Miller KH341356 Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire
Ce manuel convient également à

,~/
4
/
x~n:~,
44
~
4k
:
4k
2/
201358
Rev.
C
March
1997
En.
w/Serial
Number
KH341356
Processes
MIG
(GMAW)
Welding
Flux
Cored
(FCAW)
Welding
Description
Wire
Feeder
PDVS-II
OWNERS
MANUAL
I~A
Pow
Con
OM-171
892-C




TABLE
OF
CONTENTS
SECTION
1
SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS
-
READ
BEFORE
USING
1
1-1.
Symbol
Usage
1
1-2.
Arc
Welding
Hazards
1
1-3.
Additional
Symbols
For
Installation,
Operation,
And
Maintenance
3
1-4.
Principal
Safety
Standards
3
1-5.
EMF
Information
4
SECTION
1
CONSIGNES
DE
SECURITE
LIRE
AVANT
IJTILISATION
5
1-1.
Signification
des
symboles
5
1-2.
Dangers
relatifs
au
soudage
a
Iarc
5
1-3.
Dangers
supplOmentaires
en
relation
avec
installation,
le
fonctionnement
et
Ia
maintenance
7
1-4.
Principales
normes
de
sØcuritØ
8
1-5.
Information
sur
les
champs
electromagnetiques
8
SECTION
2
INSTALLATION
9
2-1.
Typical
Connections
9
2-2.
Installing
And
Aligning
Wire
Guide
And
Drive
Roll
10
2-3.
Gun
Recommendation
Table
11
2-4.
Connecting
Welding
Gun
And
Voltage
Sensing
Lead
11
2-5.
Connecting
Shielding
Gas
(Optional)
12
2-6.
Connecting
Weld
Cable
12
2-7.
Installing
And
Threading
Welding
Wire
13
SECTION
3OPERATION
14
3-1.
Controls
14
SECTION
4MAINTENANCE
&
TROUBLESHOOTING
15
4-1.
Routine
Maintenance
15
4-2.
Overload
Protection
15
4-3.
Calibrating
Optional
1PM
Meter
16
4-4.
Troubleshooting
17
SECTION
5
ELECTRICAL
DIAGRAM
18
SECTION
6
PARTS
LIST
20
OPTIONS
AND
ACCESSORIES
WARRANTY




SECTION
1
-
SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS
-
READ
BEFORE
USING
som
nd_5/97
1-t..
Symbol
Usage.
a
Means
Warning!
Watch
Out!
There
are
possible
hazards
with
this
procedure!
The
possible
hazards
are
shown
in
the
adjoining
symbols.
A
Marks
a
special
safety
message.
~
Means
t~Jote~
not
safety
related.
1~2
Arc
Welding
Hazards
A
The
symbols
shown
below
are
used
throughout
this
manual
to
call
attention
to
and
identity
possible
hazards.
When
you
see
the
symbol,
watch
out,
and
follow
the
related
instructions
to
avoid
the
hazard.
The
safety
information
given
below
is
only
a
summary
of
the
more
complete
safety
Information
found
in
the
Safety
Standards
listed
in
Section
1-4.
Read
and
follow
all
Safety
Standards.
A
Only
qualified
persons
should
install,
operate,
maintain,
and
repair
this
unit.
A
During
operation,
keep
everybody,
especially
children,
away.
ELEcTRIC.
SHOCK..can
icl~
Touching
live
electrical
parts
can
cause
fatal
shocks
or
severe
burns.
The
electrode
and
work
circuit
is
electrically
live
whenever
the
output
is
on.
The
input
power
circuit
and
machine
internal
circuits
are
also
live
when
power
is
on.
In
semiautomatic
or
automatic
wire
welding,
the
wire,
wire
reel,
drive
roll
housing,
and
all
metal
parts
touching
the
welding
wire
are
electrically
live.
Incorrectly
installed
or
improperly
grounded
equipment
is
a
hazard.
Do
not
touch
live
electrical
parts.
Wear
dry,
hole-tree
insulating
gloves
and
body
protection.
Insulate
yourself
from
work
and
ground
using
dry
insulating
mats
or
covers
big
enough
to
prevent
any
physical
contact
with
the
work
or
ground.
Do
not
use
AC
output
in
damp
areas,
if
movement
is
confined,
or
if
there
is
a
danger
of
falling.
Use
AC
output
ONLY
if
required
for
the
welding
process.
If
AC
output
is
required,
use
remote
output
control
if
present
on
unit.
Disconnect
input
power
or
stop
engine
before
installing
or
servicing
this
equipment.
Lockout/tagout
input
power
according
to
OSHA
29
CFR
1910.147
(see
Safety
Standards).
Properly
install
and
ground
this
equipment
according
to
its
Owners
Manual
and
national,
state,
and
local
codes.
Always
verify
the
supply
ground
check
and
be
sure
that
input
power
cord
ground
wire
is
properly
connected
to
ground
terminal
in
disconnect
box
or
that
cord
plug
is
connected
to
a
properly
grounded
receptacle
outlet.
When
making
input
connections,
attach
proper
grounding
conductor
first
double-check
connections.
Frequently
inspect
input
power
cord
for
damage
or
bare
wiring
replace
cord
immediately
if
damaged
bare
wiring
can
kill.
Turn
oft
all
equipment
when
not
in
use.
Do
not
use
worn,
damaged,
undersized,
or
poorly
spliced
cables.
Do
not
drape
cables
over
your
body.
This
group
of
symbols
means
Warning!
Watch
Out!
possible
ELECTRIC
SHOCK,
MOVING
PARTS,
and
HOT
PARTS
hazards.
Consult
symbols
and
related
instructions
below
for
necessary
actions
to
avoid
the
hazards.
If
earth
grounding
of
the
workpiece
is
required,
ground
it
directly
with
a
separate
cable
do
not
use
work
clamp
or
work
cable.
Do
not
touch
electrode
it
you
are
in
contact
with
the
work,
ground,
or
another
electrode
from
a
different
machine.
Use
only
well-maintained
equipment.
Repair
or
replace
damaged
parts
at
once.
Maintain
unit
according
to
manual.
Wear
a
safety
harness
if
working
above
floor
level.
Keep
all
panels
and
covers
securely
in
place.
Clamp
work
cable
with
good
metal-to-metal
contact
to
workpiece
or
worktable
as
near
the
weld
as
practical.
Insulate
work
clamp
when
not
connected
to
workpiece
to
prevent
contact
with
any
metal
object.
Do
not
connect
more
than
one
electrode
or
work
cable
to
any
single
weld
output
terminal.
SIGNIFICANT
DC
VOLTAGE
exists
after
removal
of
input
power
on
inverters.
Turn
Oft
inverter,
disconnect
input
power,
and
discharge
input
capacitors
according
to
instructions
in
Maintenance
Section
before
touching
any
parts.
~JM~
AND
GASES
can
be
hazardous.
Welding
produces
fumes
and
gases.
Breathing
these
fumes
and
gases
can
be
hazardous
to
your
health.
Keep
your
head
out
of
the
fumes.
Do
not
breathe
the
fumes.
If
inside,
ventilate
the
area
and/or
use
exhaust
at
the
arc
to
remove
welding
fumes
and
gases.
If
ventilation
is
poor,
use
an
approved
air-supplied
respirator.
Read
the
Material
Safety
Data
Sheets
(MSDS5)
and
the
manufacturers
instructions
for
metals,
consumables,
coatings,
cleaners,
and
degreasers.
Work
in
a
confined
space
only
if it
is
well
ventilated,
or
while
wearing
an
air-supplied
respirator.
Always
have
a
trained
watch-
person
nearby.
Welding
fumes
and
gases
can
displace
air
and
lower
the
oxygen
level
causing
injury
or
death.
Be
sure
the
breathing
air
is
safe.
Do
not
weld
in
locations
near
degreasing,
cleaning,
or
spraying
operations.
The
heat
and
rays
of
the
arc
can
react
with
vapors
to
form
highly
toxic
and
irritating
gases.
Do
not
weld
on
coated
metals,
such
as
galvanized,
lead,
or
cadmium
plated
steel,
unless
the
coating
is
removed
from
the
weld
area,
the
area
is
well
ventilated,
and
if
necessary,
while
wearing
an
air-supplied
respirator.
The
coatings
and
any
metals
containing
these
elements
can
give
off
toxic
fumes
if
welded.
OM-171
892
Page
1


ARC
RAYS
can
bum
eyes
and
skin
Arc
rays
from
the
welding
process
produce
intense
visible
and
invisible
(ultraviolet
and
infrared)
rays
that
can
burn
eyes
and
skin.
Sparks
fly
off
from
the
weld.
Wear
a
welding
helmet
fitted
with
a
proper
shade
of
filter
to
protect
your
face
and
eyes
when
welding
or
watching
(see
ANSI
Z49.1
and
Z87.1
listed
in
Safety
Standards).
Wear
approved
safety
glasses
with side
shields
under
your
helmet.
Use
protective
screens
or
barriers
to
protect
others
from
flash
and
glare;
warn
others
not
to
watch
the
arc.
Wear
protective
clothing
made
from
durable,
flame-resistant
material
(leather
and
wool)
and
foot
protection.
WELDING
can
cause
fire
or
explosion
Welding
on
closed
containers,
such
as
tanks,
drums,
or
pipes,
can
cause
them
to
blow
up.
Sparks
can
fly
off
from
the
welding
arc.
The
flying
sparks,
hot
workpiece,
and
hot
equipment
can
cause
fires
and
burns.
Accidental
contact
of
electrode
to
metal
objects
can
cause
sparks,
explosion,
overheating,
or
fire.
Check
and
be
sure
the
area
is
safe
before
doing
any
welding.
Protect
yourself
and
others
from
flying
sparks
and
hot
metal.
Do
not
weld
where
flying
sparks
can
strike
flammable
material.
Remove
all
flammables
within
35
ft
(10.7
m)
of
the
welding
arc.
If
this
is
not
possible,
tightly
cover
them
with
approved
covers.
Be
alert
that
welding
sparks
and
hot
materials
from
welding
can
easily
go
through
small
cracks
and
openings
to
adjacent
areas.
Watch
for
fire,
and
keep
a
fire
extinguisher
nearby.
Be
aware
that
welding
on a
ceiling,
floor,
bulkhead,
or
partition
can
cause
fire
on
the
hidden
side.
Do
not
weld
on
closed
containers
such
as
tanks,
drums,
or
pipes,
unless
they
are
properly
prepared
according
to
AWS
F4.1
(see
Safety
Standards).
Connect
work
cable
to
the
work
as
close
to
the
welding
area
as
practical
to
prevent
welding
current
from
traveling
long,
possibly
unknown
paths
and
causing
electric
shock
and
fire
hazards.
Do
not
use
welder
to
thaw
frozen
pipes.
Remove
stick
electrode
from
holder
or
cut
off
welding
wire
at
contact
tip
when
not
in
use.
Wear
oil-free
protective
garments
such
as
leather
gloves,
heavy
shirt,
cuffless
trousers,
high
shoes,
and
a
cap.
Remove
any
combustibles,
such
as
a
butane
lighter
or
matches,
from
your
person
before
doing
any
welding.
FLYING
METAL
can
injure
eyes
Welding,
chipping,
wire
brushing,
and
grinding
cause
sparks
and
flying
metal.
As
welds
cool,
they
can
throw
oft
slag.
Wear
approved
safety
glasses
with
side
shields
even
under
your
welding
helmet.
1
BUILDUP
OF
GAS
can
injure
or
Shutoff
shielding
gas
supply
when
not
in
use.
Always
ventilate
confined
spaces
or
use
approved
air-supplied
respirator.
HOT
PARTS
can
cause
severe
burns~
Do
not
touch
hot
parts
bare
handed.
Allow
cooling
period
before
working
on
gun
or
torch.
I
MAGNE1IG
FIELDS
can
affect
pacemakers
Pacemaker
wearers
keep
away.
Wearers
should
consult
their
doctor
before
going
near
arc
welding,
gouging,
or
spot
welding
operations.
NOISE
can
damage
hearing
Noise
from
some
processes
or
equipment
can
damage
hearing.
Wear
approved
ear
protection
if
noise
level
is
high.
CYLINDERS
can
explode
If
damag~d
Shielding
gas
cylinders
contain
gas
under
high
pressure.
If
damaged,
a
cylinder
can
explode.
Since
gas
cylinders
are
normally
part
of
the
welding
process,
be
sure
to
treat
them
carefully.
Protect
compressed
gas
cylinders
from
excessive
heat,
mechanical
shocks,
slag,
open
flames,
sparks,
and
arcs.
Install
cylinders
in
an
upright
position
by
securing
to
a
stationary
support
or
cylinder
rack
to
prevent
falling
or
tipping.
Keep
cylinders
away
from
any
welding
or
other
electrical
circuits.
Never
drape
a
welding
torch
over
a
gas
cylinder.
Never
allow
a
welding
electrode
to
touch
any
cylinder.
Never
weld
on
a
pressurized
cylinder
explosion
will
result.
Use
only
correct
shielding
gas
cylinders,
regulators,
hoses,
and
fittings
designed
for
the
specific
application;
maintain
them
and
associated
parts
in
good
condition.
Turn
face
away
from
valve
outlet
when
opening
cylinder
valve.
Keep
protective
cap
in
place
over
valve
except
when
cylinder
is
in
use
or
connected
for
use.
Read
and
follow
instructions
on
compressed
gas
cylinders,
associated
equipment,
and
CGA
publication
P-i
listed
in
Safety
Standards.
OM-17i
892
Page
2


FIRE
OR
EXPLOSION
hazard
Do
not
install
or
place
unit
on,
over,
or
near
combustible
surfaces.
Do
not
install
unit
near
flammables.
Do
not
overload
building
wiring
be
sure
power
supply
system
is
properly
sized,
rated,
and
protected
to
handle
this
unit.
FALLING
UNIT
can
cause
injury
Use
lifting
eye
to
lift
unit
only,
NOT
running
gear,
gas
cylinders,
or
any
other
accessories.
Use
equipment
of
adequate
capacity
to
lift
and
support
unit.
If
using
lift
forks
to
move
unit,
be
sure
forks
are
long
enough
to
extend
beyond
opposite
side
of
unit.
STATIC
(ESD)
can
damage.
pc
boards;
Put
on
grounded
wrist
strap
BEFORE
handling
boards
or
parts.
Use
proper
static-proof
bags
and
boxes
to
store,
move,
or
ship
PC
boards.
MOVING
PARTS
cm
cause:
Injii~,
Keep
away
from
moving
parts.
Keep
away
from
pinch
points
such
as
drive
rolls.
WELDING
WIRE
can
cause
injury
Do
not
press
gun
trigger
until
instructed
to
do
so.
Do
not
point
gun
toward
any
part
of
the
body,
other
people,
or
any
metal
when
threading
welding
wire.
1-4.
Principal
Safety
Standards
Safety
in
Welding
and
Cutting,
ANSI
Standard
Z49.
1,
from
American
Welding
Society,
550
N.W.
LeJeune
Rd,
Miami
FL
33126
Safetyand
Health
Standards,
OSHA
29
CFR
1910,
from
Superinten
dent
of
Documents,
U.S.
Government
Printing
Office,
Washington,
D.C.
20402.
Recommended
Safe
Practices
for
the
Preparation
for
Welding
and
Cutting
of
Containers
That
Have
Held
Hazardous
Substances,
American
Welding
Society
Standard
AWS
F4.1,
from
American
Welding
Society,
550
N.W.
LeJeune
Rd,
Miami,
FL
33126
National
Electrical
Code,
NFPA
Standard
70,
from
National
Fire
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
HF.
RADiATI~Ncant~seiiiterferen~e~
High-frequency
(H.F.)
can
interfere
with
radio
navigation,
safety
services,
computers,
and
communications
equipment.
Have
only
qualified
persons
familiar
with
electronic
equipment
perform
this
installation.
The
user
is
responsible
for
having
a
qualified
electrician
promptly
correct
any
interference
problem
resulting
from
the
installation.
If
notified
by
the
FCC
about
interference,
stop
using
the
equipment
at
once.
Have
the
installation
regularly
checked
and
maintained.
Keep
high-frequency
source
doors
and
panels
tightly
shut,
keep
spark
gaps
at
correct
setting,
and
use
grounding
and
shielding
to
minimize
the
possibility
of
interference.
ARC
WELDING
can
cause
Interference
Electromagnetic
energy
can
interfere
with
sensitive
electronic
equipment
such
as
computers
and
computer-driven
equipment
such
as
robots.
Be
sure
all
equipment
in
the
welding
area
is
electromagnetically
compatible.
To
reduce
possible
interference,
keep
weld
cables
as
short
as
possible,
close
together,
and
down
low,
such
as
on
the
floor.
Locate
welding
operation
100
meters
from
any
sensitive
elec
tronic
equipment.
Be
sure
this
welding
machine
is
installed
and
grounded
according
to
this
manual.
If
interference
still
occurs,
the
user
must
take
extra
measures
such
as
moving
the
welding
machine,
using
shielded
cables,
using
line
filters,
or
shielding
the
work
area.
Safe
Handling
of
Compressed
Gases
in
Cylinders,
CGA
Pamphlet
P-i,
from
Compressed
Gas
Association,
1235
Jefferson
Davis
Highway,
Suite
501,
Arlington,
VA
22202.
Code
for
Safety
in
Welding
and
Cutting,
CSA
Standard
Wi
17.2,
from
Canadian
Standards
Association,
Standards
Sales,
178
Rexdale
Boulevard,
Rexdale,
Ontario,
Canada
M9W
1
R3.
Safe
Practices
For
Occupation
And
Educational
Eye
And
Face
Protection,
ANSI
Standard
Z87.i,from
American
National
Standards
Institute,
1430
Broadway,
New
York,
NY
10018.
Cuffing
And
Welding
Processes,
NFPA
Standard
51
B,
from
National
Fire
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
I
-3~
Additional
Symbols
For
Installation,
Operation,
And
Maintenance
MOVING
PARTS
~an
cause
injury
Keep
away
from
moving
parts
such
as
fans.
Keep
all
doors,
panels,
covers,
and
guards
closed
and
securely
in
place.
OVERUSE
can
cause
OVERHEATING
Allow
cooling
period;
follow
rated
duty
cycle.
Reduce
current
or
reduce
duty
cycle
before
starting
to
weld
again.
Do
not
block
or
filter
airflow
to
unit.
OM-171
892
Page
3


1-5
EMF
Informaflon
Considerations
About
Welding
And
The
Effects
Of
Low
Frequency
1.
Keep
cables
close
together
by
twisting
or
taping
them.
Electric
And
Magnetic
Fields
Welding
current,
as
it
flows
through welding
cables,
will
cause
electro-
2.
Arrange
cables
to
one
side
and
away
from
the
operator.
magnetic
fields.
There
has
been
and
still
is
some
concern
about
such
fields.
However,
after
examining
more
than
500
studies
spanning
17
3.
Do
not
coil
or
drape
cables
around
your
body.
years
of
research,
a
special
blue
ribbon
committee
of
the
National
Research
Council
concluded
that:
The
body
of
evidence,
in
the
4.
Keep
welding
power
source
and
cables
as
far
away
from
opera
committees
judgment,
has
not
demonstrated
that
exposure
to
power-
tor
as
practical.
frequency
electric
and
magnetic
fields
is
a
human-health
hazard.
However,
studies
are
still
going
forth
and
evidence
continues
to
be
5.
Connect
work
clamp
to
workpiece
as
close
to
the
weld
as
examined.
Until
the
final
conclusions
of
the
research
are
reached,
you
possible.
may
wish
to
minimize
your
exposure
to
electromagnetic
fields
when
welding
or
cutting.
About
Pacemakers:
To
reduce
magnetic
fields
in
the
workplace,
use
the
following
Pacemakerwearersconsultyourdoctorfirst.
lfclearedbyyourdoctor,
procedures:
then
following
the
above
procedures
is
recommended.
OM-171
892
Page
4


SECTION
1
-
CONSIGNES
DE
SECURITE
-
LIRE
AVANT
UTI
LISATION
1-1
Signification
des
symboles
AA
Signifie
Mise
en
garde!
Soyez
vigilant!
Cette
procedure
prOsente
des
risques
de
danger!
Ceux-ci
sont
identifies
par
des
symboles
adjacents
aux
directives.
sorn
nd_fre
5/97
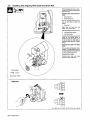
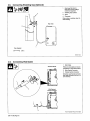
1-2.
Dangers
relatifs
au
soudage
a
~arc
A
Lea
symboles
prØsentØs
ci-aprŁs
sont
utilisØs
tout
au
long
du
present
manuel
pour
attirer
votre
attention
et
identifier
lea
risques
de
danger.
Lorsque
vous
voyez
un
symbole,
soyez
vigilant
et
suivez
lea
directives
mentionnØes
af
in
dØviter
tout
danger.
Les
consignes
de
sØcuritØ
prØsentØes
ci-aprŁs
ne
font
que
rØsumer
linformation
contenue
dana
les
normes
de
sØcuritØ
ØnumØrØes
a
Ia
section
1-4.
Veuillez
lire
et
respecter
toutes
ces
normes
de
sCcuritØ.
A
Linstallation,
lutilisation,
lentretien
et
les
reparations
ne
doi
vent
Œtre
confiØs
quA
des
personnes
qualifiees.
A
Au
cours
de
lutilisation,
tenir
toute
personne
a
lØcart
et
plus
par
ticuliŁremenlt
lea
enfants.
UN
CHOC
ELECTRIQUE
peut
tuer
Un
simple
contact
avec
des
piŁces
electriques
pout
provoquer
une
electrocution
ou
des
blessures
graves.
LOlectrode
et
le
circuit
de
soudage
sont
sous
tension
des
que
lappareil
est
sur
ON.
Le
circuit
dentre
et
les
circuits
internes
do
lappareil
sont
egalement
sous
tension
ace
moment-l.
En
soudage
semi-automatique
ou
automatique,
le
f
ii,
le
dØvidoir,
le
logement
des
galets
dentraInement
et
les
piŁces
metalliques
en
contact
avec
le
f
il
de
soudage
sont
sous
tension.
Des
matØriels
mal
installØs
ou
mal
mis
a
Ia
terre
prŁsentent
un
danger.
Ne
jamais
toucher
les
piŁces
Ølectnques
sous
tension.
Porter
des
gants
et
des
vŒtements
do
protection
secs
ne
comportant
pas
de
trous.
Sisoler
de
Ia
piŁce
et
de
Ia
terre
au
moyen
de
tapis
ou
dautres
moyens
isolants
suffisamment
grands
pour
empŒcher
le
contact
phy
sique
Øventuel
avec
Ia
piŁce
ou
Ia
terre.
No
passe
servirde
source
electnque
courant
electrique
dans
los
zones
humides,
dans
les
endroits
confines
ou
l
o~j
on
risque
do
tomber.
Se
servir
dune
source
electrique
courant
electrique
UNIQUEMENT
si
le
procØdØ
de
soudago
10
demande.
Si
lutilisation
dune
source
electriquo
courant
Ølectrique
savere
nØces
saire,
se
servir
de
Ia
fonction
de
tØlØcommande
51
lappareil
en
ost
Øquipe.
Couperlalimentation
ou
arrŒter
le
moteur
avant
do
proceder
linstal
lation,
a
Ia
rparation
ou
a
lontretien
do
lappareil.
DŁverrouiller
lalimentation
solon
Ia
norme
OSHA
29
CFR
1910.147
(voir
normes
do
sØcuritº).
Installeret
mettre
ala
terre
correctoment
cot
appareil
conformŁmont
~
son
manuel
dutilisation
et
aux
codes
nationaux,
provinciaux
et
municipaux.
Toujours
verifier
Ia
terre
du
cordon
dalimontation
Verifier
et
sassu
ror
quo
le
fil
do
terre
du
cordon
dalimontation
est
bion
raccordØ
a
Ia
borne
do
terre
du
sectionneur
ou
que
Ia
fiche
du
cordon
est
raccordŁe
a
une
prise
correctement
mise
a
Ia
terre.
En
effoctuant
los
raccordements
dentrŁe
fixer
dabord
10
conducteur
de
mise
a
Ia
terre
appropriŁ
et
contre-vŁrifier
los
connexions.
Verifier
frequemment
le
cordon
dalimentation
pour
voir
sil
nest
pas
endommagØ
ou
dŁnudØ
remplacer
le
cordon
immŁdiatement
sil
est
endommagØ
-
un
cable
dØnudØ
pout
provoquer
une
electrocution.
Mettre
lappareil
hors
tension
quand
on
ne
lutilise
pas.
Ne
pas
utiliser
des
cables
uses,
endommages,
de
grosseur
insuffi
sante
ou
mal
ŁpissØs.
Ne
pas
enrouler
los
cables
autour
du
corps.
Si
Ia
piŁce
soudØe
doit
Øtre
mise
a
laterre,
lo
faire
directement
avec
un
cable
distinct
no
pas
utiliser
le
connecteur
de
piŁce
ou
le
cable
do
retour.
Ne
pas
toucher
lØlectrode
quand
on
est
en
contact
avec
Ia
piŁce,
Ia
terre
ou
une
electrode
provenant
dune
autre
machine.
Nutilisor
quun
materiel
en
bon
Łtat.
RØparer
ou
remplacer
sur-le
champ
les
piŁces
ondommagees.
Entretenir
lappareil
conformŁmont
a
ce
manuel.
Porter
un
hamais
do
sØcuritŁ
quand
on
travaille
on
hautour.
Maintenir
solidement
en
place
tous
lea
panneaux
et
capots.
Fixer
lo
cblo
de
retour
de
facon
a
obtenir
un
bon
contact
mØtal-mØtal
avoc
Ia
piŁce
a
souderou
Ia
table
de
travail,
Ie
plus
prŁs
possible
do
Ia
soudure.
Isoler
Ia
pince
de
masso
quand
pas
mis
a
Ia
piŁce
pour
Øvitor
lo
contact
avoc
tout
objet
metallique.
Ily
a
DU
COURANT
CONTINU
IMPORTANT
dans
les
convertisseurs
aprŁs
Ia
suppression
de
IaIirnenta
tion
Øiectrique.
ArrŒter
los
convertisseurs,
dŁbrancher
le
courant
Øloctrique,
et
dØ
charger
los
condensateurs
dalimentation
selon
les
instructions
mndiquees
dans
Ia
partie
entrotion
avant
do
toucher
los
piŁces.
-.
FUMEES-
ET
.LES
GAZ--
peuvent
edangereux
-
-
.-~
-~..
-.
Le
soudago
gŁnŁre
des
fumØes
et
des
gaz.
Leur
v
inhalation
peut
Otre
dangereux
pour
votro
sante.
--
Eloignor
votre
tŒte
des
fumØes.
No
pas
respirer
los
fumØos.
A
lintŁrieur,
ventiler
Ia
zone
etlou
utiliser
un
Łchappement
au
ni
veau
do
Iarc
pour
lŁvacuation
des
fumees
et
des
gaz
do
soudage.
Si
Ia
ventilation
ost
insuftisante,
utiliser
un
respirateur
a
alimenta
tion
dair
homologuŁ.
Lire
los
specifications
do
sØcuntŁ
des
matØnaux
(MSDS5)
et
lea
ins
tructions
du
fabricant
concornant
Ies
mdtaux,
los
consommables,
lea
revŒtements,
los
nettoyants
et
los
degraisseurs.
Travailler
dans
un
espace
fermØ
seulement
sil
est
bien
ventilØ
ou
en
portant
un
respirateura
alimentation
dair.
Demander
toujours
~
un
surveillant
dCiment
formŁ
do
so
tenir
a
proximitŁ.
Des
fumŁes
ot
des
gaz
do
soudage
peuvent
dŁplacer
Iair
et
abaisser
le
niveau
doxygeno
provoquant
des
blessures
ou
des
accidents
mortols.
Sassurer
quo
lair
do
respiration
no
prØsonto
aucun
danger.
Ne
pas
soudor
dans
dos
endroits
situØs
a
proximitŁ
dopŁrations
do
dŁgraissage,
do
nettoyago
ou
do
pulvØrisation.
La
chalour
et
les
rayons
do
Iarc
peuvont
reagir
en
presonce
do
vapours
et
former
des
gaz
hautoment
toxiques
et
irritants.
No
pas
soudor
dos
mŁtaux
munis
dun
revŒtement,
tels
quo
lacier
galvanisØ,
plaque
en
p10mb
ou au
cadmium
a
moms
quo
le
revŒte
mont
nait
Ote
enlevØ
dans
Ia
zone
do
soudure,
quo
Iendroit
soit
bion
vontilØ,
ot
Si
nØcessairo,
en
portant
un
respiratour
~
alimonta
tion
dair.
Los
revŒtements
et
tous
los
mØtaux
renfermant
ces
ele
ments
pouvent
degagor
des
fumØes
toxiquos
on
cas
do
Soudage.
A
Identifie
un
message
de
sØcuritØ
particulier.
~
Signhfie
NOT4
nest
pas
re/at!!
a
Ia
sØcuritØ.
--~--~-
Ce
groupe
de
symboles
signifie
Mise
en
garde!
Soyez
vigilant!
Ily
a
des
risques
de
danger
relies
aux
CHOCS
ELECTRIQUES,
aux
PIECES
EN
MOUVEMENTetaux
PIECES
CHAUDES.
Reportez-vous
aux
symboles
et
auxdirectives
ci-dessous
atm
do
connaitre
los
mesures
a
prendre
pour
Łviter
tout
danger.
I
OM-171
892
Page
5


LES:RAYONS
DE
L~ARC
peuvent
~
voquer
des.br~1ures
dans
~es.yeux
et
sur.Iapeau~
.:
Le
rayonnement
de
larc
du
procedØ
do
soudago
genØre
des
rayons
visibles
et
invisibles
intenses
(ultraviolets
et
infrarouges)
susceptiblos
de
provoquer
des
brUlures
dans
les
yeux
et
sur
Ia
peau.
Des
Øtincelles
sont
pro;etees
pendant
le
soudage.
Porter
un
casciue
de
soudage
muni
dun
Ocran
de
filtre
appropriØ
pour
protegervotre
visage
et
vos
yeux
pendant
le
soudage
ou
pour
regar
der
(voir
ANSI
Z49.1
et
Z87.1
ØnumØrØ
dans
es
normes
de
sØcurite).
Porter
des
protections
approuvOs
pour
les
oreilles
si
le
niveau
sondre
est
trop
Ølev.
Utiliser
des
Øcrans
ou
des
barriŁros
pour
protoger
des
tiers
do
Øclair
et
de
Ieblouissement;
demander
aux
autres
personnes
do
ne
pas
re
garder
larc.
Porter
des
vOtements
de
protection
constituØ
dans
une
matiŁre
dura
ble,
resistant
au
feu
(cuir
ou
lame)
et
une
protection
des
pieds.
m
~
LE
SOUDAGE
peut.
prvoquer
~
:IflC0fldle
Ouune
explosion
:
Le
soudage
effectuO
sur
des
conteneurs
fermØs
tels
que
des
reservoirs,
tambours
ou
des
conduites
peut
provoquer
leur
Øclatement.
Des
Øtincelles
peuvent
Œtre
projetees
de
larc
de
soudure.
La
projection
dØtincel
es,
des
piŁces
chaudes
et
des
equipements
chauds
pout
provoquor
des
incendies
et
des
brOlures.
Le
contact
accidentel
de
electrode
avec
des
objets
metalliques
pout
provoquer
des
Øtincelles,
une
explosion,
un
surchauffement
ou
un
incendie.
Avant
de
commencer
to
soudage,
verifier
et
sassurer
que
lendroit
no
presente
pas
de
danger.
Se
proteger
et
dautres
porsonnes
de
Ia
projection
dØtincelles
et
do
metal
chaud.
Ne
pas
souder
dans
un
endroit
l
oO
des
Øtincefles
peuvent
tomber
sur
des
substances
inflammables.
Deplacertoutes
les
substances
inflammables
a
une
distance
de
10,7
m
de
larc
de
soudage.
En
cas
dimpossibilite
les
recouvrirsoigneuse
mont
avec
des
protections
homologues.
Des
etincelles
et
des
matØriaux
chauds
du
soudage
pouvent
facile-
mont
passer
clans
dautres
zones
en
traversant
de
petites
fissures
et
des
ouvertures.
Surveillertout
dØclenchementdincendie
ettenir
un
extincteur
a
proxi
mite.
Le
soudage
effectuØ
sur
un
plafond,
plancher,
paroi
ou
separation
pout
dØclenchor
un
incendie
de
lautre
cOtØ.
Ne
pas
effectuer
le
soudage
sur
des
conteneurs
fermØs
tels
quo
des
reservoirs,
tambours,
ou
conduites,
a
moms
quils
naient
ØtØ
prØpa
rØs
correcternent
conformØment
a
AWS
F4.1
(voir
les
normes
do
sØcuritØ).
Brancher
le
cable
sur
Ia
piŁce
le
plus
prŁs
possible
de
Ia
zone
do
sou
dage
pour
Øviter
le
transport
du
courant
sur
une
longue
distance
par
des
chemins
inconnus
Øventuols
en
provoquant
des
risques
dØlec
trocution
ot
dincendie.
Ne
pas
utiliser le
posto
de
soudage
pour
dØgeler
des
conduites
go
lees.
En
cas
de
non
utilisation,
enlever
Ia
baguette
dØloctrode
du
porte
electrode
ou
couper
le
fil
a
Ia
pointe
do
contact.
Porter
des
vCtements
de
protection
dØpourvus
dhuilo
tels
quo
des
gants
en
cuir,
une
chemise
en
matØriau
lourd,
des
pantalons
sans
re
vers,
des
chaussures
hautes
et
un
couvre
chef.
Avant
do
souder,
retirer
toute
substance
combustible
de
vos
poches
telles
quun
allumeur
au
butane
ou
des
allumettes.
DES
PARTICULESVOLANTES
_____
peuvent
blesserlesyeux.
Le
soudage,
lØcaillement,
le
passage
do
Ia
piŁce
a
Ia
brosse
en
f
ii
de
for,
et
le
meulage
genŁrent
des
Øtincelles
et
des
particulos
metalliques
volan
tes.
Pendant
Ia
periode
do
refroidissement
des
soudures,
elles
risquent
do
projeter
du
laitier.
Porter
des
lunettes
do
securitØ
avec
Øcrans
latØraux
ou un
Øcran
facial.
~LES..:ACCUMULATiONS
DE
GAZ
ris
~quŁnt
de
provcquer
des
blessures
0U
I
mŒmelamort
L.~
Fermer
alimentation
du
gaz
protecleur
en
cas
de
non
utilisation.
Veillertoujours
a
bien
aØrerles
espaces
confines
ou
se
servirdun
respi
rateur
dadduction
dair
homologuØ.
I:~DEs
PI~CES.CHAUDES:peuVent
pro
voquerdes
br
ures
graves.
.j
No
pas
toucher
des
parties
chaudes
a
mains
nues
PrØvoir
une
pØriode
de
refroidissement
avant
dutiliser
le
pistolet
ou
Ia
torche.
LES
CHAMPS
MAGNETIQUES
peuy~nt
stimulate
ard!aque4~
Porteursdestimulateurcardiaque,
restezdistance.
Les
porteurs
dun
stimulateur
cardiaque
doivent
dabord
consulter
leurmØdecin
avant
de
sapprocher
des
operations
de
soudage
a
larc,
do
gougeage
ou
de
soudage
par
points.
I.E
BRUIT
peut
affecter
Iouie~
Le
bruit
des
processus
et
des
Oqulpements
pout
affecter
IouIe.
Porter
des
protections
approuvØs
pour
les
oreilles
si
le
niveau
sondre
est
trop
ØlevO.
r>~
~I
SI
desBOUTEILLES
sont
endornr~ta.i.
lf~~~-
gees,
Łftes
ourrontexploser.
~
~
Des
bouteilles
de
gaz
protecteur
contiennent
du
gaz
~
sous
haute
prossion.
Si
une
bouteille
est
endomma
_____________
gee,
elle
pout
exploser.
Du
fait
quo
les
bouteilles
de
gaz
font
normalement
partie
du
procedO
de
soudage,
los
manipuler
avec
precaution.
Proteger
los
bouteilles
do
gaz
comprime
dune
chaleur
excessive,
dos
chocs
mecaniques,
du
laitier,
des
flammes
ouvortos,
dos
Øtin
cellos
et
des
arcs.
Placer
los
bouteilles
dobout
en
los
fixant
dans
un
support
station
naire
ou
dans
un
porte-boutoilles
pour
los
empOchor
do
tomber
ou
do
se
renvorser.
Tenir
los
bouteilles
eloignees
des
circuits
do
soudage
ou
autres
cir
cuits
electriques.
No
jamais
placer
une
torche
do
soudage
sur
une
bouteille
a
gaz.
Une
electrode
do
soudago
no
dolt
jamais
entrer
en
contact
avec
une
bouteille.
No
jamais
souder
uno
bouteille
pressurisee
risque
dexplosion.
Utiliser
seuloment
des
bouteilles
do
gaz
protecteur,
regulateurs,
tuyaux
et
raccords
convenables
pour
cette
application
specifique;
es
maintenir
ainsi
que
los
ØlØments
associØs
en
bon
Øtat.
No
pas
tenir
Ia
tŒte
en
face
do
Ia
sortie
en
ouvrant
Ia
soupape
do
Ia
bouteillo.
Maintenir
10
chapeau
do
protection
sur
Ia
soupape,
sauf
en
cas
dutilisation
ou
do
branchement
do
Ia
bouteille.
Lire
et
suivre
los
instructions
concemant
les
bouteillos
do
gaz
corn-
prime,
los
equipements
associØs
et
los
publications
P-i
CGA
Ønu
merees
dans
les
normes
do
securite.
OM-171
892
Page
6

La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
Miller KH341356 Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire
- Ce manuel convient également à
dans d''autres langues
- English: Miller KH341356 Owner's manual
Documents connexes
-
Miller LA004576 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller KH577834 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller KF909888 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller PD 22P12 POWCON Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller XMT 304 CC AND CC/CV CE (460 V) Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller INVISION 456P (575 VOLT) Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller TOUCH SENSOR Manuel utilisateur
-
Miller KJ073032 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller SGS 30A CE POWCON Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller 120 Le manuel du propriétaire































































