Miller KH374223 Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire

OWNERS
MANUAL
OMIG4
271A
September
1997
Eff.
w/SeriaJ
Number
KH374223
Processes_________________
Gas
Tungsten
Arc
(TIG)
Welding
~
Shielded
Metal
Arc
(Stick)
Welding
Description
Arc
Welding
Power
Source
1~OLSfi
sJ
~

This
limited
warranty
supersedes
all
previous
manufacturers
warranties
and
is
exclusive
with
no
other
guarantees
or
warranties
expressed
or
implied.
LIMITED
WARRANTY
Subject
to
the
terms
and
conditions
below,
warrants
to
its
original
retail
purchaser
that
new
equipment
sold
after
the
effective
date
of this
limited
warranty
is
free
of
defects
in
material
and
workmanship
at
the
time
it
is
shipped
from
factory.
THIS
WARRANTY
IS
EXPRESSLY
IN
LIEU
OF
ALL
OTHER
WARRANTIES,
EXPRESS
OR
IMPLIED,
INCLUDING
THE
WARRANTIES
OF
MERCHANTABILITY
AND
FITNESS.
Within
the
warranty
periods
listed
below,
manufacturer
will
repair
or
replace
any
warranted
parts
or
components
that
fail
due
to
such
defects
in
material
or
workmanship.
Manufacturer
must
be
notified
in
writing
within
thirty
(30)
days
of
such
defect
or
failure,
at
which
time
manufacturer
will
provide
instructions
on
the
warranty
claim
procedures
to
be
followed.
Manufacturer
shall
honor
warranty
claims
on
warranted
equipment
listed
below
in
the
event
of
such
afailure
within
the
warranty
time
periods.
All
warranty
time
periods
start
on
the
date
that
the
equipment
was
delivered
to
the
original
retail
purchaser,
or
one
year
after
the
equipment
is
sent
to
the
distributor.
1.
5
Years
Parts
3
Years
Labor
*
Original
main
power
rectifiers
2.
3
Years
Parts
and
Labor
*
Transformer/Rectifier
Power
Sources
*
Plasma
Arc
Cutting
Power
Sources
*
Semi-Automatic
and
Automatic
Wire
Feeders
*
Robots
*
Engine
Driven
Welding
Generators
(NOTE:
Engines
are
warranted
separately
by
the
engine
manufacturer.)
3.
1
Year
Parts
and
Labor
*
Motor
Driven
Guns
*
Process
Controllers
*
Positioners
and
Controllers
*
Automatic
Motion
Devices
*
Orbital
Weld
Heads
*
Water
Coolant
Systems
*
HF
Units
Grids
Spot
Welders
Load
Banks
SDX
Transformers
Running
Gear/Trailers
Field
Options
(NOTE:
Field
options
are
covered
under
the
limited
warranty
for
the
remaining
warranty
period
of
the
product
they
are
installed
in,
or
for
a
minimum
of
one
year
whichever
is
greater.)
4.
6
Months
Batteries
5.
90
Days
Parts
and
Labor
*
MIG
Guns/TIG
Torches
*
Plasma
Cutting
Torches
*
Remote
Controls
*
Accessory
Kits
*
Replacement
Parts
Limited
Warranty
shall
not
apply
to:
1.
Items
furnished
by
manufacturer,
but
manufactured
by
others,
such
as
engines
or
trade
accessories.
These
items
are
covered
by
the
manufacturers
warranty,
if
any.
2.
Consumable
components;
such
as
contact
tips,
cutting
nozzles,
contactors,
relays,
brushes,
slip
rings,
or
parts
that
fail
due
to
normal
wear.
3.
Equipment
that
has
been
modified
by
any
party
other
than
manufacturer,
or
equipment
that
has
been
improperly
installed,
improperly
operated
or
misused
based
upon
industry
standards,
or
equipment
which
has
not
had
reasonable
and
necessary
maintenance,
or
equipment
which
has
been
used
for
operation
outside
of
the
specifications
for
the
equipment.
MANUFACTURERS
PRODUCTS
ARE
INTENDED
FOR
PURCHASE
AND
USE
BY
COMMERCIAL/INDUSTRIAL
USERS
AND
PERSONS
TRAINED
AND
EXPERIENCED
IN
THE
USE
AND
MAINTENANCE
OF
WELDING
EQUIPMENT.
In
the
event
of
a
warranty
claim
covered
by
this
warranty,
the
exclusive
remedies
shall
be,
at
manufacturers
option:
(1)
repair;
or
(2)
replacement;
or,
where
authorized
in
writing
by
manufacturer
in
appropriate
cases,
(3)
the
reasonable
cost
of
repair
or
replacement
at
an
authorized
service
station;
or
(4)
payment
of
or
credit
for
the
purchase
price
(less
reasonable
depreciation
based
upon
actual
use)
upon
return
of
the
goods
at
customers
risk
and
expense.
manufacturers
option
of
repair
or
replacement
will
be
F.O.B.,
Factory
at
Appleton,
Wisconsin,
or
FOB.
at
an
authorized
service
facility
as
determined
by
manufacturer.
Therefore
no
compensation
or
reimbursement
for
transportation
costs
of
any
kind
will
be
allowed.
TO
THE
EXTENT
PERMITTED BY
LAW,
THE
REMEDIES
PROVIDED
HEREIN
ARE
THE
SOLE
AND
EXCLUSIVE
REMEDIES.
IN
NO
EVENT
SHALL
MANUFACTURER
BE
LIABLE
FOR
DIRECT,
INDIRECT,
SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL
OR
CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES
(INCLUDING
LOSS OF
PROFIT),
WHETHER
BASED
ON
CONTRACT,
TORT
OR
ANY
OTHER
LEGAL
THEORY.
-
ANY
EXPRESS
WARRANTY
NOT
PROVIDED
HEREIN
AND
ANY
IMPLIED
WARRANTY,
GUARANTY
OR
REPRESENTATION
AS TO
PERFORMANCE,
AND
ANY
REMEDY
FOR
BREACH
OF
CONTRACT
TORT
OR
ANY
OTHER
LEGAL
THEORY
WHICH,
BUT
FOR
THIS
PROVISION,
MIGHT
ARISE
BY
IMPLICATION,
OPERATION
OF
LAW,
CUSTOM
OF
TRADE
OR
COURSE
OF
DEALING,
INCLUDING
ANY
IMPLIED
WARRANTY
OF
MERCHANTABILITY
OR
FITNESS
FOR
PARTICULAR
PURPOSE,
WITH
RESPECT TO
ANY
AND
ALL
EQUIPMENT
FURNISHED
BY
MANUFACTURER
IS
EXCLUDED
AND
DISCLAIMED
BY
MANUFACTURER.
Some
states
in
the
U.S.A.
do
not
allow
limitations
of
how
long
an
implied
warranty
lasts,
or
the
exclusion
of
incidental,
indirect,
special
or
consequential
damages,
so
the
above
limitation
or
exclusion
may
not
apply
to
you.
This
warranty
provides
specific
legal
rights,
and
other
rights
may
be
available,
but
may
vary
from
state
to
state.
In
Canada,
legislation
in
some
provinces
provides
for
certain
additional
warranties
or
remedies
other
than
as
stated
herein,
and
to
the
extent
that
they
may
not
be
waived,
the
limitations
and
exclusions
set
out
above
may
not
apply.
This
Limited
Warranty
provides
specific
legal
rights,
and
other
rights
may
be
available,
but
may
vary
from
province
to
province.
Warranty
Effective
January
1,
1997
(Equipment
with
a
serial
number
preface
of
~KH
or
newer)
brand
warr
3/97

1.
Consignes
de
sØduritØ
-
lire
avant
utilisation
hi
Signification
des
symboles
a
Signifie
Mise
en
garde!
Soyez
vigilant!
Cette
procedure
prØsente
des
risques
de
danger!
Ceux-ci
sont
identifies
par
des
symboles
adjacents
aux
directives.
A
Identifie
un
message
de
sØcuritØ
particulier.
~
Signifie
NOTA
nest
pas
relatif
a
Ia
sØcuritØ.
1
2
Dangers
relatuts
au
soudage
a
Iarc
A
Les
symboles
prØsentØs
ci-aprŁs
sont
utilisØs
tout
au
long
du
present
manuel
pour
attirer
votre
attention
et
identifier
les
risques
de
danger.
Lorsque
vous
voyez
un
symbole,
soyez
vigilant
et
suivez
les
directives
mentionnØes
afin
dØviter
tout
danger.
Les
consignes
de
sØcuritØ
prØsentØes
ci-aprŁs
ne
font
que
rØsumer
linformation
contenue
dans
les
normes
de
sØcuritØ
ØnumØrØes
a
Ia
section
1-5.
Veuillez
lire
et
respecter
toutes
ces
normes
de
sØcuritØ.
A
Linstallation,
lutilisation,
lentretien
et
les
reparations
ne
doi
vent
Øtre
confiØs
qu
des
personnes
qualifiØes.
A
Au
cours
de
lutilisation,
tenir
toute
personne
a
IØcart
et
plus
par
ticuliŁrement
les
enfants.
UN
CHOC
ELECTRIQUE
peuttuer.
Un
simple
contact
avec
des
piŁces
Ølectriques
peut
provoquer
urte
electrocution
ou
des
blessures
graves.
LØlectrode
et
le
circuit
de
soudage
sont
sous
tension
des
que
lappareil
est
sur
ON.
Le
circuit
dentrŁe
et
les
circuits
internes
de
Iappareil
sont
Øgalement
sous
tension
a
ce
moment-l.
En
soudage
semi-automatique
ou
automatique,
le
fit,
te
dØvidoir,
le
logement
des
galets
dentraInement
et
es
piŁces
mØtalliques
en
contact
avec
le
fil
de
soudage
sont
sous
tension.
Des
matŁriels
mal
installØs
ou
mal
mis
a
Ia
terre
prØsentent
un
danger.
Ne
jamais
toucher
es
piŁces
Ølectriques
sous
tension.
Porter
des
gants
et
des
vŒtements
de
protection
secs
ne
comportant
pas
de
trous.
Sisoler
de
Ia
piŁce
et
de
Ia
terre
au
moyen
de
tapis
ou
dautres
moyens
isolants
suffisamment
grands
pour
empŒcher
le
contact
phy
sique
Øventuel
avec
Ia
piŁce
ou
Ia
terre.
Ne
pas
se
servir
de
source
electrique
courant
electrique
dans
es
zones
humides,
dans
les
endroits
confines
ou
l
o
on
risque
de
tomber.
Se
servir
dune
source
electrique
courant
Ølectrique
UNIQUEMENT
site
procedØ
de
soudage
le
demande.
Si
lutilisation
dune
source
Łlectrique
courant
Ølectrique
savŁre
nØces
saire,
se
servir
de
Ia
fonction
de
tØlØcommande
si
lappareil
en
est
ØquipØ.
Couper
lalimentation
ou
arrØter
le
moteur
avantde
procØder
a
linstal
lation,
a
Ia
reparation
ou
a
lentretien
de
lappareil.
DŁverrouiller
lalimentation
selon
Ia
norme
OSHA
29
CFR
191
0.147
(voir
normes
de
sŁcuritŁ).
Installer
et
mettre
ala
terre
correctement
cet
appareil
conformØment
a
son
manuel
dutilisation
et
aux
codes
nationaux,
provinciaux
et
municipaux.
Toujours
verifier
Ia
terre
du
cordon
dalimentation
Verifier
et
sassu
rer
que
le
fil
de
terre
du
cordon
dalimentation
est
bien
raccordØ
a
Ia
borne
de
terre
du
sectionneur
ou
que
Ia
fiche
du
cordon
est
raccordØe
a
une
prise
correctement
mise
a
Ia
terre.
En
effectuant
les
raccordements
dentrØe
fixer
dabord
le
conducteur
de
mise
a
Ia
terre
appropriØ
et
contre-vØrffier
les
connexions.
Verifier
frequemment
le
cordon
datimentation
pour
voir
sil
nest
pas
endommagØ
ou
dØnudØ
remplacer
le
cordon
immŁdiatement
sil
est
endommagŁ
un
cable
dØnudØ
peut
provoquer
une
electrocution.
Mettre
Iappareil
hors
tension
quand
on
ne
lutilise
pas.
Ne
pas
utiliser
des
cables
uses,
endommagØs,
de
grosseur
insuffi
sante
ou
mal
ŁpissØs.
Ne
pas
enrouter
les
cables
autour
du
corps.
Si
Ia
piŁce
soudØe
dolt
Łtre
mise
a
Ia
terre.
le
faire
directement
avec
un
cable
distinct
ne
pas
utiliser
le
connecteur
de
piŁce
ou
le
cable
de
retour.
Ne
pas
toucher
IØlectrode
quand
on
est
en
contact
avec
Ia
piŁce,
Ia
terre
ou
une
electrode
provenant
dune
autre
machine.
Ce
groupe
de
symboles
signifie
Mise
en
garde
!
Soyez
vigilant
II
y
a
des
risques
de
danger
relies
aux
CHOCS
ELECTRIQUES,
aux
PIECES
EN
MOUVEMENT
etaux
PIECES
CHAUDES.
Reportez-vous
aux
symboles
et
aux
directives
ci-dessous
afin
de
connaltre
les
mesures
a
prendre
pour
Øviter
tout
danger.
Nutiliser
quun
materiel
en
bon
etat.
RØparer
ou
remplacer
sur-le
champ
les
piŁces
endommagØes.
Entretenir
Iappareil
conformØment
ace
manuel.
Porter
un
harnais
de
sØcuritØ
quand
on
travaille
en
hauteur.
Maintenir
solidement
en
place
tous
les
panneaux
et
capots.
Fixer
le
cable
de
retour
de
facon
a
obtenir
un
bon
contact
mØtal-mØtal
avec
Ia
piŁce
a
souder
ou
Ia
table
de
travail,
le
plus
prŁs
possible
de
Ia
soudure.
Rangeret
isoler
correctement
Ia
pince
de
masse
aprŁs
utilisation
pour
Øviter
le
contact
avec
des
objets
relies
a
Ia
masse.
Ily
a
DU
COURANT
CONTINU
IMPORTANT
dans
les
convertisseurs
aprŁs
Ia
suppression
de
(alimenta
tion
Ølectrique.
ArrŒter
les
convertisseurs,
dØbrancher
le
courant
Ølectrique,
et
dØ
charger
les
condensateurs
dalimentation
selon
es
instructions
indiquØes
dans
Ia
partie
entretien
avant
de
toucher
les
piŁces.
---j
LES
FUMEES
ETLESGAzpeuvent,
Œtre
dangereux.
:
:
~
L.....
~
Le
soudage
genere
des
fumŁes
et
des
gaz.
Leur
fl
inhalation
peut
Œtre
dangereux
pour
votre
sante.
____________
Eloigner
votre
tŒte
des
fumŁes.
Ne
pas
respirer
es
tumØes.
A
IintØrieur,
ventiler
Ia
zone
et/ou
utiliser
un
Łchappement
au
ni
veau
de
arc
pour
lØvacuation
des
fumØes
et
des
gaz
de
soudage.
Si
Ia
ventilation
est
insuffisante,
utiliser
un
respirateur
a
alimenta
tion
dair
homologuØ.
Ure
les
specifications
de
sØcuritŁ
des
matØriaux
(MSDSs)
et
les
ins
tructions
du
fabricant
concernant
les
mŁtaux,
les
consommables,
les
revØtements,
les
nettoyants
et
les
dØgraisseurs.
Travailler
dans
un
espace
fermŁ
seulement
sil
est
bien
ventilØ
ou
en
portant
un
respirateur
a
alimentation
dair.
Demander
toujours
a
un
surveillant
dment
formØ
de
se
tenir
a
proximitŁ.
Des
fumØes
et
des
gaz
de
soudage
peuvent
dŁplacer
lair
et
abaisser
le
niveau
doxygene
provoquant
des
blessures
ou
des
accidents
mortels.
Sassurer
que
lair
de
respiration
ne
prØsente
aucun
danger.
Ne
pas
souder
dans
des
endroits
sltuØs
a
proximite
dopŁrations
de
degraissage,
de
nettoyage
ou
de
pulvŁrisation.
La
chaleur
et
les
rayons
de
larc
peuvent
rŁagir
en
presence
de
vapeurs
et
former
des
gaz
hautement
toxiques
et
irritants.
Ne
pas
souder
des
mŁtaux
munis
dun
revŒtement,
tels
que
lacier
galvanisØ,
plaque
en
p10mb
ou
au
cadmium
a
moms
que
le
revŒte
ment
naf
ØtØ
enlevŁ
dans
Ia
zone
de
soudure,
que
Iendroit
soit
bien
ventilŁ,
et
si
nŁcessaire,
en
portant
un
respirateur
a
alimenta
tion
dair.
Les
revŒtements
et
tous
les
mØtaux
renfermant
ces
ŁlŁ
ments
peuvent
degager
des
fumØes
toxiques
en
cas
de
soudage.
OM-164
271
1

LES
RAVONS
DELARC
pØuvent
pro-,
voquerldes
brluresldÆns
lØs
yeiet.~
sur
Ia
peau
Le
rayonnement
de
larc
du
procØdØ
de
soudage
gØnŁre
des
rayons
visibles
et
invisibles
intenses
(ultraviolets
et
infrarouges)
susceptibles
de
provoquer
des
brOlures
dans
es
yeux
et
sur
Ia
peau.
Des
Øtincelles
sont
projetØes
pendant
le
soudage.
Porter
un
casque
de
soudage
muni
dun
Øcran
de
filtre
appropriØ
pour
protØger
votre
visage
et
vos
yeux
pendant
le
soudage
ou
pour
regar
der
(voir
ANSI
Z49.1
et
Z87.
1
ØnumØrØ
dans
les
normes
de
sØcuritØ).
Porter
des
protections
approuvØs
pour
les
oreilles
Si
le
niveau
sondre
est
trop
ØtevØ.
Utiliser
des
Øcrans
ou
des
barriŁres
pour
protØger
des
tiers
de
IØclair
et
de
IØblouissement;
demander
aux
autres
personnes
de
ne
pas
re
garder
arc.
Porter
des
vŒtements
de
protection
constituØ
dans
une
matiŁre
dura
ble,
resistant
au
feu
(cuir
ou
lame)
et
une
protection
des
pieds.
LE
SOLJDAGE
peut
provoquer
un
incendieou
une
explosion.
Le
soudage
effectuØ
sur
des
conteneurs
fermØs
tels
que
des
reservoirs,
tambours
ou
des
conduites
peut
provo~uerleurØclatement.
Des
Øtincelles
peuventŒtre
projetees
de
larc
de
soudure.
La
projection
dØtincel
les,
des
piŁces
chaudes
et
des
Øquipements
chauds
peut
provoquer
des
incendies
et
des
brlures.
Le
contact
accidentel
de
IØlectrode
avec
des
objets
mØtalliques
peut
provoquer
des
Øtincelles,
une
explosion,
un
surchauffement
ou
un
incendie.
Avant
de
commencer
le
soudage,
verifier
et
sassurer
que
lendroit
ne
prØsente
pas
de
danger.
Se
protØger
et
dautres
personnes
de
Ia
projection
dØtincelles
et
de
metal
chaud.
Ne
pas
souder
dans
un
endroit
l
oii
des
Øtincelles
peuvent
tomber
sur
des
substances
inflammables.
DØplacer
toutes
les
substances
inflammables
a
une
distance
de
10,7
m
de
larc
de
soudage.
En
cas
dimpossibilitØ
les
recouvrir
soigneuse
ment
avec
des
protections
homologuØs.
Des
Øtincelles
et
des
matØriaux
chauds
du
soudage
peuvent
facile
ment
passer
dans
dautres
zones
en
traversant
de
petites
fissures
et
des
ouvertures.
Surveillertout
dØclenchement
dincendie
ettenir
un
extincteur
a
proxi
mite.
Le
soudage
effectuØ
sur
un
plafond,
plancher,
paroi
ou
separation
peut
dØclencher
un
incendie
de
Iautre
ctØ.
Ne
pas
effectuer
le
soudage
sur
des
conteneurs
fermØs
tels
que
des
reservoirs,
tambours,
ou
conduites,
a
moms
quils
naient
ØtØ
prØpa
rØs
correctement
conformØment
a
AWS
F4.1
(voir
les
normes
de
sØcuritØ).
Brancher
le
cable
sur
Ia
piŁce
le
plus
prØs
possible
de
Ia
zone
de
sou
dage
pour
Øviter
le
transport
du
courant
sur
une
longue
distance
par
des
chemins
inconnus
Øventuels
en
provoquant
des
risques
dØlec
trocution
et
dincendie.
Ne
pas
utiliser
le
poste
de
soudage
pour
dØgeler
des
conduites
ge
lees.
En
cas
de
non
utilisation,
enlever
a
baguette
dØlectrode
du
porte
electrode
ou
couper
le
fit
a
a
pointe
de
contact.
Porter
des
vŒtements
de
protection
dØpourvus
dhuile
tels
que
des
gants
en
cuir,
une
chemise
en
matØriau
lourd,
des
pantalons
sans
re
vers,
des
chaussures
hautes
et
un couvre
chef.
Avant
de
souder,
retirer
toute
substance
combustible
de
vos
poches
telles
quun
allumeur
au
butane
ou
des
atlumettes.
DES
PARTICULES
VOLANTES
peuvent
blesser
lea
yeux.
Le
soudage,
IØcaillement,
le
passage
de
Ia
piŁce
a
Ia
brosse
en
fit
de
fer,
et
le
meulage
genŁrent
des
Øtincelles
et
des
particules
mŁtalliques
volan
tes.
Pendant
Ia
pØriode
de
refroidissement
des
soudures,
elles
risquent
de
projeter
du
laitier.
Porter
des
lunettes
de
sØcuritØ
avec
Øcrans
latØraux
ou
un
Øcran
facial.
LES
ACCUMULATIONS
DE
GAZ
ris
quent
de
provoquer
des
blessures
ou
mŒrneIa~rnot;
:
:
Fermer
Ialimentation
du
gaz
protecteur
en
cas
de
non
utilisation.
Veiller
toujours
a
bien
aØrer
les
espaces
confines
ou
se
servir
dun
respi
rateur
dadduction
dair
homologue.
DES
PIECESCHAUDES
peuventpr
voquer
des
brlUres
graves..
Ne
pas
toucher
des
parties
chaudes
a
mains
flues
PrØvoir
une
pŁriode
de
refroidissement
avant
dutiliser
le
pistolet
ou
Ia
torche.
LES
CHAMPS
MAGNETIQUES
peuveæt
affecter
Ies
stimulateurs
cardiaques.
Porteursdestimulateurcardiaque,
restezdistance.
Les
porteurs
dun
stimulateur
cardiaque
doivent
dabord
consulter
leur
mØdecin
avant
de
sapprocher
des
operations
de
soudage
a
larc,
de
gougeage
ou
de
soudage
par
points.
LE
BRUIT
peut
affecter
IouIe.
Le
bruit
des
processus
et
des
Øquipements
peut
affecter
louIe.
Porter
des
protections
approuvØs
pour
tes
oreilles
Si
le
niveau
sondre
est
trop
ØlevØ.
Si
des
BOUTE1LLES
soft
endomma
gØes,
elles
pourront
exploser.
Des
bouteilles
de
gaz
protecteur
contiennent
du
gaz
sous
haute
pression.
Si
une
bouteille
est
endomma
gee,
elle
peut
exploser.
Du
fait
que
les
bouteilles
de
gaz
font
normalement
partie
du
procØdØ
de
soudage,
les
manipuler
avec
precaution.
ProtØger
les
bouteitles
de
gaz
comprime
dune
chaleur
excessive,
des
chocs
mecaniques,
du
laitier,
des
flammes
ouvertes,
des
Øtin
celles
et
des
arcs.
Placer
les
bouteilles
debout
en
les
fixant
dans
un
support
station
naire
ou
dans
un
porte-bouteilles
pour
les
empŒcher
de
tomber
ou
de
se
renverser.
Tenir
les
bouteilles
eloignees
des
circuits
de
soudage
ou
autres
cir
cuits
Ølectriques.
Ne
jamais
placer
une
torche
de
soudage
sur
une
bouteille
a
gaz.
Une
electrode
de
soudage
ne
doit
jamais
entrer
en
contact
avec
une
bouteille.
Ne
jamais
souder
une
bouteille
pressurisee
risque
dexplosion.
Utiliser
seulement
des
bouteilles
de
gaz
protecteur,
regulateurs,
tuyaux
et
raccords
convenables
pour
cette
application
specifique;
les
maintenir
ainsi
que
les
elements
associØs
en
bon
etat.
Ne
pas
tenir
Ia
tŒte
en
face
de
Ia
sortie
en
ouvrant
Ia
soupape
de
Ia
bouteille.
Maintenir
Ie
chapeau
de
protection
sur
Ia
soupape,
sauf
en
cas
dutilisation
ou
de
branchement
de
Ia
bouteille.
Lire
et
suivre
les
instructions
concernant
les
bouteilles
de
gaz
corn
prime,
les
equipements
associØs
et
les
publications
P-i
CGA
Ønu
merees
dans
les
normes
de
sØcuritØ.
I
2
OM-164
271

Risque
DINCENDIE
OU
DEXPLOSION.
Ne
pas
placer
lappareil
sur,
au-dessus
ou
a
proximitØ
de
surfaces
infilammables.
Ne
pas
installer
lappareil
a
proximitØ
de
produits
inflammables
Ne
pas
surcharger
installation
Ølectrique
sassurer
que
lalimen
tation
est
correctement
dimensionnØ
et
protØgØ
avant
de
mettre
lappareil
en
service.
LA
CHUTE
bE
LAPPAREIL
peut
btesser~
Utiliser
lanneau
de
levage
uniquement
pour
sou
lever
lappareil,
NON
PAS
les
chariot,
les
bouteil
les
de
gaz
ou
tout
autre
accessoire.
Utiliser
un
engin
dune
capacitØ
appropriØe
pour
soulever
lappareil.
En
utilisant
des
fourches
de
levage
pour
dØplacer
lunitØ,
sassurer
que
les
fourches
sont
suffisamment
longues
pour
dØpasser
du
ctØ
oppose
de
lappareil.
LEMPLOI
EXCESSIF
peut
SURCHAUFFER
LEQUIPEMENT.
PrØvoir
une
pØriode
de
refroidissement,
respec
ter
le
cycle
opØratoire
nominal.
RØduire
le
courant
ou
le
cycle
opØratoire
avant
de
recommancer
le
soudage.
Ne
pas
obstruer
les
passages
dair
du
poste.
LES
CHARGES
ELECTROSTATIQUES
peuvent
endommager
les
circuits
im
primes.
Etablir
Ia
connexion
avec
Ia
barrette
de
terre
avant
de
manipuler
des
cartes
ou
des
piŁces.
Utiliser
des
pochettes
et
des
boltes
antistatiques
pour
stocker,
dØplacer
ou
expŁdier
des
cartes
de
circuits
imprimes.
DES
ORGANES
MOBILES
peuvent
provoquer
des
blessures.
Ne
pas
sapprocher
des
organes
mobiles.
Ne
pas
sapprocher
des
points
de
coincement
tels
que
des
rouleaux
de
commande.
LES
FILS
DE
SOUDAGE
peuvent
pro
voquer
des
blessures.
Ne
pas
appuyer
sur
Ia
gachette
avant
den
avoir
recu
linstruction.
Ne
pas
diriger
le
pistolet
vers
soi,
dautres
per
sonnes
ou
toute
piŁce
mØcanique
en
engageant
le
fil
de
soudage.
DES
ORGANES
MOBILES
peuvent
provoquer
:desblessures.
Rester
a
lØcart
des
organes
mobiles
comme
le
ventilateur.
Maintenir
fermŁs
et
fixement
en
place
les
portes,
panneaux,
recouvrements
et
dispositifs
de
protection.
LE
RAYONNEMENT
HAUTE
FRE-i
QUENCE.
(HF.)
risque
dØprovoquer,
des
interferences.
Le
rayonnement
haute
frequence
peut
provoquer
des
interferences
avec
es
Øquipements
de
ra
dionavigation
et
de
communication,
les
services
de
sØcuritØ
et
les
ordinateurs.
Demander
seulement
a
des
personnes
qualifiØes
familiarisØes
avec
des
Łquipements
Ølectroniques
de
faire
fonctionner
linstalla
tion.
Lutilisateur
est
tenu
de
faire
corriger
rapidement
par
un
Łlectricien
qualifie
les
interferences
resultant
de
linstallation.
Si
le
FCC
signale
des
interferences,
arrŒter
immŁdiatement
lappa
reil.
Eftectuer
rØguliŁrement
le
contrle
et
lentretien
de
linstallation.
Maintenir
soigneusement
fermŁs
les
portes
et
les
panneaux
des
sources
de
haute
frequence,
maintenir
es
Łclateurs
a
une
distance
correcte
et
utiliser
une
terre
et
et
un
blindage
pour
rØduire
les
inter
fØrences
Øventuelles.
LE
SOUDAGE
A
LARC
risquede
provoquer
des.
interferences.
LŁnergie
ØlectromagnØtique
risque
de
provoquer
des
interferences
pour
lØquipement
Łlectronique
sensible
tel
que
les
ordinateurs
et
lØquipement
commandŁ
par
ordinateur
tel
que
les
robots.
Veiller
ace
que
tout
lØquipement
de
Ia
zone
de
soudage
soit
com
patible
electromagnØtiquement.
Pour
rØduire
Ia
possibilitØ
dinterfØrence,
maintenir
les
cables
de
soudage
aussi
courts
que
possible,
les
grouper,
et
les
poser
aussi
bas
que
possible
(ex.
par
terre).
Veiller
a
souder
a
une
distance
de 100
metres
de
tout
Łquipement
electronique
sensible.
Veiller
a
ce
que
ce
poste
de
soudage
soit
pose
et
mis
a
Ia
terre
conformØment
a
ce
mode
demploi.
En
cas
dinterfØrences
aprŁs
avoir
pris
les
mesures
prØcØdentes,
il
incombe
a
utilisateur
de
prendre
des
mesures
supplØmentaires
telles
que
le
dŁplacement
du
poste,
lutilisation
de
cables
blindŁs,
lutilisation
de
filtres
de
ligne
ou
Ia
pose
de
protecteurs
dans
Ia
zone
de
travail.
LES
CHAMPS
MAGNET1QUES
peuvent
affecter
les
stimulateurs
cardiaques.
Porteurs
de
stimulateur
cardiaque,
restez
Ł
dis
tance.
Les
porteurs
dun
stimulateur
cardiaque
doivent
dabord
consulter
leur
mŁdecin
avant
de
sappro
cher
des
operations
de
soudage
a
larc,
de
gou
geage
ou
de
soudage
par
points.
1.3
Dangers
supplØmentaires
en
relation
avec
linstallation,
le
fonctionnement.
et
la
maintenance
OM-164
271
3

.1.4
~:PrincipaIes
flormes
de
SØCUrit~.:
:~
:.
Safetyin
Welding
and
Cutting,
norme
ANSI
Z49.
1,
de
IAmerican
Wel-
Safe
Handling
of
Compressed
Gases
in
Cylinders,
CGA
Pamphlet
ding
Society,
550
N.W.
Lejeune
Rd,
Miami
FL
33126
P-i,
de
Ia
Compressed
Gas
Association,
1235
Jefferson
Davis
High
way,
Suite
501,
Arlington,
VA
22202.
Safetyand
Health
Sandards,
OSHA
29
CFR
1910,
du
Superintendent
of
Documents,
US.
Government
Printing
Office,
Washington,
D.C.
Regles
de
sØcuritØ
en
soudage,
coupage
et
procØdØs
connexes,
nor-
20402.
me
CSA
Wi
17.2,
de
lAssociation
canadienne
de
normalisation,
vente
de
normes,
178
Rexdale
Boulevard,
Rexdale
(Ontario)
Canada
M9W
Recommended
Safe
Practice
for
the
Preparation
for
Welding
and
Cut-
1
R3.
ting
of
Containers
That
Have
Held
Hazardous
Substances,
norme
Safe
Practices
For
Occupation
And
Educational
Eye
And
Face
Protec
AWS
F4.i,
de
lAmerican
Welding
Society,
550
NW.
Lejeune
Rd,
Mia-
tion,
norme
ANSI
Z87.1,
de
lAmerican
National
Standards
Institute,
mi
FL 33126
1430
Broadway,
New
York,
NY
10018.
National
Electrical
Code,
NFPA
Standard
70,
de
Ia
National
Fire
Pro-
Cutting
and
Welding
Processes,
norme
NFPA
51
B,
de
Ia
National
Fire
tection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
1
.~5
Information
sur
les
champs
ØlectromagnØtiques
DonnØes
sure
soudage
Ølectrique
et
sur
es
effets,
pour
lorganisme,
Atm
de
rØduire
les
champs
ØlectromagnØtiques
dans
lenvironnement
des
champs
magnØtiques
basse
frØquence
de
travail,
respecter
es
consignes
suivantes
Lextrait
suivant
est
tire
des
conclusions
gØnerales
du
document
intitu-
1
Garder
les
cables
ensembles
en
les
torsadant
ou en
les
lØ
Biological
Effects
of
Power
Frequency
Electric
&
Magnetic
Fields
attachant
avec
du
ruban
adhØsif.
Background
Paper,
OTA-BPE53
(Washington
DC:
U.S.
Govern-
2
Mettre
tous
les
cables
du
ctØ
oppose
de
lopØrateur.
ment
Printing
Office,
mai
1989),
publiØ
par
le
Office
of
Technology
3
Ne
pas
courber
pas
et
ne
pas
entourer
pas
les
cables
autour
de
Assessment
du
Congres
amØricain
:
i...
il
existe
maintenant
dabon-
vous.
dantes
donnØes
scientifiques
compilØes
a
Ia
suite
dexpØriences
sur
Ia
cellule
ou
dØtudes
sur
des
animaux
et
des
humains,
qul
montrent
4
Garder
le
poste
de
soudage
et
les
cables
le
plus
loin
possible
clairement
que
les
champs
ØlectromagnØtiques
basse
frequence
peu-
de
vous.
vent
avoir
des
effets
sur
lorganisme
et
mŒme
y
produire
des
5
Relier
Ia
pince
de
masse
le
plus
prØs
possible
de
Ia
zone
de
transformations.
MŒme
siI
sagit
de
travaux
de
trŁs
grande
qualite,
les
soudure.
rØsultats
sont
complexes.
Cette
dØmarche
scientifique
ne
nous
per-
Consignes
relatives
aux
stimulateurs
cardiaques
met
pas
dØtablir
un
tableau
densemble
coherent.
Pire
encore,
elle
ne
nous
permet
pas
de
tirer
des
conclusions
finales
concernant
les
ris-
LesconsignesmentionnØesprØcØdemmentfontpartiedecellesdesti
ques
Øventuels,
ni
doffrir
des
conseils
sur
les
mesures
a
prendre
pour
nØes
aux
personnes
ayant
recours
a
un
stimulateur
cardiaque.
rØduire
sinon
Øliminer
les
risques
Øventuels...
(Traduction
libre)
Veuillez
consulter
votre
mØdecin
pour
obtenir
plus
de
details.
OM-164
271

2.
Safety
Precautions
-
Read
Before
Using
2.1
Symbol
Usage
a
Means
Warning!
Watch
Out!
There
are
possible
hazards
with
this
procedure!
The
possible
hazards
are
shown
in
the
adjoining
symbols.
A
Marks
a
special
safety
message.
~
Means
Note~
not
safety
related.
22:
Arc
Welding
Hazards
A
The
symbols
shown
below
are
used
throughout
this
manual
to
call
attention
to
and
identify
possible
hazards.
When
you
see
the
symbol,
watch
out,
and
followthe
related
instructions
to
avoid
the
hazard.
The
safety
information
given
below
is
only
a
summary
of
the
more
complete
safety
information
found
in
the
Safety
Standards
listed
in
Section
2.4.
Read
and
follow
all
Safety
Standards.
A
Only
qualified
persons
should
install,
operate,
maintain,
and
repair
this
unit.
A
During
operation,
keep
everybody,
especially
children,
away.
ELECTRIC
SHOCK
can
kill.
Touching
live
electrical
parts
can
cause
fatal
shocks
or
severe
burns.
The
electrode
and
work
circuit
is
electrically
live
whenever
the
output
is
on.
The
input
power
circuit
and
machine
internal
circuits
are
also
live
when
power
is
on.
In
semiautomatic
or
automatic
wire
welding,
the
wire,
wire
reel,
drive
roll
housing,
and
all
metal
parts
touching
the
welding
wire
are
electrically
live.
Incorrectly
installed
or
improperly
grounded
equipment
is
a
hazard.
Do
not
touch
live
electrical
parts.
Wear
dry,
hole-free
insulating
gloves
and
body
protection.
Insulate
yourself
from
work and
ground
using
dry
insulating
mats
or
covers
big
enough
to
prevent
any
physical
contact
with
the
work
or
ground.
Do
not
use
AC
output
in
damp
areas,
if
movement
is
confined,
or
if
there
is
a
danger
of
falling.
Use
AC
output
ONLY
if
required
for
the
welding
process.
If
AC
output
is
required,
use
remote
output
control
if
present
on
unit.
Disconnect
input
power
or
stop
engine
before
installing
or
servicing
this
equipment.
Lockout/tagout
input
power
according
to
OSHA
29
CFR
191
0.147
(see
Safety
Standards).
Properly
install
and
ground
this
equipment
according
to
its
Owners
Manual
and
national,
state,
and
local
codes.
Always
verify
the
supply
ground
check
and
be
sure
that
input
power
cord
ground
wire
is
properly
connected
to
ground
terminal
in
disconnect
box
or
that
cord
plug
is
connected
to
a
properly
grounded
receptacle
outlet.
When
making
input
connections,
attach
proper
grounding
conductor
first
double-check
connections.
Frequently
inspect
input
power
cord
for
damage
or
bare
wiring
replace
cord
immediately
if
damaged
bare
wiring
can
kill.
Turn
off
all
equipment
when
not
in
use.
Do
not
use
worn,
damaged,
undersized,
or
poorly
spliced
cables.
OM-164
271A-
Date,
safety_som
4/97
This
group
of
symbols
means
Warning!
Watch
Out!
possible
ELECTRIC
SHOCK,
MOVING
PARTS,
and
HOT
PARTS
hazards.
Consult
symbols
and
related
instructions
below
for
necessary
actions
to
avoid
the
hazards.
Do
not
drape
cables
over
your
body.
If
earth
grounding
of
the
workpiece
is
required,
ground
it
directly
with
a
separate
cable
do
not
use
work
clamp
or
work
cable.
Do
not
touch
electrode
if
you
are
in
contact
with
the
work,
ground,
or
another
electrode
from
a
different
machine.
Use
only
well-maintained
equipment.
Repair
or
replace
damaged
parts
at
once.
Maintain
unit
according
to
manual.
Wear
a
safety
harness
if
working
above
floor
level.
Keep
all
panels
and
covers
securely
in
place.
Clamp
work
cable
with
good
metal-to-metal
contact
to
workpiece
or
worktable
as
near
the
weld
as
practical.
Insulate
work
clamp
when
not
connected
to
workpiece
to
prevent
contact
with
any
metal
object.
SIGNIFICANT
DC
VOLTAGE
exists
after
removal
of
input
power
on
inverters.
Turn
Off
inverter,
disconnect
input
power,
and
discharge
input
capacitors
according
to
instructions
in
Maintenance
Section
before
touching
any
parts.
FUMES
AND
GASES
an
be
hazardous.
L_.
~
Welding
produces
fumes
and
gases.
Breathing
these
fumes
and
gases
can
be
hazardous
to
your
health.
Keep
your
head
out
of
the
fumes.
Do
not
breathe
the
fumes.
If
inside,
ventilate
the
area
and/or
use
exhaust
at
the
arc
to
remove
welding
fumes
and
gases.
If
ventilation
is
poor,
use
an
approved
air-supplied
respirator.
Read
the
Material
Safety
Data
Sheets
(MSDS5)
and
the
manufacturers
instructions
for
metals,
consumables,
coatings,
cleaners,
and
degreasers.
Work
in
a
confined
space
only
if
it
is
well
ventilated,
or
while
wearing
an
air-supplied
respirator.
Always
have
a
tralned
watch-
person
nearby.
Welding
fumes
and
gases
can
displace
air
and
lower
the
oxygen
level
causing
injury
or
death.
Be
sure
the
breathing
air
is
safe.
Do
not
weld
in
locations
near
degreasing,
cleaning,
or
spraying
operations.
The
heat
and
rays
of
the
arc
can
react
with
vapors
to
form
highly
toxic
and
irritating
gases.
Do
not
weld
on
coated
metals,
such
as
galvanized,
lead,
or
cadmium
plated
steel,
unless
the
coating
is
removed
from
the
weld
area,
the
area
is
well
ventilated,
and
if
necessary,
while
wearing
an
air-supplied
respirator.
The
coatings
and
any
metals
containing
these
elements
can
give
off
toxic
fumes
if
welded.
OM-164
271
1

ARC
RAYS
can
burn
eyes
and
skin
Arc
rays
from
the
welding
process
produce
intense
visible
and
invisible
(ultraviolet
and
infrared)
rays
that
can
burn
eyes
and
skin.
Sparks
fly
off
from
the
weld.
Wear
a
welding
helmet
fitted
with
a
proper
shade
of
filter
to
protect
your
face
and
eyes
when
welding
or
watching
(see
ANSI
Z49.
1
and
Z87.i
listed
in
Safety
Standards).
Wear
approved
safety
glasses
with
side
shields
under
your
helmet.
Use
protective
screens
or
barriers
to
protect
others
from
flash
and
glare;
warn
others
not
to
watch
the
arc.
Wear
protective
clothing
made
from
durable,
flame-resistant
material
(leather
and
wool)
and
foot
protection.
WELDING
can
cause
tire
or
explosion.
Welding
on
closed
containers,
such
as
tanks,
drums,
or
pipes,
can
cause
them
to
blow
up.
Sparks
can
fly
oft
from
the
welding
arc.
The
flying
sparks,
hot
workpiece,
and
hot
equipment
can
cause
fires
and
burns.
Accidental
contact
of
electrode
to
metal
objects
can
cause
sparks,
explosion,
overheating,
or
fire.
Check
and
be
sure
the
area
is
safe
before
doing
any
welding.
Protect
yourself
and
others
from
flying
sparks
and
hot
metal.
Do
not
weld
where
flying
sparks
can
strike
flammable
material.
Remove
all
flammables
within
35
ft
(10.7
m)
of
the
welding
arc.
If
this
is
not
possible,
tightly
cover
them
with
approved
covers.
Be
alert
that
welding
sparks
and
hot
materials
from
welding
can
easily
go
through
small
cracks
and
openings
to
adjacent
areas.
Watch
for
fire,
and
keep
a
fire
extinguisher
nearby.
Be
aware
that
welding
on
a
ceiling,
floor,
bulkhead,
or
partition
can
cause
fire
on
the
hidden
side.
Do
not
weld
on
closed
containers
such
as
tanks,
drums,
or
pipes,
unless
they
are
properly
prepared
according
to
AWS
F4.1
(see
Safety
Standards).
Connect
work
cable
to
the
work
as
close
to
the
welding
area
as
practical
to
prevent
welding
current
from
traveling
long,
possibly
unknown
paths
and
causing
electric
shock
and
fire
hazards.
Do
not
use
welder
to
thaw
frozen
pipes.
Remove
stick
electrode
from
holder
or
cut
off
welding
wire
at
contact
tip
when
not
in
use.
Wear
oil-free
protective
garments
such
as
leather
gloves,
heavy
shirt,
cuffless
trousers,
high
shoes,
and
a
cap.
Remove
any
combustibles,
such
as
a
butane
lighter
or
matches,
from
your
person
before
doing
any
welding.
FLYING
METAL
can
injure
eyes.
Welding,
chipping,
wire
brushing,
and
grinding
cause
sparks
and
flying
metal.
As
welds
cool,
they
can
throw
off
slag.
Wear
approved
safety
glasses
with
side
shields
even
under
your
welding
helmet.
BUILDUP
OF
GAS
can
Injure
or
kill
Shut
off
shielding
gas
supply
when
not
in
use.
Always
ventilate
confined
spaces
or
use
approved
air-supplied
respirator.
HOT
PARTS
can
cause
severe
burns
o
Do
not
touch
hot
parts
bare
handed.
Allow
cooling
period
before
working
on
gun
or
torch.
MAGNETIC
FIELDS
can
affect
pacemakers.
Pacemaker
wearers
keep
away.
Wearers
should
consult
their
doctor
before
going
near
arc
welding,
gouging,
or
spot
welding
operations.
NOISE
can
damage
hearing.
Noise
from
some
processes
or
equipment
can
damage
hearing.
Wear
approved
ear
protection
if
noise
level
is
high.
Shielding
gas
cylinders
contain
gas
under
high
pressure.
If
damaged,
a
cylinder
can
explode.
Since
gas
cylinders
are
normally
part
of
the
welding
process,
be
sure
to
treat
them
carefully.
Protect
compressed
gas
cylinders
from
excessive
heat,
mechanical
shocks,
slag,
open
flames,
sparks,
and
arcs.
Install
cylinders
in
an
upright
position
by
securing
to
a
stationary
support
or
cylinder
rack
to
prevent
falling
or
tipping.
Keep
cylinders
away
from
any
welding
or
other
electrical
circuits.
Never
drape
a
welding
torch
over
a
gas
cylinder.
Never
allow
a
welding
electrode
to
touch
any
cylinder.
Never
weld
on
a
pressurized
cylinder
explosion
will
result.
Use
only
correct
shielding
gas
cylinders,
regulators,
hoses,
and
fittings
designed
for
the
specific
application;
maintain
them
and
associated
parts
in
good
condition.
Turn
face
away
from
valve
outlet
when
opening
cylinder
valve.
Keep
protective
cap
in
place
over
valve
except
when
cylinder
is
in
use
or
connected
for
use.
Read
and
follow
instructions
on
compressed
gas
cylinders,
associated
equipment,
and
CGA
publication
P-i
listed
in
Safety
Standards.
CYLINDERS
can
explode
if
damaged.
2
OM-164
271

2.3
Additional
Symbols
for
Installation,
Operation,
and.
Maintenance
FIRE
OR
EXPLOSION
hazard.
Do
not
install
or
place
unit
on,
over,
or
near
combustible
surfaces.
Do
not
install
unit
near
flammables.
Do
not
overload
building
wiring
be
sure
power
supply
system
is
properly
sized,
rated,
and
protected
to
handle
this
unit.
FALLING
UNITcan
cause
injury.
Use
lifting
eye
to
lift
unit
only,
NOT
running
gear,
gas
cylinders,
or
any
other
accessories.
Use
equipment
of
adequate
capacity
to
lift
and
support
unit.
If
using
lift
forks
to
move
unit,
be
sure
forks
are
long
enough
to
extend
beyond
opposite
side
of
unit.
OVERUSE
can
cause
OVERHEATING
Allow
cooling
period;
follow
rated
duty
cycle.
Reduce
current
or
reduce
duty
cycle
before
starting
to
weld
again.
Do
not
block
or
filter
airflow
to
unit.
STATIC
(ESD)
can
damage
PC
boards.
Put
on
grounded
wrist
strap
BEFORE
handling
boards
or
parts.
Use
proper
static-proof
bags
and
boxes
to
store,
move,
or
ship
PC
boards.
MOVING
PARTS
can
cause
injury.
Keep
away
from
moving
parts.
Keep
away
from
pinch
points
such
as
drive
rolls.
WELDING
WIRE
can
cause
injury
Do
not
press
gun
trigger
until
instructed
to
do
so.
Do
not
point
gun
toward
any
part
of
the
body,
other
people,
or
any
metal
when
threading
welding
wire.
Principal
Safety
Standards
Safety
in
Welding
and
Cutting,
ANSI
Standard
Z49.1,
from
American
Welding
Society,
550
N.W.
LeJeune
Rd,
Miami
FL
33126
Safety
and
Health
Standards,
OSHA
29
CFR
1910,
from
Supennten
dent
of
Documents,
U.S.
Government
Printing
Office,
Washington,
D.C.
20402.
Recommended
Safe
Practices
for
the
Preparation
for
Welding
and
Cutting
of
Containers
That
Have
Held
Hazardous
Substances,
American
Welding
Society
Standard
AWS
F4.1,
from
American
Welding
Society,
550
N.W.
LeJeune
Rd,
Miami,
FL
33126
National
Electrical
Code,
NFPA
Standard
70,
from
National
Fire
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
MOVING
PARTS
can
cause
injury~
Keep
away
from
moving
parts
such
as
fans.
Keep
all
doors,
panels,
covers,
and
guards
closed
and
securely
in
place.
H.F.RADIATION
can
cause
interference.
High-frequency
(H.F.)
can
interfere
with
radio
navigation,
safety
services,
computers,
and
communications
equipment.
Have
only
qualified
persons
familiar
with
electronic
equipment
perform
this
installation.
The
user
is
responsible
for
having
a
qualified
electrician
promptly
correct
any
interference
problem
resulting
from
the
installation.
If
notified
by
the
FCC
about
interference,
stop
using
the
equipment
at
once.
Have
the
installation
regularly
checked
and
maintained.
Keep
high-frequency
source
doors
and
panels
tightly
shut,
keep
spark
gaps
at
correct
setting,
and
use
grounding
and
shielding
to
minimize
the
possibility
of
interference.
ARC
WELDING
can
auseinterference.
Electromagnetic
energy
can
interfere
with
sensitive
electronic
equipment
such
as
computers
and
computer-driven
equipment
such
as
robots.
Be
sureall
equipment
in
the
welding
area
is
electromagnetically
compatible.
To
reduce
possible
interference,
keep
weld
cables
as
short
as
possible,
close
together,
and
down
low,
such
as
on
the
floor.
Locate
welding
operation
100
meters
from
any
sensitive
elec
tronic
equipment.
Be
sure
this
welding
machine
is
installed
and
grounded
according
to
this
manual.
If
interference
still
occurs,
the
user
must
take
extra
measures
such
as
moving
the
welding
machine,
using
shielded
cables,
using
line
filters,
or
shielding
the
work
area.
Safe
Handling
of
Compressed
Gases
in
Cylinders,
CGA
Pamphlet
P-i,
from
Compressed
Gas
Association,
1235
Jefferson
Davis
Highway,
Suite
501,
Arlington,
VA
22202.
Code
for
Safety
in
Welding
and
Cutting,
CSA
Standard
Wi
17.2,
from
Canadian
Standards
Association,
Standards
Sales,
178
Rexdale
Boulevard,
Rexdale,
Ontario,
Canada
M9W
1
R3.
Safe
Practices
For
Occupation
And
Educational
Eye
And
Face
Protection,
ANSI
Standard
Z87.1,
from
American
National
Standards
Institute,
1430
Broadway,
New
York,
NY
10018.
Cutting
And
Welding
Processes,
NFPA
Standard
SiB,
from
National
Fire
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
.
2.4
OM-164
271
3

25
EMF
Information
Considerations
About
Welding
And The
Effects
Of
Low
Frequency
To
reduce
magnetic
fields
in
the
workplace,
use
the
following
Electric
And
Magnetic
Fields
procedures:
The
following
is
a
quotation
from
the
General
Conclusions
Section
of
1.
Keep
cables
close
together
by
twisting
or
taping
them.
the
U.S.
Congress,
Office
of
Technology
Assessment,
Biological
Effects
of
Power
Frequency
Electric
&
Magnetic
Fields
Background
2.
Arrange
cables
to
one
side
and
away
from
the
operator.
Paper,
OTA-BP-E-53
(Washington,
DC:
U.S.
Government
Printing
3.
Do
not
coil
or
drape
cables
around
the
body.
Office,
May
1989):
.
. .
there
is
now
a
very
large
volume
of
scientific
findings
based
on
experiments
at
the
cellular
level
and
from
studies
4.
Keep
welding
power
source
and
cables
as
far
away
from
opera-
with
animals
and
people
which
clearly
establish
that
low
frequency
tor
as
practical.
magnetic
fields
can
interact
with,
and
produce
changes
in,
biological
systems.
While
most
of
this
work
is
of
very
high
quality,
the
results
are
5.
Connect
work
clamp
to
workpiece
as
close
to
the
weld
as
complex.
Current
scientific
understanding
does
not
yet
allow
us
to
in-
possible.
terpret
the
evidence
in
a
single
coherent
framework.
Even
more
frustrating,
it
does
not
yet
allow
us
to
draw
definite
conclusions
about
About
Pacemakers:
questions
of
possible
risk
or
to
offer
clear
science-based
advice
on
The
above
procedures
are
also
recommended
for
pacemaker
strategies
to
minimize
or
avoid
potential
risks.
wearers.
Consult
your
doctor
for
complete
information.
OM-164
271

3.
Introdllction
3.1
Included
with
Your
Unit
1
12
ft
(3.7
m)
Work
Cable
and
Clamp
2
150
Amp
TIG
Torch
with
12-1/2
ft
(3.8
m)
Cord
and
Flow-Through
Quick-Con
nect
(50
Hz
models
come
with
25
ft
(7.6
m)
TIG
Torch)
3
Electrode
Holder
and
Quick-Connect
Gas
Hose
Gas
Regulator
(Not
included
with
50
Hz
models)
How-To
Videotape
Foot
Control
with
20
ft
(6
m)
Cord
(60
Hz
models
only.
50
Hz
and
applicable
other
models
come
with
Fingertip
Control
instead.)
8
8
ft
(2.4
m)
Primary
Cord
(Plug
supplied
with
230
Volt
model
only)
~
Some
assembly
is
required.
For
options
and
accessories,
contact
your
distributor.
3.2
SpecIfications
Rated
Output
at
20%
Duty
Cycle
TIG:
15OAat15VDC
(GTAW)
15OAat15VAC
Stick:
130
A
at
25
VDC
(SMAW)
15OAat25VAC
*
0
While
idling.
Welding
Amperage
Range
AC
High
AC
Low
DC
TIG
Welding
A
Range
50-165 2050
30160
Stick
Welding
A
Range
35165
2050 25130
3.3
DutyCycleChati
Duty
cycle
is
percentage
of
10
minutes
that
unit
can
weld
at
rated
load
without
overheating.
A
Exceeding
duty
cycle
can
damage
unit
and
void
warranty.
-_c
-
-
- - - -
-
-
~~EE~4~EE
Net
Weight
140
lb
(64 kg)
GTAW:
20%
Duty
Cycle
at
150
A
AC/DC
SMAW:
20%
Duty
Cycle
at
130
A
DC,
or
150
A
AC
6
7
4
5
6
7
8
5~
4
3~
Max.
Open-Circuit
Voltage
78
Rated
Output
KVA
Dimensions
200
V-60
A
(3.6)*
12.0
H:
18
in
(457
mm)
230V52
A
(3.0)*
(0.64)*
W:
13
in
(330
mm)
78
0:
251/2
in
(648
mm)
ST-157
648-A
REED
Cu~ff
10
w
0.
~IC
3
50
15
10
1010
40
50
S0~I0S0150
X
DUTY
CYCLE
2
Minutes
Welding
8
Minutes
Resting
OM-164
271
5

Volt-ampere
curves
show
mini
mum
and
maximum
voltage
and
amperage
output
capabilities
of
welding
power
source.
Curves
of
other
settings
fall
between
curves
shown.
60
70
50
g250
40
~30
20
10
0
4.
InstallatIoll
4.1
Selecting
a
Location
60
70
60
40
~30
20
10
Position
unit
so
air
can
circulate.
For
information
about
sources
of
high-frequency
see
Section
8.
For
carts
and
caster
kits
see
back
of
book
or
contact
your
distributor.
4.2
Typical
Stick
Connections
1
Electrode
Holder
2
Work
Clamp
Connect
to
receptacle
as
shown.
ST-i58
075
ST-157
858-A
34
Volt-Ampere
Curves
Ssbi
.110/91
ST-i
57625-B
I
ST-157
626-B
50
100 150
200
250
300
AC
AMPERES
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
DC
AMPERES
18
in
(460
mm)
18
in
(460
mm)
18
in
(460
mm)
2
6
OM-164
271

1
Remote
Control
2
Torch
Connect
to
receptacles
as
shown.
3
Work
Clamp
4
Cylinder
Chain
or
secure
cylinder
to
running
gear,
wall,
or
other
stationary
support.
5
Cylinder
Valve
Open
valve
slightly
so
gas
flow
blows
dirt
from
valve.
Close
valve.
6
Regulator/Flow
Gauge
Install
so
face
is
vertical.
7
Flow
Adjust
Typical
flow
rate
is
20
cfh
(cubic
feet
per
hour)
(9.4
L/min).
4.3
Typical
T1G
Connections
ST-801
888
1
4
Tools
Needed:
3
5/8,1-1/8in
OM-164
271
7

44
Electrical
Service
Guide
S-0092J
O~
For
230
V
models
with
wall
receptacle,
100%
duty
cycle
used
to
calculate
data
below
20%
duty
cycle
used
for
200
V
model.
Input
Voltage
Grounding
Conductor
Size
(Mm.)
Reference:
1996
National
Electrical
Code
(NEC).
230
Volt
Model:
200
Volt
Model:
Units
come
equipped
with
input
power
cord
for
installation
into
line
disconnect
device.
Select
type
and
size
overcurrent
protection
using
Section
4.4.
200
230
1OAWG
8AWG
Input
Amperes
at
Rated
Output
59
52
Standard
Fuse
or
Circuit
Breaker
Rating
(Max.
Recommended)
90
Amps
80
Amps
Input
Conductor
Size
(Mm.)
10
AWG
6
AWG
Input
Conductor
Length
(Max.
Recommended)
42
ft
(13
m)
135
ft
(41
m)
4.5
Connecting
Input
Power
A
Have
only
qualified
persons
make
this
installation.
Tools
Needed:
A
Special
installation
may
be
required
where
gasoline
or
volatile
liquids
are
present
see
NEC
Article
511
or
CEC
Section
20.
ST-161
454-A
GND/PE
Units
come
equipped
with
input
power
cord
and
plug.
Wall
recep
tacle
is
customer
supplied.
To
install,
select
type
and
size
input
and
grounding
conductors
using
Section
4.4.
Conductor
rating
must
comply
with
national,
state,
and
local
electrical
codes.
Install
and
connect
grounding
con
ductor
and
input
conductors
in
conduit
or
equivalent
between
wall
receptacle
and
deenergized
line
disconnect
device.
GND/PE
Connect
first.
Li
L2
200
Volt
Model
230
Volt
Model
8
OM-164
271

5.
OperatioN
Use
switch
to
select
weld
process.
In
Stick
position
(down),
weld
output
goes
On
and
Off with
Power
switch.
In
GTAW
(TIG)
position
(up),
remote
control
device
turns
on
and
adjusts
weld
output
of
unit
as
limited
by
Amperage
control.
Built-in
arc
starter
comes
on
when
needed
to
start
or
sta
bilize
welding
arc.
No
adjustments
needed
for
arc
starter.
2
Pilot
Light
3
Power
Switch
Use
switch
to
turn
unit,
fan,
and
pilot
light
On
and
Off.
4
Amperage
Control
8
7
For
Stick
(SMAW),
use
control
to
adjust
am
perage
within
range
selected
by
the
Range!
Polarity
Switch.
5
Stick
(SMAW)
Table
Use
table
to
find
approximate
Stick
amperage
output
at
Amperage
control
sethng.
See
Section
5.2
for
example
of front
panel
am
perage
control.
For
remote
amperage
control
used
when
TIG
(GTAW)
welding,
front
panel
Amperage
con
trol
setting
is
the
maximum
amperage
percen
tage
available
at
the
remote
control
device.
See
Section
5.3
for
example
of
remote
amper
age
control.
6
Range/Polarity
Switch
Use
switch
to
select
range
and
polarity
of
weld
output.
For
Direct
Current
Electrode
Negative
(DCEN),
use
Electrode
Negative
position.
For
Direct
Current
Electrode
Positive
(DCEP),
use
Electrode
Positive
position.
For
alternating
current
(AC),
use
range
need
ed
for
welding
application
AC
Low
or
AC
High
position
see
Warning.
See
Section
5.4
to
find
suggested
type
of
weld
output
for
application.
7
High
Temperature
Shutdown
Light
Lights
when
unit
overheats
and
shuts
down
(see
Section
6.2).
8
Output
On
(Contactor)
Light
Lights
when
output
(contactor)
and
unit
power
are
on.
2
3
4
5
1
Weld
Process
Switch
Ret
ST-Th9
691-0
20.
.
~.
Wa.
z
HIGH
TB.~P
4
sHtrrDowN
L~
~
V
~
~
N
~
N
N
N
24
40
21
N
20
24
20
20
20
27
J2
0
JO
N
24
I?
~4
25
20
43
~1
N
N
AMPERAGE
RATED
OIIIPUT
~
VC
snoc
Via
VOLTS
Vi
Vi
ii
_S
IX
IX
IX
WTY
OflE
Vi%
Vi!.
XX
MMia
Vi
75
Vi
OM-164
271
9

ARC
STARTER
ACTIVE
34i6~~
IN
hG
MODE
~
DO
NOT
SWITCH
UNDER
LOAD
STICK
Connect
remote
control
(see
Section
4.3).
GTAW
Wel
AC
Low
ding
Amperage
Range
AC
High
DC
20-50
A
60-165
A
30-165
A
In
Example:
Range
=
DCEN
Percentage
of
Range
=
50%
Remote
weld
amperage
=
30-98
A
DC
(50%
of
30i
65
A
DC)
52
Example
of
Front
Panel
Amperage
Control
DC
~PR~M~E
CUIPUT
AMPER.~
VS.
DIALZ
20
A
100%
X
~L0W
#CII~1
DC
i~
20
18
38
23
i~
19
39
24
21
48
28
~---
~-- ~-~
80
27
79
43
70
32
94
30
37
184
36
43
161
113
100
60
ISO
AMPERAGE
Select
weld
process.
Select
range
and
polarity.
Select
percentage.
In
Example:
j
Range
=
DC
Percentage
of
Range
=
50%
Weld
Amperage
=
33
A
DC
DC
5.3
Example
of
Remote
Amperage
Control
ARC
STARTER
ACTIVE
34~
66A
~
IN
hG
MODE
~
DO
NOT
SWITCH
UNDER
LOAD
L~O
STICK
Select
weld
process.
80
Select
range
and
polarity.
.....4
A
100%
AMPERAGE
Select
percentage.
or
10
OM-164
271

54
Process
and
Material
Thickness
Guide
Label
Guideline
For
Welding
Process
And
Output
For
Material
MaterialAnd
Weld
Output
Material
Thickness
22ga
2Oga
0.033
in
0.036
in
0.8
mm
0.9
mm
l8ga
l6ga
l4ga
l2ga
ilga
lOga
6ga
0.048
in
0.06
in
0.07
in
0.1
in
0.125
in
0.14
in
0.186
in
1.2
mm
1.5
mm
1.8
mm
2.5
mm
3.2
mm
3.6
mm
4.8
mm
2ga
0.25
in
0.25+
in
6.3
mm
6.3+
mm
Steel
Or
Stainless
Steel
(-)/t.
.I.
DCEN
ELECTRODE
NEGATIVE
:~
.
GTAW
:
GTAW
,~
~
Difficult
Recommended
..
.
SMAW
,=
j~
With
DCEP
Output
/
~GTAW
~
~
Not
RecommŁndŁd
Aluminum
,.t
\/
AC
S-167
338
OM-164271
11

0.
Maintenance
and
Troubleshooting
6,1
Routine
Maintenance
r!1~PHH
~
A
Disconnect
power
before
maintaining.
fl~
Maintain
more
often
during
severe
conditions.
3
Months
Replace
unreadable
labels.
Repair
or
replace
cracked
weld
cable.
Replace
0-ring
in
Electrode/Gas
Output
receptacle
if
cracked.
6
Months
Blow
out
or
vacuum
inside.
Clean
and
tighten
weld
terminals.
Repair
or
replace
cracked
gas
hose.
/~
/~
6.2
Troubleshooting
Trouble
Remedy
No
weld
output;
fan
does
not
run.
Place
line
disconnect
switch
in
On
position
(see
Section
4.5).
Check
and
replace
line
fuse(s),
if
necessary,
or
reset
circuit
breaker
(see
Section
4.5).
Check
for
proper
input
power
connections
(see
Section
4.5).
No
weld
output;
fan
on.
Be
sure
Range/Polarity
switch
is
not
set
between
positions.
Tighten
remote
control
connection
to
Remote
14
receptacle.
Check
remote
control
(see
remote
control
Owners
Manual).
Unit
overheated.
Allow
unit
to
cool
(see
Section
3.3).
Fan
not
operating;
weld
output
available.
Check
for
and
remove
anything
blocking
fan
movement.
Have
Factory
Authorized
Service
Agent
check
fan
motor.
Or
12
OM-164
271

7.
Electrical
Diagrams
230
VAC
13
7
1
Circuit
Diagram
SB-154
141-C
U
a
N
010
010
I I
I
I
I I
1.00
U
LI
.00
C.,
a
0
CIIt~~I0~O
(~CD(~CDCD0CD
S
~S
~ ~ ~ ~
~
0JP~1~I0S00
OC)0000
aaaaaao
a
J
-01
I
I I
I
S050
00
a
a
PCI
9>
0
I
I
.00
~
RCI-II>>.---IR~J
vv
I
~TJ~T
I-
CII
CD
-J
a
OM-164
271

8.
High
Frequeocy
8.1
Welding
Processes
Requiring
High
Frequency
1
High-Frequency
Voltage
Helps
arc
jump
air
gap
between
torch
and
workpiece
and/or
stabilize
the
arc.
high_freqi
11/96
-
5-0693
18.2
Inorrect
Installation
Sources
of
Direct
High-Frequency
Radiation
1
High-Frequency
Source
(welding
power
source
with
built-in
HF
or
separate
HF
unit)
2
Weld
Cables
3
Torch
4
Work
Clamp
5
Workpiece
6
Work
Table
/
Sources
of
Conduction
of
High
Frequency
7
Input
Power
Cable
8
Line
Disconnect
Device
9
Input
Supply
Wiring
Sources
of
Reradiation
of
High
Frequency
10
Ungrounded
Metal
Objects
11
Lighting
12
Wiring
13
Water
Pipes
and
Fixtures
14
External
Phone
and
Power
Lines
S-0694
TIG
Weld
Zone
S.
14
OM-164
271
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
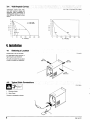 12
12
-
 13
13
-
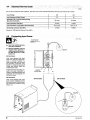 14
14
-
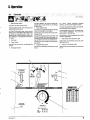 15
15
-
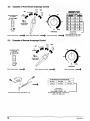 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
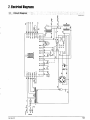 19
19
-
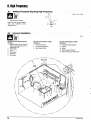 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
Miller KH374223 Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire
dans d''autres langues
- English: Miller KH374223 Owner's manual
Documents connexes
-
Miller LA004576 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller KJ109577 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller DYNASTY DX Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller KJ073032 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller 190 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller MATIC 400 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller MW175 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller MW225 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller Electric MATIC 400 Manuel utilisateur
-
Miller MATIC 400 Le manuel du propriétaire