Toro Flex-Force Power System 24in 60V Hedge Trimmer Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Taille-haies électriques
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur

Form No. 3460-673 Rev A
Flex-Force Power System™ 24in 60V Hedge T rimmer
51841
Cortasetos Flex-Force Power System™ de 61 cm
(24") de 60 V
51841
T aille-haie Flex-Force Power System™ 60 V de 61
cm (24 po)
51841
www .T oro.com.
*3460-673*


Form No. 3460-670 Rev A
Flex-Force Power System
™
24in
60V Hedge T rimmer
Model No. 51841 —Serial No. 323000001 and Up
Register at www .T oro.com.
Original Instructions (EN)
*3460-670*

For assistance, please see
www .T oro.com/support
for instructional videos
or contact 1-888-384-9939
before returning this
product.
W ARNING
CALIFORNIA
Proposition 65 W arning
The power cord on this product contains
lead, a chemical known to the State
of California to cause birth defects
or other reproductive harm. W ash
hands after handling.
Use of this product may cause exposure
to chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer , birth defects,
or other reproductive harm.
Introduction
This hedge trimmer is intended to be used by
residential homeowners to maintain bushes and
hedges. It is designed to use T oro 60V lithium-ion
battery packs. These battery packs are designed
to be charged only by T oro 60V lithium-ion battery
chargers. Using these products for purposes other
than their intended use could prove dangerous to you
and bystanders.
Read this information carefully to learn how to operate
and maintain your product properly and to avoid
injury and product damage. Y ou are responsible for
operating the product properly and safely .
V isit www .T oro.com for more information, including
safety tips, training materials, accessory information,
help nding a dealer , or to register your product.
Whenever you need service, genuine the
manufacturer parts, or additional information, contact
an Authorized Service Dealer or the manufacturer
Customer Service and have the model and serial
numbers of your product ready . Figure 1 identies
the location of the model and serial numbers on the
product. W rite the numbers in the space provided.
Important: W ith your mobile device, you can
scan the QR code (if equipped) on the serial
number plate to access warranty , parts, and other
product information.
g308284
Figure 1
1. Model and serial number location
Model No.
Serial No.
© 2023—The T oro® Company
81 1 1 L yndale A venue South
Bloomington, MN 55420
2
Contact us at www .T oro.com.
Printed in China
All Rights Reserved

Safety-Alert Symbol
The safety-alert symbol ( Figure 2 ) shown in this
manual and on the machine identies important safety
messages that you must follow to prevent accidents.
g000502
Figure 2
Safety-alert symbol
The safety-alert symbol appears above information
that alerts you to unsafe actions or situations and
is followed by the word DANGER ,W ARNING , or
CAUTION .
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious
injury .
W ARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious
injury .
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate
injury .
This manual uses two other words to highlight
information. Important calls attention to special
mechanical information and Note emphasizes general
information worthy of special attention.
Safety
W ARNING
Read all safety warnings, instructions,
illustrations and specications provided with
this power tool.
Failure to follow all instructions listed below
may result in electric shock, re and/or
serious injury .
Save all warnings and instructions for future
reference.
The term “power tool” in all the warnings refers
to your mains-operated (corded) power tool or
battery-operated (cordless) power tool.
IMPORT ANT SAFETY
INSTRUCTIONS
I. W ork area safety
1. Keep work area clean and well lit. Cluttered
or dark areas invite accidents.
2. Do not operate power tools in explosive
atmospheres, such as in the presence of
ammable liquids, gases, or dust. Power
tools create sparks which may ignite the dust
or fumes.
3. Keep children and bystanders away while
operating a power tool. Distractions can cause
you to lose control.
II. Electrical safety
1. Power tool plugs must match the outlet.
Never modify the plug in any way . Do not use
any adapter plugs with earthed (grounded)
power tools. Unmodied plugs and matching
outlets will reduce risk of electric shock.
2. A void body contact with earthed or grounded
surfaces, such as pipes, radiators, ranges
and refrigerators. There is an increased risk
of electric shock if your body is earthed or
grounded.
3. Do not expose power tools to rain or wet
conditions. W ater entering a power tool will
increase the risk of electric shock.
4. Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord
for carrying, pulling or unplugging the power
tool. Keep cord away from heat, oil, sharp
edges or moving parts. Damaged or entangled
cords increase the risk of electric shock.
3

5. When operating a power tool outdoors, use
an extension cord suitable for outdoor use.
Use of a cord suitable for outdoor use reduces
the risk of electric shock.
6. If operating a power tool in a damp location
is unavoidable, use a residual current device
(RCD) protected supply . Use of an RCD
reduces the risk of electric shock.
III. Personal safety
1. Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use
common sense when operating a power tool.
Do not use a power tool while you are tired
or under the inuence of drugs, alcohol, or
medication. A moment of inattention while
operating power tools may result in serious
personal injury .
2. Use personal protective equipment. Always
wear eye protection. Protective equipment
such as dust mask, non-skid safety shoes, hard
hat, or hearing protection used for appropriate
conditions reduces personal injuries.
3. Prevent unintentional starting. Ensure
the switch is in the O FF -position before
connecting to power source and/or battery
pack, picking up or carrying the tool. Carrying
power tools with your nger on the switch or
energizing power tools that have the switch on
invites accidents.
4. Remove any adjusting key or wrench before
turning the power tool on. A wrench or a key
left attached to a rotating part of the power tool
may result in personal injury .
5. Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and
balance at all times. This enables better control
of the power tool in unexpected situations.
6. Dress properly . Do not wear loose clothing
or jewelry . Keep your hair and clothing away
from moving parts. Loose clothes, jewelry , or
long hair can be caught in moving parts.
7. If devices are provided for the connection
of dust extraction and collection facilities,
ensure these are connected and properly
used. Use of dust collection can reduce
dust-related hazards.
8. Do not let familiarity gained from frequent
use of tools allow you to become complacent
and ignore tool safety principles. A careless
action can cause severe injury within a fraction
of a second.
IV . Power tool use and care
1. Do not force the power tool. Use the correct
power tool for your application. The correct
power tool will do the job better and safer at the
rate for which it was designed.
2. Do not use the power tool if the switch
does not turn it on and off. Any power tool
that cannot be controlled with the switch is
dangerous and must be repaired.
3. Disconnect the plug from the power source
and/or remove the battery pack, if detachable,
from the power tool before making any
adjustments, changing accessories, or
storing power tools. Such preventive safety
measures reduce the risk of starting the power
tool accidentally .
4. Store idle power tools out of the reach of
children and do not allow persons unfamiliar
with the power tool or these instructions
to operate the power tool. Power tools are
dangerous in the hands of untrained users.
5. Maintain power tools and accessories.
Check for misalignment or binding of moving
parts, breakage of parts, and any other
condition that may affect the power tool’ s
operation. If damaged, have the power tool
repaired before use. Many accidents are
caused by poorly maintained power tools.
6. Keep cutting tools sharp and clean. Properly
maintained cutting tools with sharp cutting edges
are less likely to bind and are easier to control.
7. Use the power tool, accessories, and tool bits
etc. in accordance with these instructions,
taking into account the working conditions
and the work to be performed. Use of the
power tool for operations different from those
intended could result in a hazardous situation.
8. Keep handles and grasping surfaces dry ,
clean and free from oil and grease. Slippery
handles and grasping surfaces do not allow
for safe handling and control of the tool in
unexpected situations.
4

V . Battery tool use and care
1. Recharge only with the charger specied by
the manufacturer . A charger that is suitable for
one type of battery pack may create a risk of re
when used with another battery pack.
2. Use power tools only with specically
designated battery packs. Use of any other
battery packs may create a risk of injury and re.
3. When battery pack is not in use, keep it away
from other metal objects, like paper clips,
coins, keys, nails, screws or other small
metal objects, that can make a connection
from one terminal to another . Shorting the
battery terminals together may cause burns or
a re.
4. Under abusive conditions, liquid may be
ejected from the battery; avoid contact. If
contact accidentally occurs, ush with water .
If liquid contacts eyes, additionally seek
medical help. Liquid ejected from the battery
may cause irritation or burns.
5. Do not use a battery pack or tool that is
damaged or modied. Damaged or modied
batteries may exhibit unpredictable behavior
resulting in re, explosion or risk of injury .
6. Do not expose a battery pack or tool to re
or excessive temperature. Exposure to re or
temperature above 130 °C (265 °F) may cause
explosion.
7. Follow all charging instructions and do
not charge the battery pack or tool outside
the temperature range specied in the
instructions. Charging improperly or at
temperatures outside the specied range may
damage the battery and increase the risk of re.
VI. Service
1. Have your power tool serviced by a
qualied repair person using only identical
replacement parts. This will ensure that the
safety of the power tool is maintained.
2. Never service damaged battery packs.
Service of battery packs should only be
performed by the manufacturer or authorized
service providers.
VII. Hedge trimmer safety warnings
1. Do not use the hedge trimmer in bad weather
conditions, especially when there is a risk
of lightning. This decreases the risk of being
struck by lightning.
2. Keep all power cords and cables away from
cutting area. Power cords or cables may
be hidden in hedges or bushes and can be
accidentally cut by the blade.
3. W ear ear protection. Adequate protective
equipment will reduce the risk of hearing loss.
4. Hold the hedge trimmer by insulated gripping
surfaces only , because the blade may
contact hidden wiring. Blades contacting a
"live" wire may make exposed metal parts of the
hedge trimmer "live" and could give the operator
an electric shock.
5. Keep all parts of the body away from the
blade. Do not remove cut material or hold
material to be cut when blades are moving.
Blades continue to move after the switch is
turned off. A moment of inattention while
operating the hedge trimmer may result in
serious personal injury .
6. When clearing jammed material or servicing
the hedge trimmer , make sure all power
switches are off and the battery pack is
removed or disconnected. Unexpected
actuation of the hedge trimmer while clearing
jammed material or servicing may result in
serious personal injury .
7. Carry the hedge trimmer by the handle with
the blade stopped and taking care not to
operate any power switch. Proper carrying
of the hedge trimmer will decrease the risk of
inadvertent starting and resultant personal injury
from the blades.
8. When transporting or storing the hedge
trimmer , always use the blade cover . Proper
handling of the hedge trimmer will decrease the
risk of personal injury from the blades.
SA VE THESE
INSTRUCTIONS
5

Safety and Instructional Decals
Safety decals and instructions are easily visible to the operator and are located near any area
of potential danger . Replace any decal that is damaged or missing.
decal144-3094
144-3094
1. The battery pack is
charging.
3. The battery pack is over
or under the appropriate
temperature range.
2. The battery pack is fully
charged.
4. Battery pack charging fault
decal144-3098
144-3098
decal144-3096
144-3096
6

decal140-8475
140-8475
1. Read the Operator ’ s
Manual .
3. Keep away from open re
or ames.
2. Call2Recycle® battery
recycling program
4. Do not expose to rain.
decal144-3087
144-3087
1. W arning—read the
Operator ’ s Manual; wear
eye protection; do not
expose to rain.
2. Cutting/dismemberment
hazard of hand—stay
away from moving parts;
keep all guards and
shields in place.
decal137-9461
137-9461
1. Battery charge status
7

Setup
Important: The battery pack is not fully charged
when it is purchased. Before using the machine
for the rst time, refer to Charging the Battery
Pack ( page 1 1 ) .
Product Overview
g308470
Figure 3
Left side of the machine shown.
1. Blades 6. Lock switch
2. Guard
7. T rigger
3. Auxiliary-handle switch 8. Battery latch
4. Auxiliary handle 9. Battery pack
5. Handle-rotation button 10. Protective cover
g330065
Figure 4
1. Battery charger Model
88610 (included with
Model 51841)
2. Battery pack Model 88620
(included with Model
51841)
8

Specications
Model 51841
Cutting
Length
610 mm (24 inches)
Rated
V oltage
60V DC maximum, 54 VDC nominal usage
Cutting
width
19 mm (3/4 inch)
Charger
T ype
T oro 60V lithium-ion chargers
Battery T ype T oro 60V lithum-ion batteries
Appropriate T emperature Ranges
Charge/store the battery pack
at
5°C (41°F) to 40°C (104°F)*
Use the battery pack at
-30°C (-22°F) to 49°C (120°F)*
Use the machine at
0°C (32°F) to 49°C (120°F)*
*Charging time will increase if you do not charge the
battery pack within this range.
Store the machine, battery pack, and battery charger
in an enclosed clean, dry area.
Attachments/Accessories
A selection of T oro approved attachments and
accessories is available for use with the machine
to enhance and expand its capabilities. Contact
your Authorized Service Dealer or authorized T oro
distributor or go to www .T oro.com for a list of all
approved attachments and accessories.
T o ensure optimum performance and continued safety
certication of the machine, use only genuine T oro
replacement parts and accessories. Replacement
parts and accessories made by other manufacturers
could be dangerous.
Operation
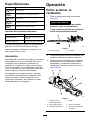
Starting the Hedge T rimmer
1. Remove the protective cover from the blades
(Figure 5 ).
W ARNING
The hedge trimmer blades can cause
cuts or amputation.
Be careful when handling the hedge
trimmer with the protective cover
removed.
g308414
Figure 5
1. Protective cover 2. Blades
2. Make sure that the vents on the hedge trimmer
are clear of any dust and debris.
3. Align the cavity of the battery pack with the
tongue in the handle housing, grasp the handle,
and push the battery pack into the handle until
the latch locks into place ( Figure 6 ).
g308413
Figure 6
1. Auxiliary-handle switch 4. T rigger
2. Auxiliary handle 5. Battery latch
3. Lock switch 6. Hedge trimmer venting
areas
4. Place 1 hand on the trigger handle. Place the
other hand on the auxiliary handle ( Figure 6 ).
9

5. Press the lock switch and then squeeze
the trigger switch while engaging the
auxiliary-handle switch to turn on the hedge
trimmer ( Figure 6 ).
The trimmer stays on as long as the
auxiliary-handle switch is engaged and the
trigger is squeezed. Y ou may release the
lock switch once the hedge trimmer is running
(Figure 6 ).
Rotating the Hedge T rimmer
Handle
1. Press and hold the rotational lock button (A of
Figure 7 ).
2. Rotate the handle 90° to the right or left
depending on desired cutting direction, then
release the rotational lock button to lock the
handle in the desired position (B of Figure 7 ).
g308389
Figure 7
Shutting Off the Hedge
T rimmer
T o shut of f the hedge trimmer , release the trigger ,
auxiliary-handle switch, or both ( Figure 6 ). Allow at
least 5 seconds for the cutting blade to stop moving.
Whenever you are not using the trimmer or are
transporting the trimmer to or from the work area,
remove the battery pack.
Removing the Battery Pack
Press the battery latch on the tool to release the
battery pack and slide the battery pack out of the tool
(Figure 8 ).
g308388
Figure 8
1. Battery latch
10

Charging the Battery Pack
Important: The battery pack is not fully charged
when you purchase it. Before using the tool for
the rst time, place the battery pack in the charger
and charge it until the LED display indicates the
battery pack is fully charged. Read all safety
precautions.
Important: Charge the battery pack only in
temperatures that are within the appropriate
range; refer to Specications ( page 9 ) .
Note: At any time, press the battery-charge-indicator
button on the battery pack to display the current
charge (LED indicators).
1. Ensure that the vents on the battery and charger
are clear of any dust and debris.
g330066
Figure 9
1. Battery pack cavity
5. LED indicators (current
charge)
2. Battery pack venting areas 6. Handle
3. Battery pack terminals
7. Charger
4. Battery-charge-indicator
button
2. Line up the charger with the cavity on the back
of the battery pack ( Figure 9 ).
3. Slide the charger into the battery pack until it is
fully seated ( Figure 9 ).
4. T o remove the charger , slide the charger
backward out of the battery .
5. Refer to the following table to interpret the LED
indicator light on the battery charger .
Indicator
light
Indicates
Of f
No battery pack inserted
Green
blinking
Battery pack is charging
Green
Battery pack is charged
Red
Battery pack and/or battery charger is over or under
the appropriate temperature range
Red
blinking
Battery pack charging fault*
*Refer to T roubleshooting ( page 14 ) for more
information.
Important: The battery can be left on the charger
for short periods between uses.
If the battery will not be used for longer periods,
remove the battery from the charger; refer to
Storage ( page 13 ) .
Operating T ips
•Use the power tool for cutting in either direction in
a slow , sweeping action.
•When trimming new growth, use a wide sweeping
action so that the stems are fed directly into the
cutting blade.
•Use a dif ferent tool to trim stems that are too large
for the trimmer .
•If desired, you can use a string to help cut your
hedge level. Decide how high you want the hedge.
Stretch a piece of string along the hedge at the
desired height as a guideline. T rim the hedge just
above the string guideline.
1 1

Maintenance
After each use of the trimmer , complete the following:
1. Remove the battery pack from the trimmer
before maintaining or cleaning.
2. Wipe the trimmer clean with a damp cloth any
time there is an accumulation of debris. Do not
hose the trimmer down or submerge it in water .
W ARNING
The hedge trimmer blades can cause
cuts or amputation.
Be careful when handling the hedge
trimmer with the protective cover
removed.
3. Inspect the machine, check and tighten all
fasteners. If any part is damaged or lost, repair
or replace it.
Important: Use only the manufacturer ’ s
recommended replacement parts and
accessories.
Have the product repaired only by an
Authorized Service Dealer .
4. Brush debris away from air intake vents and
exhaust on motor housing to prevent the motor
from overheating.
Lubricating the Blades
Service Interval : After each use
W ARNING
The hedge trimmer blades can cause cuts or
amputation.
Be careful when handling the hedge trimmer
with the protective cover removed.
1. Shut of f the trimmer , remove the battery pack,
and place the trimmer on a at surface.
2. Clean dirt and debris from the hedge trimmer ,
using a brush or a damp cloth with a mild
detergent.
3. Apply light weight machine oil (such as #10)
along the edge of the top blades ( Figure 10 ).
g426760
Figure 10
1. Apply machine oil to the top edge of the blades.
12

Preparing the Battery Pack
for Recycling
Important: Upon removal, cover the terminals of
the battery pack with heavy-duty adhesive tape.
Do not attempt to destroy or disassemble the
battery pack or remove any of its components.
Lithium-ion battery packs labeled with the
Call2Recycle seal can be recycled at any
participating retailer or battery recycling
facility in the Call2Recycle program (US
and Canada only). T o locate a participating
retailer or facility closest to you, please call
1-800-822-8837 or visit www .call2recycle.org.
If you cannot locate a participating retailer or
facility nearby , or if your rechargeable battery
is not labeled with the Call2Recycle seal,
please contact your local municipality for more
information on how to responsibly recycle the
battery . If you are located outside of the US
and Canada, please contact your authorized
T oro distributor .
Storage
Important: Store the tool, battery pack, and
charger only in temperatures that are within the
appropriate range; refer to Storage ( page 13 ) .
Important: If you are storing the battery pack for
the off-season, remove the battery pack from the
tool and charge the battery pack until 2 or 3 LED
indicators turn green on the battery . Do not store
a fully charged or fully depleted battery . When you
are ready to use the tool again, charge the battery
pack until the left indicator light turns green on
the charger or all 4 LED indicators turn green on
the battery .
•Disconnect the product from the power supply
(i.e., remove the plug from the power supply or the
battery pack) and check for damage after use.
•Clean all foreign material from the product.
•Do not store the tool with the battery pack installed.
•When not in use, store the tool, battery pack, and
battery charger out of the reach of children.
•Keep the tool, battery pack, and battery charger
away from corrosive agents, such as garden
chemicals and de-icing salts.
•T o reduce the risk of serious personal injury , do
not store the battery pack outside or in vehicles.
•Store the tool, battery pack, and battery charger
in an enclosed clean, dry area.
13

T roubleshooting
Perform only the steps described in these instructions. All further inspection, maintenance, and repair work
must be performed by an authorized service center or a similarly qualied specialist if you cannot solve the
problem yourself.
Always remove the battery from the tool when troubleshooting, inspecting, maintaining, or cleaning the tool.
Problem
Possible Cause Corrective Action
1. The battery is not fully installed in the
tool.
1. Remove and then replace the battery
into the tool, making sure that it is fully
installed and latched.
2. The battery pack is not charged.
2. Remove the battery pack from the tool
and charge it.
3. The battery pack is over or under the
appropriate temperature range.
3. Move the battery pack to a place
where it is dry and the temperature is
between 5°C (41°F) and 40°C (104°F).
4. There is moisture on the leads of the
battery pack.
4. Allow the battery pack to dry or wipe it
dry .
5. The battery pack is damaged. 5. Replace the battery pack.
6. There is another electrical problem
with the tool.
6. Contact an Authorized Service Dealer .
The tool does not run or does not run
continuously .
7. Both the auxiliary handle switch and
the trigger are not pressed.
7. Press both the trigger and the auxiliary
handle switch simultaneously .
1. The speed switch is in the low speed
or anti-jam position.
1. T urn the speed switch to the high
speed position.
2. The battery pack charge capacity is
too low .
2. Remove the battery pack from the tool
and fully charge the battery pack.
The tool does not reach full power .
3. The air vents are blocked.
3. Clean the air vents.
1. The air vents are blocked.
1. Clean the air vents.The gearbox is hot.
2. The gearbox is not being lubricated
properly .
2. Lubricate the gearbox.
1. The blades are dull or damaged.
1. Contact an Authorized Service Dealer .The tool is producing excessive vibration
or noise.
2. The machine is not being lubricated
properly .
2. Lubricate the blades and gearbox.
1. The battery pack is over or under the
appropriate temperature range.
1. Move the battery pack to a place
where it is dry and the temperature is
between 5°C (41°F) and 40°C (104°F).
The battery pack loses charge quickly .
2. The trimmer is overloaded 2. T rim at a slower pace.
1. The battery charger is over or under
the appropriate temperature range.
1. Unplug the battery charger and move
it to a place where it is dry and the
temperature is between 5°C (41°F)
and 40°C (104°F).
The battery charger is not working.
2. The outlet that the battery charger is
plugged into does not have power .
2. Contact your licensed electrician to
repair the outlet.
The LED indicator light on the battery
charger is red.
1. The battery charger and/or battery
pack is over or under the appropriate
temperature range.
1. Unplug the battery charger and move
the battery charger and battery pack
to a place where it is dry and the
temperature is between 5°C (41°F)
and 40°C (104°F).
14

Problem
Possible Cause Corrective Action
1. There is an error in the communication
between the battery pack and the
charger .
1. Remove the battery pack from the
battery charger , unplug the battery
charger from the outlet, and wait 10
seconds. Plug the battery charger into
the outlet again and place the battery
pack on the battery charger . If the LED
indicator light on the battery charger is
still blinking red, repeat this procedure
again. If the LED indicator light on
the battery charger is still blinking red
after 2 attempts, properly dispose of
the battery pack at a battery recycling
facility .
The LED indicator light on the battery
charger is blinking red.
2. The battery pack is weak.
2. Contact your authorized service dealer
if the battery is in warranty , or properly
dispose of the battery pack at a battery
recycling facility .
15

California Proposition 65 W arning Information
What is this warning?
Y ou may see a product for sale that has a warning label like the following:
W ARNING: Cancer and Reproductive Harm—www .p65W arnings.ca.gov .
What is Prop 65?
Prop 65 applies to any company operating in California, selling products in California, or manufacturing products that may be sold in or brought into
California. It mandates that the Governor of California maintain and publish a list of chemicals known to cause cancer , birth defects, and/or other
reproductive harm. The list, which is updated annually , includes hundreds of chemicals found in many everyday items. The purpose of Prop 65 is to
inform the public about exposure to these chemicals.
Prop 65 does not ban the sale of products containing these chemicals but instead requires warnings on any product, product packaging, or literature with
the product. Moreover , a Prop 65 warning does not mean that a product is in violation of any product safety standards or requirements. In fact, the
California government has claried that a Prop 65 warning “is not the same as a regulatory decision that a product is ‘safe’ or ‘unsafe.’” Many of these
chemicals have been used in everyday products for years without documented harm. For more information, go to https://oag.ca.gov/prop65/faqs-view-all .
A Prop 65 warning means that a company has either (1) evaluated the exposure and has concluded that it exceeds the “no signicant risk level”; or (2)
has chosen to provide a warning based on its understanding about the presence of a listed chemical without attempting to evaluate the exposure.
Does this law apply everywhere?
Prop 65 warnings are required under California law only . These warnings are seen throughout California in a wide range of settings, including but not
limited to restaurants, grocery stores, hotels, schools, and hospitals, and on a wide variety of products. Additionally , some online and mail order
retailers provide Prop 65 warnings on their websites or in catalogs.
How do the California warnings compare to federal limits?
Prop 65 standards are often more stringent than federal and international standards. There are various substances that require a Prop 65 warning
at levels that are far lower than federal action limits. For example, the Prop 65 standard for warnings for lead is 0.5 μg/day , which is well below
the federal and international standards.
Why don’t all similar products carry the warning?
•Products sold in California require Prop 65 labelling while similar products sold elsewhere do not.
•A company involved in a Prop 65 lawsuit reaching a settlement may be required to use Prop 65 warnings for its products, but other companies
making similar products may have no such requirement.
•The enforcement of Prop 65 is inconsistent.
•Companies may elect not to provide warnings because they conclude that they are not required to do so under Prop 65; a lack of warnings for a
product does not mean that the product is free of listed chemicals at similar levels.
Why does the manufacturer include this warning?
the manufacturer has chosen to provide consumers with as much information as possible so that they can make informed decisions about the products
they buy and use. the manufacturer provides warnings in certain cases based on its knowledge of the presence of one or more listed chemicals without
evaluating the level of exposure, as not all the listed chemicals provide exposure limit requirements. While the exposure from the manufacturer products
may be negligible or well within the “no signicant risk” range, out of an abundance of caution, the manufacturer has elected to provide the Prop 65
warnings. Moreover , if the manufacturer does not provide these warnings, it could be sued by the State of California or by private parties seeking to
enforce Prop 65 and subject to substantial penalties.
Rev A

Form No. 3460 - 671 Rev A
Cortasetos Flex - Force Power
System
™
de 61 cm (24") de 60 V
Nº de modelo 51841 —Nº de serie 323000001 y superiores
Registre su producto en www .T oro.com.
T raducción del original (ES)
*3460 - 671*

Si necesita ayuda, consulte
los vídeos instruccionales
en www .T oro.com/support
o llame al 1 - 888 - 384 - 9939
antes de devolver este
producto.
ADVERTENCIA
CALIFORNIA
Advertencia de la Propuesta 65
El cable eléctrico de este producto
contiene plomo, que el Estado de
California sabe que causa defectos
congénitos u otros peligros para la
reproducción. Lávese las manos después
de manejar el material.
El uso de este producto puede provocar la
exposición a sustancias químicas que el
Estado de California considera causantes
de cáncer , defectos congénitos u otros
trastornos del sistema reproductor .
Introducción
Este cortasetos está indicado para el mantenimiento
de arbustos y setos por parte de usuarios domésticos.
Está diseñada para usar baterías de ion litio de 60
V de T oro. Estas baterías están diseñadas para ser
cargadas únicamente con cargadores de batería de
ion litio de 60 V de T oro. El uso de estos productos
para propósitos diferentes a los previstos puede ser
peligroso para usted y para otras personas.
Lea este manual detenidamente para aprender a
utilizar y mantener correctamente su producto, y
para evitar lesiones y daños al producto. Usted es
responsable de utilizar el producto de forma correcta
y segura.
V isite www .T oro.com para obtener más información,
incluidos consejos de seguridad, materiales de
formación, información sobre accesorios, ayuda
para encontrar a un distribuidor o para registrar su
producto.
Si necesita asistencia técnica, piezas genuinas
del fabricante o información adicional, póngase en
contacto con un Servicio Técnico Autorizado o con el
Servicio de atención al cliente del fabricante y tenga a
mano el número de serie y de modelo del producto.
Figura 1 identica la ubicación de los números de
modelo y serie en el producto. Escriba los números
en el espacio provisto.
Importante: Con su dispositivo móvil, puede
escanear el código QR (en su caso) de la place
del número de serie para acceder a información
sobre la garantía, las piezas, y otra información
sobre el producto.
g308284
Figura 1
1. Ubicación de los números de modelo y de serie
Nº de modelo
Nº de serie
© 2022—The T oro® Company
81 1 1 L yndale A venue South
Bloomington, MN 55420
2
Póngase en contacto con nosotros en www .T oro.com.
Impreso en China
Reservados todos los derechos
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
Toro Flex-Force Power System 24in 60V Hedge Trimmer Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Taille-haies électriques
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur
dans d''autres langues
Documents connexes
-
Toro Flex-Force Power System 24in 60V Hedge Trimmer Manuel utilisateur
-
Toro Flex-Force Power System 24in 60V Hedge Trimmer Manuel utilisateur
-
Toro Flex-Force Power System 13in or 15in 60V MAX String Trimmer Manuel utilisateur
-
Toro Flex-Force Power System 13in or 15in 60V MAX String Trimmer Manuel utilisateur
-
Toro Cordless Hedge Trimmer 60V Flex-Force Power System 51855T - Tool Only Manuel utilisateur
-
Toro Cordless Hedge Trimmer 60V Flex-Force Power System 51855T - Tool Only Manuel utilisateur
-
Toro PowerPlex 24in 40V MAX Hedge Trimmer Manuel utilisateur
-
Toro PowerPlex 24in 40V MAX Hedge Trimmer Manuel utilisateur
























































