen
Lichtbogenspannung.
15 Seriennummer der Fabrikation
In Tab.1 ist die Schneidegeschwindigkeit in Abhängigkeit
von der Dicke für Aluminium , Eisen und Stahlmaterial
beim Höchststrom von 25 A dargestellt.
Durch Drücken und Loslassen des Brennerknopfes wird
15

das Ausströmen von Luft ermöglicht (≥20 Sekunden
Nachluft).
(Bild G)
cSchiefer Schnitt (nicht lotrecht)
Position des Brenners nicht korrekt
Assymetrischer Verbrauch der Düsenöffnung und/oder
Lassen Sie den Luftausfluß, spontan beenden um die nicht korrekte Montage der Brennerteile
Beseitigung von erwaigem Kondenswasser, das sich im dExtreme Abnützung der Düse und der Elektrode:
Brenner angesammelt hat, zu beseitigen. Luftdruck zu nieder
Verschmutzte Luft (Feuchtigkeit Öl)
Düsentragarm defekt
Zu häufiges Anfahren des Pilotbogens in der Luft
INSTANDHALTUNG
Achtung !
NÄHERN SIE SICH NIE DEM INNEREN DER
STROMQUELLE (ABNAHME DER ABDECKUNGEN)
ODER HANTIEREN SIE NIE AM BRENNER
(DEMONTAGE) OHNE DASS VORHER DER STECKER
HERAUSGEZOGEN WURDE.
KONTROLLEN, DIE UNTER SPANNUNG DES GERÄTES
ODER DES BRENNERS DURCHGEFÜHRT WERDEN,
KÖNNEN SCHWERE ELEKTROSCHOCKS DURCH
KONTAKT MIT SPANNUNGSGELADENEN TEILEN
HERVORRUFEN.
BRENNER
Überprüfen Sie je nach Arbeitsintensität oder bei
Auftreten von Schneidefehlern (siehe Par. 5) den Zustand
folgender Brennerteile:
1 DÜSENHALTERUNG (Bild G 1)
Bild (E) Position des Brenners auf dem Werkstück. Schrauben Sie sie vom Brennerkopf ab.
Winkel des Bogens Säubern Sie sie sorgfältig oder ersetzen Sie sie, wenn
Die Entfernung des Brenners vom Werkstück und das beschädigt (Brandzeichen, Verformungen etc.)
Fehlen von Material (Ende Schneidvorgang) verursacht Überprüfen Sie die Unversehrteil des oberen
sofort die Unterbrechung des Lichtbogens Metallabschnittes (Auslösen der Brennerabsicherung)
Der Bogen (Pilot oder Schneidebogen) wird immer durch 2 DÜSE (Bild G 2)
Auslassen des Brennerschalter unterbrochen. Überprüfen Sie das Durchgangsloch des Plasmabogens
Bohren: Wenn Sie diese Arbeit durchführen müssen oder und die inneren und äußeren Flächen.
in der Mitte des Stückes beginnen müssen, fahren Sie mit Ersetzen Sie die Düse, wenn das Loch verbreitet zum
gebeugtem Brenner an und richten Sie ihn mit ursprünglichen Durchmesser erscheint oder verformt ist.
fortlaufender Bewegung in vertikale Position auf. Wenn die Oberflächen sehr oxidiert sind, säubern sie mit
Das verhindert, das Rückschläge des Bogens oder sehr feinem Reibepapier
Schmelzteilchen das Düsenloch beschädigen und so 3 LUFTVERTEILERRING (Bild G 3)
sehr schnell die Funktionstücktigkeit verringern. Achten Sie, daß keine Brandzeichen vorhanden sind oder
daß die Luftdurchlaßlöcher verstopft sind.
Bild (F) Anfahren mit gebeugtem Brenner Wenn beschädigt, dann sofortiger Austausch.
Dieses Vorgehen vermeidet es, daß der Lichtbogen oder 4 ELEKTRODE (Bild G 4)
lose Partikel zurückschlagen, die Düsenöffnung schädigen Ersetzen Sie die Elektrode, wenn die Kratertiefe, die sich
und zur schnellen Abnahme deren Funktionstüchtigkeit auf der emittierenden Oberfläche bildet, ca. 1,5mm beträgt.
führen.
Löcher in Werkstücken mit einer Dicke 25% des Bild (G) Explosionszeichnung Brenner
Maximums, das vorgesehen ist, können sofort
durchgeführt werden. Bild (H) Elektrode mit Krater
HÄUFIGE SCHNEIDEFEHLER ACHTUNG !
Während der Schneidearbeit können einige Defekte bei der Vor Eingriffen am Brenner lassen Sie den Brenner
Ausführung auftreten, die nicht auf Anomalien des Gerätes auskühlen, zumindestens bis die Postluft Zeit
zurückzuführen sind, sondern auf andere Aspekte, wie: abgelaufen ist
aUngenügendes Eindringen oder exzessive Bildung von Bis auf spezielle Fälle ist es ratsam, die Elektrode und die
Rückständen: Düse GLEICHZEITIG auszutauschen
Schneidegeschwindigkeit ist zu hoch Halten Sie die Reihenfolge beim Zusammenbau der
Der Brenner wird zuviel gebeugt Brennerkomponenten ein .
Zu große Dicke des Stückes Achten Sie, daß der Verteilerring im richtigen Drehsinn
Elektrode und Brennerdüse schon abgenutzt montiert wird.
bUnterbrechen des Schneidebogens: Befestigen Sie die Düsenhalterung so, daß Sie sie
Schneidegeschwindigkeit ist zu gering händisch mit leichtem Druck festdrehen.
Zu große Distanz zwischen Brenner und Stück Montieren Sie die Düsenhalterungauf keinen Fall ohne
Elektrode verbraucht vorher präventiv die Elektrode, den Verteilerring und die
Einsetzen des Sicherheitsschutzes Düse befestigt zu haben.
SCHNEIDEN
Vorgehensweise beim Schneiden:
BEI VERWENDUNG DES BRENNERS muß mit
KONTAKTDÜSE gearbeitet werden.
VORSICHT!
Das Kontaktschneideverfahren verursacht dort, wo es
nicht vorgesehen ist, den vorzeitigen Verschleiß der
Brennerdüse. Die Brennerdüse dem Werkstückrand
annähern (= 3 mm.) und den Brennerknopf drücken. Nach
etwa 0,5 Sekunden (Luftvorströmung) zündet die
Pilotenflamme (Dauer max. 2 Sekunden). Wenn die
richtige Distanz gewählt wurde, wird die Pilotenflamme
sofort zum Werkstück übertragen und läßt dort den
Schneidelichtbogen entstehen.
Nun den Brenner auf der Oberfläche des Werkstückes
gleichmäßig entlang der Ideallinie weiterführen. Passen
Sie die Schnittgeschwindigkeit an die Dicke und den
gewählten Strom an. Der Lichtbogen, der aus der unteren
Fläche des Werkstückes tritt, muß gegen die
Vorschubrichtung einen Neigungswinkel von 5 10° im
Verhältnis zur Senkrechten haben.
16


Het niveau van de persoonlijke DAGELIJKSE
BLOOTSTELLING aan het lawaai verifiëren.
Adequate individuele beschermingsmiddelen gebruiken
ingeval de toegestane limieten overschreden worden.
VUUR EN ONTPLOFFINGEN KUNNEN ONTSTAAN
DOOR VONKEN EN HETE METAALSLAK
Niet snijden op bakken, recipiënten of buizen die
ontvlambare producten of vloeibare en gasachtige
verbrandingsstoffen bevatten of bevat hebben.
Uit de snijzone, op een minimum straal van 10 m, alle
brandbare materialen verwijderen inbegrepen de
afvalproducten (vodden, kartons, enz.).
In de snijzone de toegang verzekeren voor de geschikte
inrichtingen. tegen brand.
(in dotatie)
INPUT
OUTPUT
ALGEMEEN
DE PLASMABOOG EN HET TOEPASSINGSPRINCIPE
VAN HET PLASMASNIJBRANDEN.
HANDBEDIENDE BRANDER VOOR
PLASMASNIJBRANDEN
Figuur (A) afbeelding buitenafmetingen van het
apparaat.
LET OP !
BEVEILIGING VAN HET PLASMA SNIJSYSTEEM.
De door de fabrikant getroffen beveiligingsvoorzieningen
SAMENSTELLING VAN HET APPARAAT (grendelingssysteem) zijn uitsluitend gegarandeerd als het
Het volledige snijapparaat omvat: in de “TECHNISCHE GEGEVENS” vermelde
EEN PLASMA brandermodel en de bijbehorende stroombron worden
bestaande uit : gebruikt.
Voedingskabel GEEN branders en bijbehorende onderdelen van andere
Massakabel met klem oorsprong GEBRUIKEN.
Toorts voor plasmasnijden NIET POGEN branders ontworpen voor SNIJ of
LASWERKZAAMHEDEN die niet in deze handleiding
STROOMBRON VOOR PLASMASNIJBRANDEN zijn behandeld OP DE STROOMBRON AAN TE
PLASMA SLUITEN.
Elektrische beveiliging : Klasse I HET NIET RESPECTEREN VAN DEZE REGELS kan
Beschermingsniveau behuizing: IP 23 ERNSTIG gevaar opleveren voor de lichamelijke
Thermische isolatieklasse : H gezondheid van de gebruiker en de apparatuur
Afmetingen (mm) : 475x170x340 beschadigen.
Het plasma is een gas verwarmd aan een uiterst hoge
temperatuur en geïoniseerd zodanig dat het een
elektrische geleider wordt.
Deze snijprocedure gebruikt het plasma om de
elektrische boog over te brengen naar het stuk metaal dat
door de warmte gesmolten wordt en afgescheiden.
De fakkel maakt gebruik van perslucht afkomstig van een
afzonderlijke voeding zowel voor het plasmagas als voor
het koel en beschermingsgas. GEWICHT DER MASCHINE (Tabelle 1)
Het vertrek van de cyclus wordt bepaald door een boog,
genoemd pilootboog die zich vormt tussen de mobiele
elektrode (polariteit ) en de sproeier van de fakkel
(polariteit +) als effect van de stroom van de kortsluiting
tussen deze twee elementen. Gebruikt gas: : Droge perslucht
Door de fakkel in rechtstreeks contact te brengen met het Druk perslucht: : 2,5 bar
te snijden stuk ( verbonden aan de polariteit + van de Totaal luchtvermogen (voor Plasma en koeling): 30 L / min
stroombron) wordt de pilootboog overgebracht tussen de Systeem geactiveerd : met contact mobiele
elektrode en het stuk zelf, waarbij een plasmaboog wordt elektrode sproeier
gevormd, ook snijboog genoemd. Stroom snijden : 7 ÷ 25 A
De tijd van het aanhouden van de pilootboog ingesteld in Massa ( Kg ) : 1 Kg
de fabriek bedraagt 2s ; indien de overbrenging niet wordt
uigevoerd binnen deze tijd, wordt de cyclus automatisch
geblokkeerd, afgezien van het aanhouden van de
koellucht.
Om de cyclus opnieuw te hervatten moet men de
drukknop fakkel loslaten en terug indrukken.
18

geleverde snijstroom, en die afhankelijk van de toepassing
INSTALLATIE (dikte van het materiaal/snelheid) dient te worden gebruikt.
Zie hiervoor de TECHNISCHE GEGEVENS voor de juiste
functioneren pauze onderbrekingsverhouding, te
gebruiken op basis van het gekozen gamma(periode = 10
min.).
TAB.1
AANSLUITING VAN DE MASSAKABEL 3 BRANDER GEACTIVEERD (GELE controlelampje
De klemverbinding van de massakabel op het te snijden aanwezigheid spanning op de brander) (Fig.B 3)
stuk of op de metalen ondersteuningsbank aanbrengen, Als het rode controlampje brandt is het snijcircuit
met inachtneming van de volgende voorzorgsmaatregelen: geactiveerd:
ZORGEN VOOR EEN GOED ELEKTRISCH CONTACT, Voorontsteekboog of Snijboog “ON”.
VOORAL ALS GEOXYDEERDE PLATEN OF PLATEN Het controlelampje is gewoonlijk uit (snijcircuit non actief)
MET EEN ISOLERENDE BEKLEDING MOETEN met de knop van de brander NIET geactiveerd (stand by
WORDEN GESNEDEN, ENZ. positie)
DE MASSAVERBINDING ZO DICHT MOGELIJK IN DE Is uit, bij geactiveerde brander, onder de volgende
NABIJHEID VAN HET SNIJGEBIED AANBRENGEN. omstandigheden:
HET GEBRUIK VAN METALEN STRUCTUREN ALS Tijdens de fase POSTARIA (>20s).
GELEIDER VAN DE RETOURSTROOM VAN DE Als de voorontsteekboog niet binnen een maximale tijd
SNIJDER, DIE GEEN DEEL UITMAKEN VAN HET TE van 2 seconden naar het stuk wordt overgebracht.
SNIJDEN STUK KAN DE VEILIGHEID IN GEVAAR Als de snijboog wordt onderbroken als gevolg van een
BRENGEN EN SLECHTE SNIJRESULTATEN te grote afstand tussen de brander en het stuk, door
OPLEVEREN. overmatige slijtage van de elektrode of door een
DE MASSAVERBINDING NIET OP HET WEG TE noodzakelijke vergroting van de afstand tussen de
SNIJDEN GEDEELTE AANBRENGEN. brander en het stuk.
Als een beveiligingssysteem heeft ingegrepen.
PLAATSING EN TRANSPORT VAN DE STROOMBRON.
Een positie voor het apparaat kiezen die een goede 4 THERMISCHE BEVEILIGING EN AFWIJKINGEN
luchtcirculatie, zonder stof, dampen of geleidende of VAN DE NETSPANNING (controlelampje voor
bijtende gassen waarborgt. algemeen alarm) (Fig.B 4)
Controleren of eventuele obstakels de luchtstroom voor
het afkoelen vanuit de openingen aan de voor en
achterkant van het apparaat niet belem
meren.
Rekening houden met een vrije ruimte van niet minder
dan 500 mm rondom het apparaat.
Bij verplaatsing van het apparaat altijd de stekker uit het
stopcontact verwijderen en kabels en slangen
samenbinden om beschadigingen tijdens het transport te
voorkomen.
Controleer de correcte plaatsing van de riem voor het
heffen van de machine (Fig. L).
CONTROLE, WAARSCHUWINGS- 6 PLAATJE MET TECHNISCHE GEGEVENS (Fig.I)
EN BEVEILIGINGSINRICHTINGEN
STROOMVOORZIENING
Figuur (C) Figuur D, Zie tekening paneel vóór en achter
1 HOOFDSCHAKELAAR O I (Fig.B C)
In de stand I (ON) is het apparaat gereed voor het gebruik,
en zal het *GROENE (Fig.B 6) controlelampje van de
onderbrekingsschakelaar plus GROENE controlelampje
ter indicatie van de aanwezigheid van netspanning (gaan
branden).
De besturings en hulpcircuits worden gevoed, maar er
zal geen spanning op de brander staan (STAND BY).
In de stand O (OFF) is elke functie onderbroken; de
besturingseenheden zijn uitgeschakeld en het
controlelampje is uit.
2 POTENTIOMETER SNIJSTROOM (FIG. B D)
Voor de instelling van de sterkte van de door de machine
AANSLUITING OP HET ELEKTRISCH NET
De machine moet aangesloten zijn op een systeem Lijn
Neutraal met een aardegeleider met bescherming "PE".
Verifiëren of de desbetreffende terminal van het contact
inderdaad aangesloten is op de aardeaansluiting van de
distributie.
Indien deze brandt, wijst dit op een verhitting van een
component van het potentiecircuit, of op een anomalie
van de voedingsspanning aan de ingang (onder of
overspanning).
Tijdens deze fase wordt de functie van de machine
belemmerd.
Het herstellen gebeurt automatisch (de led gaat uit) 4s
nadat één van de voornoemde anomalieën binnen de
toegelaten limieten terugkeert.
5 THERMISCHE BEVEILIGING COMPRESSOR (rode
LED van alarm, Fig. B 5) Indien deze brandt wijst dit
op een verhitting van de wikkelingen van de elektrische
motor aan boord van de luchtcompressor.
In Tab. 2 ist die Schneidegeschwindigkeit in Abhängigkeit
von der Dicke für Aluminium , Eisen und Stahlmaterial
beim Höchststrom von 25 A dargestellt.
een horizontaal
vlak
a Betriebsdaten (Schneidezyklus).
1 Leerlaufspannung (U ).
0
2 Schneidestrom/ spannung (I /U )
22
3 Aussetzungsverhältnis (X) bei der Verwendung.
b Leiterdaten (Versorgung).
4 Phasenzahl und Versorgungsspannung 50/60 Hz.
5 Versorgungsspannung (U ).
1
6 Maximale Stromaufnahme RMS I1max
Nennstromaufnahme RMS I .
1eff
c Allgemeine Daten
7 Schutzart Umhüllung
8 Symbol für Apparate, die für Umgebungen mit erhöhter
Stromschlaggefahr geeignet sind
9 Symbol für den Prozeßtyp
10 Schema für die Energieumwandlung
11 Verweise auf Vorschriften
12 Identifikation des Apparates
13 Herstellername
19

14 Bereich des Schneidestroms (min/max) und der
entsprechenden konventionellen
Lichtbogenspannung.
15 Seriennummer der Fabrikation
16 Werte der verzögert ansprechenden Sicherungen, die
zum Schutz der Leitung einzubauen sind.
17 Symbole beziehen sich auf Sicherheitsvorschriften.
SNIJDEN
Modaliteiten van het snijden:
MET FAKKEL moet men werken met DE SPROEIER IN
CONTACT.
OPGELET!
De uitvoering van het snijden met contact, daar waar dit
niet voorzien is, veroorzaakt een snelle slijtage van de
sproeier van de fakkel. De sproeier van de fakkel naar de
boord van het stuk brengen (= 3 mm.), de drukknop fakkel
indrukken; na ongeveer 0.5 seconden (pre lucht) bekomt
men de activering van de pilootboog (maximum duur 2
seconden). Indien de afstand adequaat is, wordt de
pilootboog onmiddellijk overgebracht naar het stuk,
waarbij de snijboog wordt uitgevoerd.
De fakkel verplaatsen op het oppervlak van het stuk langs
de ideale snijlijn met regelmatige voorwaartse
bewegingen. De snelheid van het snijden aanpassen op
basis van de dikte en van de geselecteerde stroom; hierbij
verifiëren of de boog die uit het onderste oppervlak van
het stuk komt een inclinatie heeft van 5 10° op de
verticale lijn in de tegenovergestelde richting van de
voorwaartse beweging.
loslaten van de branderknop worden onderbroken.
Het snijbranden van gaten:
Voor het uitvoeren van deze operatie, of om vanuit het
midden van een stuk te beginnen, moet de boog met een
schuine brander worden gevormd, om die vervolgens
met een versnellende beweging in een vertikale stand te
brengen.
Deze procedure zal voorkomen dat terugslagen van de
BRANDER boog of gesmolten deeltjes het gat van het mondstuk
beschadigen en diens werking versneld benadelen.
De branderknop is het enige bedieningsorgaan om het
begin en het eind van de snijoperaties mee te kunnen
regelen. Figuur (F) afbeelding start met brander in schuine
Zodra de druk van de knop wordt afgenomen zal, met positie.
uitzondering van de koellucht (lucht na) het snijproces Deze procedure voorkomt dat terugslag van de boog of
onmiddellijk, en in onwillekeurig welke fase hij zich ook van gesmolten deeltjes het gat van de sproeier
bevindt, worden onderbroken. beschadigen waardoor de werking ervan snel achteruit
Ongewenste handelingen: om de procedure te laten zou gaan.
beginnen, moet, gedurende ten minste 500 ms
(milliseconden) druk op de knop worden uitgeoefend. ALGEMENE SNIJDEFEKTEN
Tijdens het snijden kunnen zich uitvoeringsdefekten
voordoen die gewoonlijk niet aan werkingsproblemen
SNIJWERKZAAMHEDEN van het apparaat, maar aan andere gebruiksaspecten te
VOORAF wijten zijn, namelijk:
De stand van zaken en de handelingen beschreven in de aOnvoldoende penetratie of overmatige produktie van
paragrafen (1) VEILIGHEID en (3) INSTALLATIE van slakken:
deze handleiding controleren en/of uitvoeren. snijsnelheid te hoog,
Eerst de automatische lijnschakelaar en vervolgens de de brander te schuin,
hoofdschakelaar van het apparaat sluiten (in stand I te snijden stuk te dik,
zetten). elektrode en mondstuk versleten.
Door middel van de op de potentiometer van de bOnderbreking van de snijboog:
snijstroom ingrijpen de meest geschikte stand voor de uit snijsnelheid te laag,
te voeren werkzaamheden instellen. afstand brander stuk te hoog,
De toortsknop indrukken en loslaten voor de elektrode versleten,
luchtuitstroming (≥20 seconden nalucht). beveiliging heeft ingegrepen.
Wachten tot de luchtstroom vanzelf ophoudt om de cScheef snijoppervlak (niet in een rechte hoek)
verwijdering van eventueel in de brander verzameld foute positie van de brander,
condens te vergemakkelijken. asymmetrische slijtage van het gat van het mondstuk
en/of onjuiste montage van de branderonderdelen.
dOvermatige slijtage van het mondstuk en de elektrode:
luchtdruk te laag,
vervuilde lucht (vocht),
mondstukhouder beschadigd,
voorontsteekboog te vaak in de lucht ontstoken.
ONDERHOUD
LET OP !
IN GEEN GEVAL DE PANELEN VERWIJDEREN OM
TOEGANG TOT DE BINNENKANT VAN DE
STROOMBRON TE VERKRIJGEN, OF INGREPEN OP
DE BRANDER UITVOEREN (UIT ELKAAR HALEN)
ZONDER VOORAF DE STEKKER UIT HET
STOPCONTACT TE HEBBEN VERWIJDERD.
BIJ ONDER SPANNING UITGEVOERDE CONTROLES
BINNEN HET APPARAAT OF DE BRANDER BESTAAT,
ALS GEVOLG VAN RECHTSTREEKSE CONTACTEN
MET DELEN ONDER SPANNING, HET GEVAAR VOOR
ERNSTIGE ELEKTRISCHE SCHOKKEN.
BRANDER
Van tijd tot tijd, afhankelijk van de mate waarin het apparaat
Figuur (E) beeldt de brander af in de werkstand met wordt gebruikt, of bij snijproblemen, (zie Paragraaf 5) de
betrokken branderonderdelen van de plasmaboog op
booghoek. slijtage controleren.
Het verwijderen van de toorts van het stuk of de 1 MONDSTUKHOUDER
afwezigheid van materiaal (einde snede) veroorzaakt de Met de hand van de branderkop afdraaien.
onmiddellijke onderbreking van de boog. Goed schoonmaken of, indien beschadigd, vervangen
De boog (snij of voorontsteekboog) zal altijd door het
20
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
dans d''autres langues
- italiano: Telwin TEL034 Manuale utente
- English: Telwin TEL034 User manual
- español: Telwin TEL034 Manual de usuario
- Nederlands: Telwin TEL034 Handleiding
- português: Telwin TEL034 Manual do usuário
- slovenčina: Telwin TEL034 Používateľská príručka
- dansk: Telwin TEL034 Brugermanual
- eesti: Telwin TEL034 Kasutusjuhend
- svenska: Telwin TEL034 Användarmanual
Autres documents
-
 Elettro C.F. PLASMA 55 Instructions Manual
Elettro C.F. PLASMA 55 Instructions Manual
-
Cebora 946 Plasma Prof 122 Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora CP-101 Manuel utilisateur
-
 Elettro C.F. PLASMA 46 COMPRESSOR INVERTER Instructions Manual
Elettro C.F. PLASMA 46 COMPRESSOR INVERTER Instructions Manual
-
GYS PLASMA CUTTER 85A TRI Le manuel du propriétaire
-
GYS PLASMA CUTTER 45 CT Le manuel du propriétaire
-
BORMANN PRO BIW4020 Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora Power Plasma 3035/M Manuel utilisateur

























































