Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur
Ce manuel convient également à

I -MANUALE DI ISTRUZIONI PER SALDATRICE AD ARCO pag. 2
GB -INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR ARC WELDING MACHINE page 10
D -BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG FÜR LICHTBOGENSCHWEISSMASCHINEN Seite 18
E -MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIONES PARA SOLDADORAS DE ARCO pag. 27
F -MANUEL D’INSTRUCTIONS POUR POSTES A SOUDER A L’ARC page 36
P -MANUAL DE INSTRUÇÕES PARA MÁQUINA DE SOLDAR A ARCO pag. 45
SF -KÄYTTÖOPAS KAARIHITSAUSLAITTEELLE sivu. 53
DK -INSTRUKTIONSMANUAL FOR SVEJSEAPPARAT TIL BUESVEJSNING side. 61
NL -GEBRUIKSAANWIJZING VOOR BOOGLASMACHINE pag. 69
S -INSTRUKTIONSMANUAL FÖR BÅGSVETS sid. 77
GR -ODHGOS CRHSEWS GIA SUSKEUHV TOXOEIDOUV" SUGKOVLLHSH" sel. 85
Parti di ricambio e schema elettrico
Spare parts and electrical schematic
Ersatzteile und Schaltplan
Pièces détachées et schéma électrique
Partes de repuesto y esquema eléctrico
Partes sobressalentes e esquema eléctrico
Varaosat ja sähkökaavio
Reservedele og elskema
Reserveonderdelen en elektrisch schema
Reservdelar och elschema
Antallaktikav kai hlektrikov scediav-
gramma
Pagg. Seiten
sel.: 95 ÷ 105
29/02/2016
3.300.271/G

2
IMPORTANTE: PRIMA DELLA MESSA IN OPERA DEL-
L'APPARECCHIO LEGGERE IL CONTENUTO DI QUESTO
MANUALE E CONSERVARLO, PER TUTTA LA VITA OPE-
RATIVA, IN UN LUOGO NOTO AGLI INTERESSATI.
QUESTO APPARECCHIO DEVE ESSERE UTILIZZATO
ESCLUSIVAMENTE PER OPERAZIONI DI SALDATURA.
1 PRECAUZIONI DI SICUREZZA
LA SALDATURA ED IL TAGLIO AD ARCO
POSSONO ESSERE NOCIVI PER VOI E
PER GLI ALTRI, pertanto l'utilizzatore deve
essere istruito contro i rischi, di seguito riassunti, derivanti
dalle operazioni di saldatura. Per informazioni più dettaglia-
te richiedere il manuale cod.3.300758
RUMORE
Questo apparecchio non produce di per se rumo-
ri eccedenti gli 80dB. Il procedimento di taglio
plasma/saldatura può produrre livelli di rumore
superiori a tale limite; pertanto, gli utilizzatori dovranno
mettere in atto le precauzioni previste dalla legge.
CAMPI ELETTROMAGNETICI- Possono essere dannosi.
· La corrente elettrica che attraversa qual-
siasi conduttore produce dei campi elettro-
magnetici (EMF). La corrente di saldatura o
di taglio genera campi elettromagnetici
attorno ai cavi e ai generatori.
· I campi magnetici derivanti da correnti elevate posso-
no incidere sul funzionamento di pacemaker. I portatori
di apparecchiature elettroniche vitali (pacemaker) devo-
no consultare il medico prima di avvicinarsi alle ope-
razioni di saldatura ad arco, di taglio, scriccatura o di
saldatura a punti.
· L’ esposizione ai campi elettromagnetici della saldatura o
del taglio potrebbe avere effetti sconosciuti sulla salute.
Ogni operatore, per ridurre i rischi derivanti dall’ esposi-
zione ai campi elettromagnetici, deve attenersi alle
seguenti procedure:
- Fare in modo che il cavo di massa e della pinza
portaelettrodo o della torcia rimangano affiancati. Se
possibile, fissarli assieme con del nastro.
- Non avvolgere i cavi di massa e della pinza porta
elettrodo o della torcia attorno al corpo.
- Non stare mai tra il cavo di massa e quello della
pinza portaelettrodo o della torcia. Se il cavo di
massa si trova sulla destra dell’operatore anche
quello della pinza portaelettrodo o della torcia deve
stare da quella parte.
- Collegare il cavo di massa al pezzo in lavorazione
più vicino possibile alla zona di saldatura o di taglio.
- Non lavorare vicino al generatore.
ESPLOSIONI
· Non saldare in prossimità di recipienti a pressione
o in presenza di polveri, gas o vapori esplosivi.
· Maneggiare con cura le bombole ed i regolatori
di pressione utilizzati nelle operazioni di saldatura.
COMPATIBILITÀ ELETTROMAGNETICA
Questo apparecchio è costruito in conformità alle indica-
zioni contenute nella norma IEC 60974-10(Cl. A) e deve
essere usato solo a scopo professionale in un
ambiente industriale. Vi possono essere, infatti,
potenziali difficoltà nell'assicurare la compatibilità
elettromagnetica in un ambiente diverso da quello
industriale.
SMALTIMENTO APPARECCHIATURE ELETTRI-
CHE ED ELETTRONICHE
Non smaltire le apparecchiature elettriche assie-
me ai rifiuti normali!
In ottemperanza alla Direttiva Europea 2002/96/CE sui
rifiuti da apparecchiature elettriche ed elettroniche e rela-
tiva attuazione nell'ambito della legislazione nazionale, le
apparecchiature elettriche giunte a fine vita devono esse-
re raccolte separatamente e conferite ad un impianto di
riciclo ecocompatibile. In qualità di proprietario delle appa-
recchiature dovrà informarsi presso il nostro rappresen-
tante in loco sui sistemi di raccolta approvati. Dando appli-
cazione a questa Direttiva Europea migliorerà la situazione
ambientale e la salute umana!
IN CASO DI CATTIVO FUNZIONAMENTO RICHIEDETE
L’ASSISTENZA DI PERSONALE QUALIFICATO.
1.1 TARGA DELLE AVVERTENZE
Il testo numerato seguente corrisponde alle caselle
numerate della targa.
B. I rullini trainafilo possono ferire le mani.
C. Il filo di saldatura ed il gruppo trainafilo sono sotto
tensione durante la saldatura. Tenere mani eoggetti
metallici a distanza.
1. Le scosse elettriche provocate dall’elettrodo di sal-
datura o dal cavo possono essere letali. Proteggersi
adeguatamente dal pericolo di scosse elettriche.
MANUALE DI ISTRUZIONI PER SALDATRICI AD ARCO

1.1 Indossare guanti isolanti. Non toccare l’elettrodo a
mani nude. Non indossare guanti umidi o danneggiati.
1.2 Assicurarsi di essere isolati dal pezzo da saldare e dal
suolo
1.3 Scollegare la spina del cavo di alimentazione prima di
lavorare sulla macchina.
2. Inalare le esalazioni prodotte dalla saldatura può
essere nocivo alla salute.
2.1 Tenere la testa lontana dalle esalazioni.
2.2 Utilizzare un impianto di ventilazione forzata o di sca-
rico locale per eliminare le esalazioni.
2.3 Utilizzare una ventola di aspirazione per eliminare le
esalazioni.
3. Le scintille provocate dalla saldatura possono causa-
re esplosioni od incendi.
3.1 Tenere i materiali infiammabili lontano dall’area di sal-
datura.
3.2 Le scintille provocate dalla saldatura possono causa-
re incendi Tenere un estintore nelle immediate vici-
nanze e far sì che una persona resti pronta ad utiliz-
zarlo.
3.3 Non saldare mai contenitori chiusi.
4. I raggi dell’arco possono bruciare gli occhi e ustiona-
re la pelle.
4.1 Indossare elmetto e occhiali di sicurezza. Utilizzare
adeguate protezioni per le orecchie e camici con il
colletto abbottonato. Utilizzare maschere a casco
con filtri della corretta gradazione. Indossare una pro-
tezione completa per il corpo.
5. Leggere le istruzioni prima di utilizzare la macchina
od eseguire qualsiasi operazione su di essa.
6. Non rimuovere né coprire le etichette di avvertenza
2 DESCRIZIONI GENERALI
2.1 SPECIFICHE
Questa saldatrice è un generatore di corrente continua
costante realizzata con tecnologia INVERTER, progettata
per saldare gli elettrodi rivestiti (con esclusione del tipo cel-
lulosico) e con procedimento TIG con accensione a contat-
to e con alta frequenza.
NON DEVE ESSERE USATA PER SGELARE I TUBI.
2.2 SPIEGAZIONE DEI DATI TECNICI RIPORTATI
SULLA TARGA DI MACCHINA.
L’apparecchio è costruito secondo le seguenti norme:
IEC 60974.1 - IEC 60974.3 - IEC 60974.10 Cl. A -
IEC 61000-3-11 - IEC 61000-3-12 (vedi nota 2).
N°. Numero di matricola da citare sempre per qual-
siasi richiesta relativa alla saldatrice.
Convertitore statico di frequenza trifase trasfor-
matore-raddrizzatore.
Caratteristica discendente.
MMA Adatto per saldatura con elettrodi rivestiti.
TIG. Adatto per saldatura TIG.
U0. Tensione a vuoto secondaria
X. Fattore di servizio percentuale. % di 10 minuti in cui
la saldatrice può lavorare ad una determinata cor-
rente senza causare surriscaldamenti.
I2. Corrente di saldatura
U2. Tensione secondaria con corrente I2
U1. Tensione nominale di alimentazione
La macchina è provvista di selezione automatica
della tensione di alimentazione.
3~ 50/60Hz Alimentazione trifase 50 oppure 60 Hz
l1 max. E’ il massimo valore della corrente assorbita.
3
l1 eff. E’ il massimo valore della corrente effettiva assorbi-
ta considerando il fattore di servizio.
IP23S Grado di protezione della carcassa.
Grado 3 come seconda cifra significa che
questo apparecchio può essere immagazzinato,
ma non impiegato all’esterno durante le precipi-
tazioni, se non in condizione protetta.
Idoneità ad ambienti con rischio accresciuto.
NOTE:
1- L’apparecchio è inoltre stato progettato per lavorare in
ambienti con grado di inquinamento 3. (Vedi IEC 60664).
2- Questa attrezzatura è conforme alla norma IEC
61000-3-12 a condizione che l’impedenza massima
ZMAX ammessa dell’impianto sia inferiore o uguale a
0,117(Art. 362) - 0,137 (Art. 360) al punto di interfaccia fra
l’impianto dell’utilizzatore e quello pubblico. E’ responsa-
bilità dell’’installatore o dell’utilizzatore dell’attrezzatura
garantire, consultando eventualmente l’operatore della
rete di distribuzione, che l’attrezzatura sia collegata a
un’alimentazione con impedenza massima di sistema
ammessa ZMAX inferiore o uguale a 0,117(Art. 362) -
0,137 (Art. 360).
2.3 DESCRIZIONE DELLE PROTEZIONI
2.3.1 Protezione tremica
Questo apparecchio è protetto da una sonda di temperatu-
ra la quale, se si superano le temperature ammesse, impe-
disce il funzionamento della macchina. In queste condizioni
il ventilatore continua a funzionare ed il led M si accende.
2.3.2 - Protezione di blocco.
Questa saldatrice è provvista di diverse protezioni che fer-
mano la macchina prima che subisca danni.
La saldatrice può funzionare all'interno delle seguenti
gamme di tensione:
Per tensione nominale 208/220/230V da 175 a 270V
Per tensione nominale 400/440V da 340 a 490V
Attenzione: se la tensione di alimentazione non è com-
presa tra i valori sopracitati non si accende nessun led
e il ventilatore è alimentato.
Se, Alla accensione della macchina, il collegamento delle
fasi non è corretto sul display P compaiono 3 punti lumino-
si (accensione fissa).
Se, a macchina accesa, la tensione è scesa sotto i 175 V
(U1 = 230 V) o 340 V (U1 = 400 V) sul display P compare la
sigla E3.
Se, a macchina, accesa, la tensione è salita sopra i 275 V
(U1 = 230 V) o 490 V (U1 = 400 V) sul display P compare la
sigla E4.
In questi casi spegnere la macchina, ripristinare la giusta
tensione e riaccenderla. Se l'inconveniente è stato risolto la
saldatrice ricomincerà a funzionare.
Se, a macchina accesa, sul display P compare la scritta E2
oppure E1 controllare la tensione di alimentazione della
macchina, se questa è corretta la macchina necessita di un
intervento tecnico.
Se viene rilevato un basso livello di acqua per il gruppo
di raffreddamento comparirà la sigla H2O lampeggian-
te sul display P.
3 INSTALLAZIONE
Controllare che la tensione di alimentazione corrisponda alla
tensione indicata sulla targa dei dati tecnici della saldatrice.
S

4
Collegare una spina di portata adeguata al cavo di alimenta-
zione assicurandosi che il conduttore giallo/verde sia colle-
gato allo spinotto di terra.
La portata dell'interruttore magnetotermico o dei fusibili, in
serie alla alimentazione, deve essere uguale alla corrente I1
assorbita dalla macchina.
ATTENZIONE!: Le prolunghe fino a 30m devono essere
almeno di sezione 2,5mm
2
.
3.1. MESSA IN OPERA
L'installazione della macchina deve essere fatta da persona-
le esperto. Tutti i collegamenti debbono essere eseguiti in
conformità alle norme vigenti e nel pieno rispetto della legge
antinfortunistica.
3.2 DESCRIZIONE DELL'APPARECCHIO
AL - Selettore di procedimento
Tramite questo pulsante avviene la scelta del procedi-
mento di saldatura (Elettrodo o Tig). Ad ogni pressione si
ottiene una selezione. L'accensione dei led in corrisponden-
za ai simboli visualizzano la Vostra scelta.
B - Led saldatura ad elettrodo (MMA)
Questa macchina può fondere tutti i tipi di elettrodi rivestiti
escluso il tipo cellulosico. Con questo procedimento la cor-
rente viene regolata tramite la manopola O ed è possibile
regolare la funzione di "arc force" (Led AN) e di "hot start"
(Led AM).
AH - Led saldatura Tig in continuo
AI - Led saldatura Tig con pulsazione
La frequenza di pulsazione è regolabile da 0,16 a 500Hz (led
T), la corrente di picco e la corrente di base sono attivabili
rispettivamente con i led X e W, e sono regolabili tramite la
manopola O.
Da 0,16 fino a 1,1 Hz di frequenza di pulsazione il display P
visualizza alternativamente la corrente di picco (principale) e
la corrente di base. I led X e W si accendono alternativa-
mente; oltre 1,1 Hz il display P visualizza la media delle due
correnti e i led X e W restano entrambi accesi.
A - Selettore di modo
Ad ogni pressione si effettua una selezione che è visua-
lizzata dall'accensione del led C o D insieme ad altri led che
visualizzano il modo di saldatura.
AH
AI
G
A
AL
Y
Z
AA
AA
AB
W
V
Y
AB
UTSAOANAMRQ
B
CEF DHILMP AP O X N
Z
Fig. 1

5
C - Led Accensione dell'arco senza alta frequenza.
Per accendere l'arco premere il pulsante torcia, toccare con
l'elettrodo di tungsteno il pezzo da saldare e rialzarlo. Il movi-
mento deve essere deciso e rapido.
D - Led accensione dell'arco con alta frequenza
Per accendere l'arco premere il pulsante torcia, una scintilla
pilota di alta tensione/frequenza accenderà l'arco.
E - Led saldatura TIG 2 tempi (manuale)
Premendo il pulsante della torcia la corrente inizia ad aumen-
tare ed impiega un tempo corrispondente allo "slope up", pre-
ventivamente regolato, per raggiungere il valore regolato con
manopola O. Quando si lascia il pulsante la corrente inizia a
diminuire ed impiega un tempo corrispondente allo "slope
down", preventivamente regolato, per ritornare a zero.
In questa posizione si può collegare l’accessorio comando a
pedale ART. 193,
F - Led saldatura TIG 4 tempi (automatico).
Questo programma differisce dal precedente perché sia
l'accensione che lo spegnimento vengono comandati pre-
mendo e rilasciando il pulsante della torcia
G - Led saldatura Tig con doppio livello di cor-
rente quattro tempi (automatico).
Prima di accendere l'arco impostare i due livelli di corrente:
Primo livello: premere il tasto R fino ad accendere il led X e
regolare la corrente principale con la manopola O.
Secondo livello: premere il tasto R fino ad accendere il led W
e regolare la corrente con la manopola O.
Dopo l'accensione dell'arco la corrente inizia ad aumentare
ed impiega un tempo corrispondente allo "slope up" (led S
acceso), preventivamente regolato, per raggiungere il valore
regolato con manopola O. Il led X si accende e il display P
la visualizza.
Se durante la saldatura vi è la necessità di diminuire la cor-
rente senza spegnere l'arco (per esempio cambio del mate-
riale d'apporto, cambio di posizione di lavoro, passaggio da
una posizione orizzontale ad una verticale ecc.…) premere e
rilasciare immediatamente il pulsante torcia, la corrente si
porta al secondo valore selezionato, il led W si accende e X
si spegne.
Per tornare alla precedente corrente principale ripetere l'a-
zione di pressione e di rilascio del pulsante torcia, il led X si
accende mentre il led W si spegne. In qualsiasi momento si
voglia interrompere la saldatura premere il pulsante torcia
per un tempo maggiore di 0,7 secondi poi rilasciarlo, la
corrente comincia a scendere fino al valore di zero nel tempo
di "slope down", preventivamente stabilito (led U acceso).
Durante la fase di "slope down", se si preme e si rilascia
immediatamente il pulsante della torcia, si ritorna in "slope
up" se questo è regolato ad un valore maggiore di zero,
oppure alla corrente minore tra i valori regolati.
N.B. il termine "PREMERE E RILASCIARE IMMEDIATAMEN-
TE" fa riferimento ad un tempo massimo di 0,5 sec.
H - Led saldatura Tig con tre livelli di corrente
quattro tempi (automatico).
Per impostare le tre correnti di saldatura agire come segue:
Premere il selettore R fino ad accendere il led X quindi rego-
lare il valore della massima corrente con la manopola O.
Premere il selettore R fino ad accendere il led W quindi rego-
lare il valore della corrente intermedia con la manopola O.
Premere il selettore R fino ad accendere il led AP quindi
regolare il valore della corrente di accensione con la mano-
pola O.
La logica di funzionamento è quella descritta precedente-
mente per la saldatura con doppio livello di corrente (led G).
I - Led programma speciale
Per accendere l'arco premere il pulsante della torcia e tenen-
dolo premuto, la corrente inizia ad aumentare con un incre-
mento fisso. Se si rilascia il pulsante la corrente sale imme-
diatamente al valore di saldatura (led X). Per terminare la sal-
datura premere il pulsante torcia e mantenendolo premuto la
corrente inizia a diminuire con un decremento fisso. Se si
rilascia il pulsante la corrente si azzera istantaneamente.
L - Led puntatura (Manuale).
Dopo avere scelto la corrente di saldatura (led X) e il tempo
di puntatura (led T) tramite il selettore R, impostarne i valori
tramite la manopola O.
Si esegue questo modo di saldatura solo se viene selezio-
nata la accensione con alta frequenza (led D acceso). In que-
sta modo di saldatura l'operatore preme il pulsante della tor-
cia, si accende l'arco, e dopo il tempo di puntatura regolato,
l'arco si spegne automaticamente. Per eseguire il punto suc-
cessivo è necessario rilasciare il pulsante torcia e poi ripre-
merlo.
M - LED - PROTEZIONE TERMICA
Si accende quando l'operatore supera il fattore di ser-
vizio o di intermittenza percentuale ammesso per la macchi-
na e blocca contemporaneamente l'erogazione di corrente.
N.B. In questa condizione il ventilatore continua a raf-
freddare il generatore.
O - Manopola
Normalmente regola la corrente di saldatura.
Inoltre se si seleziona una funzione con il selettore R
questa manopola ne regola la grandezza.
P - Display
Visualizza la corrente di saldatura e le imposta-
zioni selezionate con il pulsante R e regolate con
la manopola O. Nelle procedure di blocco (vedi 2.3.2) della
macchina visualizza.:
-Tre punti lampeggianti o accesi di continuo
-Le sigle E1 E2 E3 E4
-La sigla H20
N - Display
Normalmente visualizza la tensione d'arco in
relazione al processo di saldatura in atto.
Nell'impostazione del funzionamento del gruppo di raffred-
damento ne visualizza lo stato.
Q - SELETTORE
Seleziona e memorizza i programmi.
La saldatrice ha la possibilità di memorizzare nove programmi
di saldatura P01…..P09 e di poterli richiamare tramite questo
pulsante. Inoltre è disponibile un programma lavoro PL .
Selezione
Premendo brevemente questo pulsante viene visualizzato
sul display P il numero del programma successivo a quello
in cui si sta lavorando. Se questo non è stato memorizzato

6
la scritta sarà lampeggiante, contrariamente sarà fissa.
Memorizzazione
Una volta selezionato il programma, premendo per un
tempo maggiore di 3 secondi, si memorizzano i dati. A con-
ferma di questo, il numero del programma, visualizzato sul
display P, terminerà di lampeggiare
R - SELETTORE
Premendo questo pulsante si illuminano in succes-
sione i led:
Attenzione si illumineranno solo i led che si riferiscono al
modo di saldatura scelto; es. in saldatura TIG continuo non si
illuminerà il led T che rappresenta la frequenza di pulsazione.
Ogni led indica il parametro che può essere regolato tramite
la manopola O durante il tempo di accensione del led stes-
so. Dopo 5 secondi dall'ultima variazione il led interessato si
spegne e viene indicata la corrente di saldatura principale e
si accende il corrispondente led X.
AO - Led Pre-gas
Regolazione 0,05-2,5 secondi.
Tempo di uscita del gas prima del-
l'inizio della saldatura.
AP - Led corrente di inizio salda-
tura.
E' una percentuale della corrente di
saldatura (led X).
S - Led Slope up.
E' il tempo in cui la corrente rag-
giunge, partendo dal minimo, rag-
giunge il valore di corrente imposta-
to. (0-10 sec.)
X - Led Corrente di saldatura-
principale.
W - Led secondo livello di cor-
rente di saldatura o di base.
Questa corrente è sempre una per-
centuale della corrente principale.
T - Led Frequenza di pulsazione
(0,16-500 Hz).
I tempi di picco e di base sono
uguali. Quando viene selezionata la
puntatura (led L) l'accensione di questo led indica che il
display H visualizza il tempo di puntatura che è regolabile
tramite la manopola O da 0,1 a 3 secondi.
U - Led Slope down.
E' il tempo in cui la corrente rag-
giunge il minimo e lo spegnimento
dell'arco.(0-10 sec.)
V - Led Post gas.
Regola il tempo di uscita del gas al
termine della saldatura. (0-30 sec.)
AM - Led Hot-Sart
Si può selezionare tramite il pulsante R solo se è seleziona-
to il procedimento MMA (led B).
L'accensione di questo led indica che il display P visualizza
il tempo, espresso in secondi, in cui la saldatrice eroga una
sovracorrente per migliorare l'accensione dell'elettrodo. La
regolazione avviene tramite la manopola O.
AF
AE
AD
AC
AC
AD
AG
Fig. 2

7
AN - Led Arc-Force
Si può selezionare tramite il pulsante R solo se è seleziona-
to il procedimento MMA (led B). E' una percentuale della
corrente di saldatura. Il display P ne visualizza il valore e la
manopola O lo regola. In pratica questa sovracorrente favo-
risce il trasferimento delle gocce di metallo fuso.
Y - Connettore 10 poli
A questo connettore vanno collegati i coman-
di remoti descritti nel paragrafo 4.
E' disponibile tra i pin 3 e 6 un contatto pulito
che segnala la accensione dell'arco (5A
230V).
Z - RACCORDO 1/4 GAS)
Vi si connette il tubo gas della torcia di salda-
tura TIG.
AA - morsetto di uscita negativo (-)
AB -morsetto di uscita positivo (+)
AC - interruttore
Accende e spegne la macchina
AD - Raccordo ingresso gas
AE - Presa
A cui collegare il gruppo di raffreddamento
Art.1341
Attenzione: Potenza max: 360VA - Ampere: 1,6.
Non collegare utensili quali smerigliatrici o simila-
ri.
AF - Connettore
Connettore a tre poli a cui và collegato il cavetto
del pressostato del gruppo di raffreddamento.
AG - Porta fusibile
3.3. NOTE GENERALI
Prima dell'uso di questa saldatrice leggere attentamente le
norme CEI 26/9 - CENELEC HD 407 e CEI 26.11 - CENE-
LEC HD 433 inoltre verificare l'integrità dell'isolamento dei
cavi, delle pinze porta elettrodi, delle prese e delle spine e
che la sezione e la lunghezza dei cavi di saldatura siano
compatibili con la corrente utilizzata.
3.4. SALDATURA DI ELETTRODI RIVESTITI (MMA)
- Questa saldatrice è idonea alla saldatura di tutti i tipi di elet-
trodi ad eccezione del tipo cellulosico (AWS 6010).
- Assicurarsi che l'interruttore AC sia in posizione 0, quindi
collegare i cavi di saldatura rispettando la polarità richiesta
dal costruttore di elettrodi che andrete ad utilizzare e il mor-
setto del cavo di massa al pezzo nel punto più vicino possi-
bile alla saldatura assicurandosi che vi sia un buon contatto
elettrico.
- Non toccare contemporaneamente la torcia o la pinza
porta elettrodo ed il morsetto di massa.
- Accendere la macchina mediante l'interruttore AC.
- Selezionare, premendo il pulsante A, il procedimento
MMA, led B Acceso.
- Regolare la corrente in base al diametro dell'elettrodo, alla
posizione di saldatura e al tipo di giunto da eseguire.
- Terminata la saldatura spegnere sempre l'apparecchio e
togliere l'elettrodo dalla pinza porta elettrodo.
Se si vogliono regolare le funzioni di Hot-start (led AM) e di
Arc force (led AN) vedere il paragrafo precedente.
3.5. SALDATURA TIG
Questa saldatrice è idonea a saldare con procedimento TIG
l'acciaio inossidabile, il ferro, il rame.
Collegare il connettore del cavo di massa al polo positivo (+)
della saldatrice e il morsetto al pezzo nel punto più vicino
possibile alla saldatura assicurandosi che vi sia un buon
contatto elettrico.
Collegare il connettore di potenza della torcia TIG al polo
negativo (-) della saldatrice.
Collegare il connettore di comando della torcia al connetto-
re Y della saldatrice.
Collegare il raccordo del tubo gas della torcia al raccordo Z
della macchina ed il tubo gas proveniente dal riduttore di
pressione della bombola al raccordo gas AD.
3.5.1 Gruppo di raffreddamento.
Se si utilizza una torcia raffreddata ad acqua utilizzare il
gruppo di raffreddamento.
3.5.1.1 Spiegazione dati tecnici
U1 Tensione nominale di alimentazione
1x230V Alimentazione monofase
50/60 Hz Frequenza
I1max Corrente massima assorbita
Pmax Pressione massima
P (1l/min) Potenza refrigerante misurata a 1L/min
3.5.1.2 Descrizione delle protezioni
- Protezione pressione liquido refrigerante.
Questa protezione è realizzata mediante un pressostato,
inserito nel circuito di mandata del liquido, che comanda un
microinterruttore. Lapressione insufficente è segnalata dalla
sigla H2O lampeggiante sul display N.
- Fusibile (T 2A/250V-Ø 5x20).
Questo fusibile è stato inserito a protezione della pompa.

8
3.5.1.3 Messa in opera
Svitare il tappo BW e riempire il serbatoio (l'apparecchio è
fornito con circa un litro di liquido).
E' importante controllare periodicamente, attraverso l'asola
BX, che il liquido sia mantenuto al livello "max".
Utilizzare, come liquido refrigerante acqua (preferibilmente
del tipo deionizzato) miscelata con alcool in percentuale
definita secondo la tabella seguente:
temperatura acqua/alcool
-0°C fino a -5°C 4L/1L
-5°C fino a -10°C 3,8L/1,2L
NB Se la pompa ruota in assenza del liquido refrigerante è
necessario togliere l'aria dai tubi.
In questo caso spegnere il generatore, riempire il serbatoio,
collegare un tubo al raccordo ( ) e inserire l'altra estremità
del tubo nel serbatoio. Accendere il generatore per circa
10/15 secondi quindi ricollegare i tubi.
Accendere la macchina. Per selezionare il modo di funziona-
mento del gruppo di raffreddamento agire come segue:
1. Selezionare un qualsiasi procedimento TIG.
2. Premere il tasto Q e mantenendolo premuto premere il
tasto R. Mantenerli premuti fino a quando sul display P
compare la sigla H2O.
3. Selezionare il funzionamento tramite la manopola O
tenendo presente che i numeri che compaiono sul
display N hanno questo significato:
1 = Gruppo spento,
2 = Funzionamento in continuo,
3 = Funzionamento in automatico.
Per uscire dalla selezione premere brevemente il tasto Q.
N.B. Per "Funzionamento automatico" si intende che il grup-
po di raffreddamento si mette in moto alla pressione del pul-
sante torcia e smette di funzionare dopo circa 2 minuti dal
rilascio del pulsante torcia.
Attenzione! Se selezionata la saldatura in elettrodo, il raf-
freddamento non è acceso e non è selezionabile. E' norma-
le che alla accensione della macchina il display P visualizzi,
in modo lampeggiante, la sigla H2O.
3.5.1.4 Gruppo di raffreddamento per Art. 360.
Se si utilizza una torcia raffreddata ad acqua utilizzare il
gruppo di raffreddamento.
Per il posizionamento e il trasporto della saldatrice insieme
al gruppo di raffreddamento è necessario il carrello Art 1432.
Dopo avere riempito di liquido refrigerante il serbatoio colle-
gare la spina del cavo rete alla presa AE della saldatrice,
quindi collegare il connettore maschio volante 3 poli al con-
nettore AF.
3.5.1.5 Descrizione del gruppo di raffreddamento per
362 (Fig. 3)
AG- Asola:
Asola per l'ispezione del livello del liquido refrigerante
AH - Rubinetti ad innesto rapido:
A questi rubinetti vanno gollegati i tubi di raffreddamento
della torcia
NB: non debbono essere cortocircuitati.
AI - Tappo.
3.5.2 Accendere la macchina.
Non toccare parti sotto tensione e i morsetti di uscita quan-
do l'apparecchio è alimentato.
Alla prima accensione della macchina selezionare il modo
mediante il pulsante A e i parametri di saldatura mediante il
tasto R e la manopola O come indicato al paragrafo 3.2..
Il flusso di gas inerte deve essere regolato ad un valore (in litri
al minuto) di circa 6 volte il diametro dell'elettrodo.
Se si usano accessori tipo il gas-lens la portata di gas può
essere ridotta a circa 3 volte il diametro dell'elettrodo. Il dia-
metro dell'ugello ceramico deve avere un diametro da 4 a 6
volte il diametro dell'elettrodo.
Normalmente il gas più usato è l'ARGON perché ha un costo
minore rispetto agli altri gas inerti, ma possono essere usate
anche miscele di ARGON con un massimo del 2% IDRO-
GENO per la saldatura dell'acciaio inossidabile e ELIO o
miscele di ARGON-ELIO per la saldatura del rame. Queste
miscele aumentano il calore il calore dell'arco in saldatura
ma sono molto più costose. Se si usa gas ELIO aumentare
litri al minuto fino a 10 volte il diametro dell'elettrodo (Es. dia-
metro 1,6 x10= 16 lt/min di Elio).
Usare vetri di protezione D.I.N. 10 fino a 75A e D.I.N. 11 da
75A in poi.
3.6. MEMORIZZAZIONE
E' possibile memorizzare solo dopo avere saldato.
Il pulsante Q, premuto brevemente, effettua una scelta;
premuto per un tempo maggiore di 3 secondi, effettua
una memorizzazione.
Ad ogni accensione, la macchina presenta sempre l'ulti-
ma condizione utilizzata in saldatura.
3.6.1. Memorizzare i dati del programma PL
Utilizzando la macchina per la prima volta
Alla accensione della macchina il display visualizza la sigla
PL questa, dopo 5, scompare e viene visualizzata una cor-
rente di lavoro. Seguire le indicazioni dei paragrafi 3.2 e 3.5
quindi, per memorizzare i dati nel programma P01, proce-
dere nel seguente modo:
· Premere brevemente il pulsante Q (mem+mem-) compa-
rirà la scritta P01 lampeggiante.
· Premere il pulsante Q per un tempo maggiore di 3 secondi
fino a che la sigla P01 smetta di lampeggiare, a questo
punto la memorizzazione è avvenuta.
· Ovviamente se invece di memorizzare nel programma P01
si vuole memorizzare in un programma diverso si premerà il
pulsante Q in maniera breve tante volte quante necessarie
per visualizzare il programma desiderato. Alla riaccensione
della macchina viene visualizzato P01.
AH
AI
AG
Fig. 3

9
IL PULSANTE Q PREMUTO BREVEMENTE EFFETTUA
UNA SCELTA, PREMUTO PER UN TEMPO MAGGIORE
DI 3 SECONDI EFFETTUA UNA MEMORIZZAZIONE.
3.6.2. Memorizzare da un programma libero
L'operatore può modificare e memorizzare un programma
scelto procedendo nel seguente modo:
· Premere il pulsante Q in modo breve e scegliere il numero
di programma desiderato.
I programmi liberi hanno la sigla lampeggiante.
Premere il pulsante AL e scegliere il procedimento di salda-
tura e con il pulsante A scegliere il modo (paragrafo 3.1).
· Girare la manopola O ed impostare la corrente di saldatura.
Se è stato scelto il procedimento TIG, attivare il led V (post
gas) tramite il pulsante R e regolare tramite la manopola O il
valore desiderato (paragrafo 3.1.)
Se dopo queste regolazioni, necessarie per saldare, si
vogliono regolare i tempi di "slope" o altro agire come
descritto al paragrafo 3.1.
Eseguire una saldatura anche breve e decidere dove
memorizzare
Per memorizzare nel programma scelto precedentemente,
premere il pulsante Q per più di 3 secondi fino a che il nume-
ro smette di lampeggiare.
Per memorizzare in un programma diverso, fare la scelta
premendo brevemente il pulsante Q quindi premere il pul-
sante Q per più di 3 secondi.
3.6.3 Memorizzare da un programma memorizzato
Partendo da un programma già memorizzato l'operatore
può modificare i dati in memoria per aggiornare il program-
ma stesso o per trovare nuovi parametri da memorizzare in
un altro programma.
3.6.3.1 Aggiornare
· Dopo avere acceso la macchina selezionare i parametri da
modificare e modificarli.
· Eseguire una saldatura anche breve.
· Premere per un tempo maggiore di 3 secondi il tasto Q fino
alla conferma della memorizzazione (sigla del programma da
lampeggiante a continua).
3.6.3.2 Memorizzare in un nuovo programma
· Dopo avere acceso la macchina selezionare i parametri da
modificare e modificarli.
· Eseguire una saldatura anche breve.
· Premere brevemente il selettore Q fino alla visualizzazione
del programma da Voi desiderato.
· Premere di continuo il tasto Q fino alla conferma della
memorizzazione ( sigla del programma da lampeggiante a
continua).
4 COMANDI A DISTANZA
Per la regolazione della corrente di saldatura a questa salda-
trice possono essere connessi i seguenti comandi a distanza:
Art.1260 Torcia TIG solo pulsante.(raffreddamento ad aria).
Art.1256 Torcia TIG solo pulsante.(raffreddamento ad acqua).
Art.1262 Torcia TIG UP/DOWN.(raffreddamento ad aria)
Art.1258 Torcia TIG UP/DOWN.(raffreddamento ad acqua)
Art. 193 Comando a pedale (usato in saldatura TIG)
Art 1192+Art 187 (usato in saldatura MMA)
Art. 1180 Connessione per collegare contemporaneamente
la torcia e il comando a pedale. Con questo accessorio l’Art.
193 può essere utilizzato in qualsiasi modo di saldatura TIG.
I comandi che includono un potenziometro regolano la
corrente di saldatura dal minimo fino alla massima cor-
rente impostata con la manopola O.
I comandi con logica UP/DOWN regolano dal minimo al
massimo la corrente di saldatura.
Le regolazioni dei comandi a distanza sono sempre attive nel
programma PL mentre in un programma memorizzato non
lo sono.
5 MANUTENZIONE
Ogni intervento di manutenzione deve essere eseguito da
personale qualificato nel rispetto della norma CEI 26-29
(IEC 60974-4).
5.1 MANUTENZIONE GENERATORE
In caso di manutenzione all'interno dell’apparecchio, assicu-
rarsi che l'interruttore AC sia in posizione "O" e che il cavo
di alimentazione sia scollegato dalla rete.
Periodicamente, inoltre, è necessario pulire l’interno dell’ap-
parecchio
dalla polvere metallica accumulatasi, usando aria
compressa.
5.2 ACCORGIMENTI DA USARE DOPO UN
INTERVENTO DI RIPARAZIONE.
Dopo aver eseguito una riparazione, fare attenzione a
riordinare il cablaggio in modo che vi sia un sicuro isola-
mento tra il lato primario ed il lato secondario della macc-
china. Evitare che i fili possano andare a contatto con
parti in movimento o parti che si riscaldano durante il fun-
zionamento. Rimontare tutte le fascette come sull’appa-
recchio originale in modo da evitare che, se accidental-
mente un conduttore si rompe o si scollega, possa avve-
nire un collegamento tra il primario ed il secondario.
Rimontare inoltre le viti con le rondelle dentellate come
sull’apparecchio originale.

10
IMPORTANT: BEFORE STARTING THE EQUIPMENT,
READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS MANUAL, WHICH MUST
BE STORED IN A PLACE FAMILIAR TO ALL USERS FOR
THE ENTIRE OPERATIVE LIFE-SPAN OF THE MACHINE.
THIS EQUIPMENT MUST BE USED SOLELY FOR WELD-
ING OPERATIONS.
1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WELDING AND ARC CUTTING CAN BE
HARMFUL TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS.
The user must therefore be educated
against the hazards, summarized below, deriving from weld-
ing operations. For more detailed information, order the
manual code 3.300.758
NOISE
This machine does not directly produce noise
exceeding 80dB. The plasma cutting/welding proce-
dure may produce noise levels beyond said limit;
users must therefore implement all precautions required by
law.
ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS - May be dangerous.
· Electric current following through any conduc-
tor causes localized Electric and Magnetic
Fields (EMF). Welding/cutting current creates
EMF fields around cables and power sources.
· The magnetic fields created by high currents
may affect the operation of pacemakers. Wearers of vital
electronic equipment (pacemakers) shall consult their physi-
cian before beginning any arc welding, cutting, gouging or
spot welding operations.
· Exposure to EMF fields in welding/cutting may have other
health effects which are now not known.
· All operators should use the followingprocedures in order to
minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding/cutting cir-
cuit:
- Route the electrode and work cables together - Secure
them with tape when possible.
- Never coil the electrode/torch lead around your body.
- Do not place your body between the electrode/torch
lead and work cables. If the electrode/torch lead cable is
on your right side, the work cable should also be on your
right side.
- Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as
possible to the area being welded/cut.
- Do not work next to welding/cutting power source.
EXPLOSIONS
· Do not weld in the vicinity of containers under pres-
sure, or in the presence of explosive dust, gases or
fumes. · All cylinders and pressure regulators used in
welding operations should be handled with care.
ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY
This machine is manufactured in compliance with the
instructions contained in the standard IEC 60974-10 (CL. A),
and must be used solely for professional purposes in an
industrial environment. There may be potential difficul-
ties in ensuring electromagnetic compatibility in non-
industrial environments.
DISPOSAL OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC
EQUIPMENT
Do not dispose of electrical equipment together
with normal waste!In observance of European
Directive 2002/96/EC on Waste Electrical and Electronic
Equipment and its implementation in accordance with
national law, electrical equipment that has reached the
end of its life must be collected separately and returned
to an environmentally compatible recycling facility. As the
owner of the equipment, you should get information on
approved collection systems from our local representa-
tive. By applying this European Directive you will improve
the environment and human health!
IN CASE OF MALFUNCTIONS, REQUEST ASSISTANCE
FROM QUALIFIED PERSONNEL.
1.1 WARNING LABEL
The following numbered text corresponds to the label
numbered boxes.
B. Drive rolls can injure fingers.
C. Welding wire and drive parts are at welding voltage
during operation — keep hands and metal objects
away.
1 Electric shock from welding electrode or wiring can
kill.
1.1 Wear dry insulating gloves. Do not touch electrode
with bare hand. Do not wear wet or damaged gloves.
1.2 Protect yourself from electric shock by insulating
yourself from work and ground.
1.3 Disconnect input plug or power before working on
machine.
INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR ARC WELDING MACHINE

11
2 Breathing welding fumes can be hazardous to your
health.
2.1 Keep your head out of fumes.
2.2 Use forced ventilation or local exhaust to remove
fumes.
2.3 Use ventilating fan to remove fumes.
3 Welding sparks can cause explosion or fire.
3.1 Keep flammable materials away from welding.
3.2 Welding sparks can cause fires. Have a fire extin-
guisher nearby and have a watchperson ready to use
it.
3.3 Do not weld on drums or any closed containers.
4 Arc rays can burn eyes and injure skin.
4.1 Wear hat and safety glasses. Use ear protection and
button shirt collar. Use welding helmet with correct
shade of filter. Wear complete body protection.
5 Become trained and read the instructions before
working on the machine or welding.
6 Do not remove or paint over (cover) label.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTIONS
2.1 SPECIFICATIONS
This welding machine is a constant current power source
built using INVERTER technology, designed to weld covered
electrodes (not including cellulosic) and for TIG procedures,
with contact starting and high frequency.
IT MUST NOT BE USED TO DEFROST PIPES.
2.2 EXPLANATION OF THE TECHNICAL SPECIFI-
CATIONS LISTED ON THE MACHINE PLATE.
This machine is manufactured according to the following
international standards: IEC 60974.1 - IEC 60974.3 -
IEC 60974.10 CL. A - IEC 61000-3-11 - 61000-3-12 (see
note 2).
N°. Serial number, which must be indicated on any
type of request regarding the welding machine.
Three phase static transformer-rectifier frequency
converter.
Drooping-characteristic.
MMA Suitable for welding with covered electrodes.
TIG Suitable for TIG welding.
U0. Secondary open-circuit voltage
X. Duty cycle percentage. % of 10 minutes during
which the welding machine may run at a certain
current without overheating.
I2. Welding current
U2. Secondary voltage with current I2
U1. Rated supply voltage
The machine has an automatic supply voltage
selector.
3~ 50/60Hz 50- or 60-Hz three-phase power supply
I1 max. This is the maximum value of the absorbed current.
I1 eff. This is the maximum value of the actual current
absorbed, considering the duty cycle.
IP23S Protection rating for the housing.
Grade 3 as the second digit means that this
equipment may be stored, but it is not
suitable for use outdoors in the rain, unless
it is protected.
Suitable for hazardous environments.
S
Note:
1- The machine has also been designed for use in envi-
ronments with a pollution rating of 1. (See IEC 60664).
2- This equipment complies with IEC 61000-3-12 provided
that the maximum permissible system impedance ZMAX
is less than or equal to 0,117(Art. 362) - 0,137 (Art. 360)
at the interface point between the user's supply and the
public system. It is the responsibility of the installer or
user of the equipment to ensure, by consultation with the
distribution network operator if necessary, that the equip-
ment is connected only to a supply with maximum per-
missible system impedance ZMAX less than or equal to
0,117(Art. 362) - 0,137 (Art. 360).
2.3 DESCRIPTION OF PROTECTIVE DEVICES
2.3.1. Thermal protection
This machine is protected by a temperature probe, which
prevents the machine from operating if the allowable tem-
peratures are exceeded. Under these conditions the fan
keeps running and the LED M lights.
2.3.2 - Block protection art. 338
This welding machine is equipped with various safety
devices that stop the machine before it can suffer damage.
The welding machine may operate within the following volt-
age ranges:
For rated voltage 208/220/230V, from 175 to 270V
For rated voltage 400/440V, from 340 to 490V
Caution: if the supply voltage does not fall between the
above values, no LED will light and the fan is powered.
If the phases are not properly connected, 3 light points will
appear (steadily lit) on the display P when the machine is
started.
If, with the machine on, the voltage falls below 175 V (U1 =
230V) or 340 V (U1 = 400V), the display P will show the
abbreviation E3.
If, with the machine on, the voltage rises above 275 V (U1 =
230V) or 490 V (U1 = 400V), the display P shows the abbre-
viation E4.
In this case turn off the machine, restore the proper voltage
and restart. If the problem has been corrected, the welding
machine will begin operating again.
If, with the machine on, the display P shows the message E2
or E1, check the supply voltage of the machine; if it is cor-
rect, the machine requires technical service.
If a low water level is detected for the cooling unit the
abbreviation H2O flashes on the display P.
3 INSTALLATION
Make sure that the supply voltage matches the voltage indi-
cated on the specifications plate of the welding machine.
When mounting a plug, make sure it has an adequate
capacity, and that the yellow/green conductor of the power
supply cable is connected to the earth pin.
The capacity of the overload cutout switch or fuses installed
in series with the power supply must be equivalent to the
absorbed current I1 of the machine.
WARNING! Extension cords of up to 30m must have a
cross-section of at least 2.5 mm2.

12
3.1 START-UP
Only skilled personnel should install the machine. All con-
nections must be carried out according to current regula-
tions, and in full observance of safety laws.
3.2 DESCRIPTION OF THE EQUIPMENT
AL - Process selector switch
This button is used to choose the welding process
(MMA or TIG). The selection changes each time it is pressed.
The LEDs light alongside the various symbols to display your
choice.
B - MMA welding LED
This machine can weld all types of coated electrodes except
cellulosic. With this process the current is adjusted using the
knob O, and it is possible to adjust the "arc force" (LED AN)
and "hot start" function (LED AM).
AH - Continuous TIG welding LED
AI - Pulsed TIG welding LED
The pulse frequency is adjustable from 0.16 to 500Hz (LED
T), the peak current and the base current may be activated
via the LEDs X and W, respectively, and are adjustable using
the knob O.
From a pulse frequency of 0.16 to 1.1 Hz, the display P alter-
nates displaying the peak current (main) and the base cur-
rent. The LEDs X and W light alternately; beyond 1.1 Hz the
display P displays the mean of the two currents and the
LEDs X and W both remain lit.
A - Mode selector switch
The selection changes each time it is pressed, and is
displayed by lighting the LED C or D together with other
LEDs displaying the welding mode.
C - Arc starting without high frequency LED.
To light the arc, press the torch trigger, touch the workpiece
with the tungsten electrode, and lift it again. This move must
be quick and decisive.
D - Arc starting with high frequency LED.
To light the arc, press the torch trigger: a high voltage/fre-
quency pilot spark will light the arc.
AH
AI
G
A
AL
Y
Z
AA
AA
AB
W
V
Y
AB
UTSAOANAMRQ
B
CEF DHILMP AP O X N
Z
Fig. 1

13
E - 2-stage TIG welding LED (manual)
When the torch trigger is pressed, the current begins to
increase over the previously set "slope up" time, until it
reaches the value set by means of the knob O. When the
trigger is released, the current begins to drop over the previ-
ously set "SLOPE DOWN" time, until it returns to zero.
In this position, you may connect the pedal control acces-
sory ART. 193.
F - 4-stage TIG welding LED (automatic)
This program differs from the previous one in that the arc is
both started and shut off by pressing and releasing the torch
trigger.
G - four-stage TIG welding LED with dual cur-
rent level, (automatic).
Set the two current levels before lighting the arc:
First level: press the R key until the LED X lights, and adjust
the main current using the knob O.
Second level: press the R key until the LED W lights, and
adjust the main current using the knob O.
When the torch trigger is pressed, the current begins to
increase over the previously set "slope up" time (led S lit),
until it reaches the value set by means of the knob O. The
LED X lights and appears on the display P.
Should it be necessary to reduce the current during welding,
without shutting of the arc (for instance when changing the
welding material or working position, moving from horizontal
to upright, etc.…), press and immediately release the torch
trigger: the current will switch to the second value selected,
the LED W will light and X will go off.
To return to the previous main current, press and release the
torch trigger once again. The LED X will light, and the LED W
will go off. To stop welding at any time, simply hold down the
torch trigger for more than 0.7 seconds, then release. The
current begins to fall to zero within the previously set "slope
down" time interval (LED U lit).
If you press and immediately release the torch trigger during
the "slope down" phase, you will return to "slope up" if it is set
to greater than zero, or to the lesser current value of those set.
NOTE: The expression "PRESS AND IMMEDIATELY
RELEASE" refers to a maximum time of 0.5 seconds.
H - four-stage TIG welding LED with three lev-
els of current (automatic).
To set the three minimum welding currents, proceed as fol-
lows:
Press the selector switch R until the LED X lights, then adjust
the maximum current value using the knob O.
Press the selector switch R until the LED W lights, then
adjust the intermediate current value using the knob O.
Press the selector switch R until the LED AP lights, then
adjust the starting current value using the knob O.
The operating logic is the same as previously described for
welding with dual current level (LED G).
I - special program LED
To light the arc, press the torch trigger and hold it down; the
current begins to increase at a fixed rate. If the torch trigger
is released, the current immediately rises to the welding
value (LED X). To stop welding, press the torch trigger and
hold it down; the current begins to drop at a fixed rate. The
current immediately returns to zero if the trigger is released.
L - spot-welding LED (Manual).
After selecting the welding current (LED X) and the spot
welding time (LED T) using the selector switch R, set the val-
ues using the knob O.
This welding mode is to be used only if start-up with high fre-
quency is selected (LED D lit). In this welding mode, the
operator presses the torch trigger, the arc lights, and after
the set spot welding time the arc shuts off automatically. To
do the next spot, you must therefore release the torch trig-
ger and press it again.
M - LED - THERMAL PROTECTION
Lights when the operator exceeds the duty cycle or per-
centage intermittence admissible for the machine, and
simultaneously blocks the current output.
NOTE: In this condition the fan continues cooling the
power source.
O - Knob
Normally adjusts the welding current.
Also, if you select a function with the selector switch
R, this knob adjusts its size.
P - Display
Displays the welding current and the settings
selected by means of the push-button R and
adjusted via the knob O.
In the machine blocking procedures (see 2.3.2), it displays:
Three flashing or steadily lit points
The abbreviations E1 E2 E3 E4
The abbreviation H20
N - Display
Normally displays the arc voltage in relation to
the current welding process.
When setting the cooling unit operation, it displays the sta-
tus of the unit.
Q - SELECTOR
Selects and saves programs.
The welding machine can save nine welding pro-
grams P01…..P09, and call them up using this button. A
working program PL is also available.
Selecting
When this push-button is pressed briefly, the display P
shows the next program number after the one being worked
on. If it has not been saved the message will flash, otherwise
it will remain steady.
Saving
Once the program has been selected, hold for more than 3
seconds to save the data. In confirmation, the program num-
ber on the display P will stop flashing
R - SELECTOR
When this button is pressed, the LEDs light in suc-
cession:
Warning: only those LEDs that refer to the chosen welding
mode will light; i.e., in continuous TIG welding the LED T,
representing the pulse frequency, will not light.
Each LED indicates the parameter that may be adjusted by
means of the knob O while the LED itself is lit. Five seconds
after the last variation, the LED involved will shut off; the
main welding current will be displayed, and the correspond-
ing LED X lights.

14
AO - Pre-gas LED
Adjustment 0.05-2.5 seconds. Gas
output time before starting weld-
ing.
AP - Welding start current LED.
Welding start current. This is a per-
centage of the welding current
(LED X).
S - Slope up LED .
This is the time in which the cur-
rent, starting from the minimum,
reaches the set current value. (0-10
sec.)
X - Main welding current LED .
W - Second level of welding or
base current LED.
This current is always a percentage
of the main current.
T - Pulse frequency LED (0.16-
550 Hz).
The peak and base times are
equal.
When spot-welding is selected (LED L) this LED lights to
indicate that the display H displays the spot welding time
that may be adjusted using the knob O from 0.1 to 3 sec-
onds.
U - Slope down LED.
This is the time in which the current
reaches the minimum value and the
arc shuts off. (0-10 sec.)
V - Post gas LED.
Adjusts the time gas flows after
welding ends. (0-30 sec.)
AM - Hot-Start LED
May be selected via the button R only if MMA welding is
selected (LED B).
This LED lights to indicate that the display P displays the
time, expressed in seconds, during which the welding
machine delivers an overcurrent to improve electrode start-
ing. It may be adjusted using the knob O.
AN - Arc-force LED
May be selected via the button R only if MMA welding is
selected (LED B).
It is a percentage of the welding current. The display P dis-
plays its value, and the knob O adjusts it. This overcurrent
essentially aids in the transfer of drops of molten metal.
Y - 10-pin connector
This connector is connected to the remote
controls described in paragraph 4.
A clean contact is available between pins 3
and 6 to signal when the arc is lit (5A 230V).
AF
AE
AD
AC
AC
AD
AG
Fig. 2

15
Z - 1/4 GAS FITTING
This is where the gas hose of the TIG welding
torch is to be connected.
AA - Negative output terminal (-)
AB -Positive output terminal (+)
AC - switch
Turns the machine on and off
AD - gas intake fitting
AE - Socket
To which to connect the cooling unit Art. 1341
Caution: Max. power: 360VA - Amps: 1.6.
Do not connect tools such as polishers or similar.
AF - Connector
Three-pin connector to which to connect the wire
of the cooling unit pressure switch.
AG - Fuse Holder
3.3. GENERAL NOTES
Before using this welding machine, carefully read the stan-
dards CEI 26/9 - CENELEC HD 407 and CEI 26.11 - CEN-
ELEC HD 433. Also make sure the insulation of the cables,
electrode clamps, sockets and plugs are intact, and that the
size and length of the welding cables are compatible with the
current used.
3.4 MMA WELDING (MANUAL METAL ARC)
- This welding machine is suitable for welding all types of
electrodes, with the exception of cellulosic (AWS 6010)*.
- Make sure that the switch AC is in position 0, then connect
the welding cables, observing the polarity required by the
manufacturer of the electrodes you will be using; also con-
nect the clamp of the ground cable to the workpiece, as
close to the weld as possible, making sure that there is good
electrical contact.
- Do NOT touch the torch or electrode clamp simultaneous-
ly with the earth clamp.
- Turn the machine on using the switch AC.
- Select the MMA procedure by pressing the button A:
LED B lit.
- Adjust the current based on the diameter of the electrode,
the welding position and the type of joint to be made.
- Always remember to shut off the machine and remove
the electrode from the clamp after welding.
If you wish to adjust the Hot-start (LED AM) and Arc force
functions (LED AN), see the previous paragraph.
3.5 TIG WELDING
This welding machine is suitable for welding stainless steel,
iron, or copper using the TIG procedure.
Connect the earth cable connector to the positive pole (+) of
the welding machine, and the clamp to the workpiece as
close as possible to the welding point, making sure there is
good electrical contact.
Connect the power connector of the TIG torch to the nega-
tive pole (-) of the welding machine.
Connect the torch connector to the welding machine con-
nector Y.
Connect the torch gas hose fitting to the fitting Z on the
machine, and the gas hose from the cylinder pressure regu-
lator to the gas fitting AD on the rear panel.
3.5.1 Cooling unit
If using a water-cooled torch, use the cooling unit.
3.5.1.1 Explanation of technical specifications
U1 Rated supply voltage
1x400V Single-phase power supply
50/60 Hz Frequency
I1max Maximum absorbed current
Pmax Maximum pressure
P (1l/min) Refrigerant power measured at 1L/min
3.5.1.2 Description of protections
- Coolant pressure protection
This protection is achieved by means of a pressure swit-
ch, inserted in the fluid delivery circuit, which controls a
microswitch.
- Fuse (T 2A/250V-Ø 5x20)
This fuse was inserted to protect the pump.
3.5.1.3 Installation
Unscrew the cap and fill the tank (the equipment is supplied
with approximately one liter of fluid).
It is important to periodically check, through the slot, that the
fluid remains at the "max" level.
As a coolant, use water (preferably deionized) mixed with
alcohol in percentages defined according to the following table:
temperature water/alcohol
0°C up to -5°C 4L/1L
-5°C up to -10°C 3.8L/1.2L
NOTE If the pump turns with no coolant present, you must
remove all air from the tubes.
If so, turn off the power source, disconnect the torche hoses,
fill the tank, connect a hose to the fitting ( ), Insert the
other end of the hose in the tank. Start the power source for
approximately 10/15 seconds, then connect the torche
hoses.

16
Turn on the machine. To select the operating mode of the
cooling unit, proceed as follows:
1. Select any TIG welding mode.
2. Press the key Q and, while holding it down, press the
key R. Keep them pressed until the abbreviation H2O
appears on the display P.
3. Select the operating mode using the knob O, keeping in
mind that the numbers that appear on the display N
have the following meaning:
1 = Unit off,
2 = Continuous operation,
3 = Automatic operation.
To exit selection, briefly press the key Q.
NOTE: "Automatic mode" means that the cooling unit starts
when the torch button is pressed and stops running approx-
imately 2 minutes after the torch button is released.
Warning! If MMA electrode welding is selected, cooling is not
on and may not be selected. It is normal for the machine display
P to display, on start-up, the flashing abbreviation H2O.
3.5.1.4 Cooling unit for Art. 360
If using a water-cooled torch, use the cooling unit.
The trolley Art. 1432 is required to position and transport the
welding machine together with the cooling unit.
After filling the tank with coolant, connect the plug of the
mains cable to the socket AE of the welding machine, then
connect the 3-pin male patch connector to the connector AF.
3.5.1.5 Description of the cooling unit for Art.362 (Fig. 3)
AG - Slot:
Slot to inspect the coolant fluid level
AH - Quick-fitting sockets:
Use only for TIG welding systems.
NOTE: they must not be linked together.
AI - Cap.
Turn on the machine.
Do not touch live parts and output terminals while the
machine is powered.
The first time the machine is turned on, select the mode
using the push-button A and the welding parameters by
means of the key R and the knob O as described in para-
graph 3.2.
The flow of inert gas must be set to a value (in liters per
minute) approximately 6 times the diameter of the electrode.
If you are using gas-lens type accessories, the gas through-
put may be reduced to approximately 3 times the diameter
of the electrode. The diameter of the ceramic nozzle must be
4 to 6 times the diameter of the electrode.
The most commonly used gas is normally ARGON, because
it is less costly than other inert gases, but you may also use
blends of ARGON with a maximum of 2% HYDROGEN for
welding stainless steel, and HELIUM or ARGON-HELIUM
blends for welding copper. These blends increase the heat
of the arc while welding, but are much more expensive.
If you are using HELIUM gas, increase the liters per minute
to 10 times the diameter of the electrode (Ex. diameter 1.6
x10= 16 lt./min of Helium).
Use D.I.N. 10 protective glasses for up to 75A, and D.I.N. 11
from 75A up.
3.6. SAVING
You may save parameters only after welding.
Pressing the push-button Q briefly makes a selection;
held down for more than 3 seconds, it saves the data.
Each time it is turned on, the machine always shows the
last welding condition used.
3.6.1. Saving data from the PL program
Using the machine for the first time
When the machine is turned on, the display shows the sym-
bol PL; this disappears after 5 seconds, and a working cur-
rent is displayed. Follow the instructions in paragraphs 3.2
and 3.5, then proceed as follows to save the data in the pro-
gram P01:
· Briefly press the push-button Q (mem+mem-) the message
P01 will appear flashing.
· Press push-button Q for more than 3 seconds, until the sym-
bol P01 stops flashing: at this point, the data have been
saved.
· Obviously, if you wish to save in a program other than P01,
you should briefly press the push-button Q as many times as
necessary to display the desired program. P01 will be dis-
played the next time the machine is turned on.
PRESSING THE Q PUSH-BUTTON BRIEFLY MAKES A
SELECTION, WHILE HOLDING IT DOWN FOR MORE
THAN 3 SECONDS SAVES THE DATA.
3.6.2. Save from a free program
The operator may edit and save a selected program by pro-
ceeding as follows:
· Press the push-button Q briefly and select the desired pro-
gram number.
· The symbol of free programs is flashing.
· Press the button AL and choose the welding procedure,
press the torch trigger A to select the mode (paragraph 3.1).·
Turn the knob O and set the welding current.
· If the TIG procedure has been selected, activate the LED V
(post gas) by means of the push-button R, and set the
desired value via the knob O (paragraph 3.1.)
· If you wish to adjust the "slope" times or other parameters,
after making these adjustments which are necessary in
order to weld, follow the steps described in paragraph 3.1.
· Weld, even briefly, and decide where to save
· To save in the previously selected program, press the
button Q for more than 3 seconds, until the number stops
flashing.
· To save in a different program, make your selection by
AH
AI
AG
Fig. 3

17
briefly pressing the push-button Q, then hold down the
push-button Q for more than 3 seconds.
3.6.3 Save from a saved program
Beginning with a previously saved program, the operator
may edit the data in memory to update the program itself, or
to find new parameters to save in another program.
3.6.3.1 Update
· After turning on the machine, select the parameters to be
edited and edit them.
· Weld, even briefly.
· Hold down the Q button for more than 3 seconds, until the
save is confirmed (program symbol changes from flashing to
steady).
3.6.3.2 Save in a new program
· After turning on the machine, select the parameters to be
edited and edit them.
· Weld, even briefly.
· Briefly press the selector Q until the desired program is dis-
played.
· Hold down the Q button until the save is confirmed (pro-
gram symbol changes from flashing to steady).
4 REMOTE CONTROLS
The following remote controls may be connected to adjust
the welding current for this welding machine:
Art. 1270 TIG torch button only.(air-cooling)
Art. 1273 TIG torch button only.(water-cooling)
Art. 1266 TIG torch UP/DOWN.(air-cooling)
Art. 1274 TIG torch UP/DOWN.(water-cooling)
ART. 193 may be used in any TIG welding mode with this
accessory.
Remote controls that include a potentiometer regulate
the welding current from the minimum to the maximum
current set via the knob O.
Remote controls with UP/DOWN logic regulate the
welding current from the minimum to the maximum.
The remote control settings are always active in the PL pro-
gram, while they are not active in a saved program.
5 MAINTENANCE
Any maintenance operation must be carried out by qua-
lified personnel in compliance with standard CEI 26-29
(IEC 60974-4).
5.1 GENERATOR MAINTENANCE
In the case of maintenance inside the machine, make
sure that the switch AC is in position "O" and that the
power cord is disconnected from the mains.
It is also necessary to periodically clean the interior of the
machine from the accumulated metal dust, using com-
pressed air.
5.2 PRECAUTIONS AFTER REPAIRS.
After making repairs, take care to organize the wiring so that
there is secure insulation between the primary and secon-
dary sides of the machine. Do not allow the wires to come
into contact with moving parts or those that heat up during
operation. Reassemble all clamps as they were on the origi-
nal machine, to prevent a connection from occurring
between the primary and secondary circuits should a wire
accidentally break or be disconnected.
Also mount the screws with geared washers as on the ori-
ginal machine.

18
WICHTIG: VOR DER INBETRIEBNAHME DES GERÄTS
DEN INHALT DER VORLIEGENDEN BETRIEBSANLEI-
TUNG AUFMERKSAM DURCHLESEN; DIE BETRIEBS-
ANLEITUNG MUß FÜR DIE GESAMTE LEBENSDAUER
DES GERÄTS AN EINEM ALLEN INTERESSIERTEN
PERSONEN BEKANNTEN ORT AUFBEWAHRT WER-
DEN.
DIESES GERÄT DARF AUSSCHLIEßLICH ZUR
AUSFÜHR- UNG VON SCHWEIßARBEITEN VERWEN-
DET WERDEN.
1 SICHERHEITSVORSCHRIFTEN
DAS LICHTBOGENSCHWEIßEN UND -
SCHNEIDEN KANN FÜR SIE UND ANDE-
RE GESUNDHEITSSCHÄDLICH SEIN;
daher muß der Benutzer über die nachstehend kurz dar-
gelegten Gefahren beim Schweißen unterrichtet werden.
Für ausführlichere Informationen das Handbuch Nr.
3.300758 anfordern.
LÄRM
Dieses Gerät erzeugt selbst keine Geräusche, die 80
dB überschreiten. Beim Plasmaschneid- und
Plasmaschweißprozeß kann es zu einer
Geräuschentwicklung kommen, die diesen Wert überschrei-
tet. Daher müssen die Benutzer die gesetzlich vorgeschrie-
benen Vorsichtsmaßnahmen treffen.
ELEKTROMAGNETISCHE FELDER - Schädlich können sein:
· Der elektrische Strom, der durch einen beliebi-
gen Leiter fließt, erzeugt elektromagnetische
Felder (EMF). Der Schweiß- oder Schneidstrom
erzeugt elektromagnetische Felder um die
Kabel und die Stromquellen.
• Die durch große Ströme erzeugten magnetischen Felder
können den Betrieb von Herzschrittmachern stören. Träger von
lebenswichtigen elektronischen Geräten (Herzschrittmacher)
müssen daher ihren Arzt befragen, bevor sie sich in die Nähe
von Lichtbogenschweiß-, Schneid-, Brennputz- oder
Punktschweißprozessen begeben.
• Die Aussetzung an die beim Schweißen oder Schneiden
erzeugten elektromagnetischen Felder kann bislang unbe-
kannte Auswirkungen auf die Gesundheit haben.
Um die Risiken durch die Aussetzung an elektromagnetische
Felder zu mindern, müssen sich alle SchweißerInnen an die
folgenden Verfahrensweisen halten:
- Sicherstellen, dass das Massekabel und das Kabel
der Elektrodenzange oder des Brenners nebeneinan
der bleiben. Die Kabel nach Möglichkeit mit einem
Klebeband aneinander befestigen.
- Das Massekabel und das Kabel der
Elektrodenzange oder des Brenners nicht um den
Körper wickeln.
- Sich nicht zwischen das Massekabel und das Kabel
der Elektrodenzange oder des Brenners stellen.
Wenn sich das Massekabel rechts vom Schweißer
bzw. der Schweißerin befindet, muss sich auch das
Kabel der Elektrodenzange oder des Brenners auf
dieser Seite befinden.
- Das Massekabel so nahe wie möglich an der
Schweiß- oder Schneidstelle an das Werkstück
anschließen.
- Nicht in der Nähe der Stromquelle arbeiten.
EXPLOSIONSGEFAHR
· Keine Schneid-/Schweißarbeiten in der Nähe von
Druckbehältern oder in Umgebungen ausführen, die
explosiven Staub, Gas oder Dämpfe enthalten. Die
für den Schweiß-/Schneiprozeß verwendeten Gasflaschen
und Druckregler sorgsam behandeln.
ELEKTROMAGNETISCHE VERTRÄGLICHKEIT
Dieses Gerät wurde in Übereinstimmung mit den Angaben der
harmonisierten Norm IEC 60974-10 (Cl. A) konstruiert und
darf ausschließlich zu gewerblichen Zwecken und nur in
industriellen Arbeitsumgebungen verwendet werden. Es ist
nämlich unter Umständen mit Schwierigkeiten verbunden
ist, die elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit des Geräts in
anderen als industriellen Umgebungen zu gewährleisten.
ENTSORGUNG DER ELEKTRO- UND
ELEKTRONIKGERÄTE
Elektrogeräte dürfen niemals gemeinsam mit
gewöhnlichen Abfällen entsorgt werden! In Über-
einstimmung mit der Europäischen Richtlinie 2002/96/EG
über Elektro- und Elektronik-Altgeräte und der jeweiligen
Umsetzung in nationales Recht sind nicht mehr verwen-
dete Elektrogeräte gesondert zu sammeln und einer
Anlage für umweltgerechtes Recycling zuzuführen. Als
Eigentümer der Geräte müssen Sie sich bei unserem ört-
lichen Vertreter über die zugelassenen
Sammlungssysteme informieren. Die Umsetzung
genannter Europäischer Richtlinie wird Umwelt und
menschlicher Gesundheit zugute kommen!
IM FALLE VON FEHLFUNKTIONEN MUß MAN SICH AN
EINEN FACHMANN WENDEN.
1.1 WARNHINWEISSCHILD
Die Nummerierung der Beschreibungen entspricht der
Nummerierung der Felder des Schilds.
B. Die Drahtförderrollen können Verletzungen an den
Händen verursachen.
C. Der Schweißdraht und das Drahtvorschubgerät stehen
während des Schweißens unter Spannung. Die Hände
und Metallgegenstände fern halten.
1. Von der Schweißelektrode oder vom Kabel verursachte
Stromschläge können tödlich sein. Für einen angemes-
senen Schutz gegen Stromschläge Sorge tragen.
1.1 Isolierhandschuhe tragen. Die Elektrode niemals mit blo-
ßen Händen berühren. Keinesfalls feuchte oder schad-
hafte Schutzhandschuhe verwenden.
1.2 Sicherstellen, dass eine angemessene Isolierung vom
Werkstück und vom Boden gewährleistet ist.
1.3 Vor Arbeiten an der Maschine den Stecker ihres
Netzkabels abziehen.
2. Das Einatmen der beim Schweißen entstehenden
Dämpfe kann gesundheitsschädlich sein.
2.1 Den Kopf von den Dämpfen fern halten.
2.2 Zum Abführen der Dämpfe eine lokale Zwangslüftungs-
oder Absauganlage verwenden.
2.3 Zum Beseitigen der Dämpfe einen Sauglüfter verwen-
den.
BETRIEBSANLEITUNG FÜR LICHTBOGENSCHWEIßMASCHINE

19
3. Die beim Schweißen entstehenden Funken können
Explosionen oder Brände auslösen.
3.1 Keine entflammbaren Materialien im Schweißbereich
aufbewahren.
3.2 Die beim Schweißen entstehenden Funken können
Brände auslösen. Einen Feuerlöscher in der unmittelba-
ren Nähe bereit halten und sicherstellen, dass eine
Person anwesend ist, die ihn notfalls sofort einsetzen
kann.
3.3 Niemals Schweißarbeiten an geschlossenen Behältern
ausführen.
4. Die Strahlung des Lichtbogens kann Verbrennungen an
Augen und Haut verursachen.
4.1 Schutzhelm und Schutzbrille tragen. Einen geeigneten
Gehörschutztragen und bei Hemden den Kragen
zuknöpfen. Einen Schweißerschutzhelm mit einem Filter
mit der geeigneten Tönung tragen. Einen kompletten
Körperschutz tragen.
5. Vor der Ausführung von Arbeiten an oder mit der
Maschine die Betriebsanleitung lesen.
6. Die Warnhinweisschilder nicht abdecken oder entfernen.
2 ALLGEMEINE BESCHREIBUNG
2.1. EIGENSCHAFTEN
Bei dieser Schweißmaschine handelt es sich um eine
Konstant-Gleichstromquelle mit INVERTER-Technologie,
die zum WIG-Schweißen mit umhüllten Elektroden
(Zelluloseumhüllungen ausgenommen) und mit
Berührungs- und Hochfrequenzzündung entwickelt
wurde. NICHT ZUM ENTFROSTEN VON
ROHRLEITUNGEN VERWENDEN.
2.2. ERLÄUTERUNG DER TECHNISCHEN DATEN
Die Konstruktion des Geräts entspricht den folgenden
Normen: IEC 60974.1 - IEC 60974.3 -IEC 60974.10 Cl. A-
IEC 61000-3-11 - IEC 61000-3-12 (siehe Anm. 2).
Nr. Seriennummer; sie muß bei allen Anfragen zur
Schweißmaschine stets angegeben werden.
Statischer Einphasen-Frequenzumrichter
Transformator-Gleichrichter.
Fallende Kennlinie.
MMA Geeignet zum Schweißenmit umhülten
Elektroden.
WIG - Geeignet zum WIG-Schweißen..
U
0. Leerlaufspannung Sekundärseite (Scheitelwert).
X. Einschaltdauer. Die Einschaltdauer ist der auf
eine Spieldauer von 10 Minuten bezogene
Prozentsatz der Zeit, die das Gerät bei einer
bestimmten Stromstärke arbeiten kann, ohne
sich zu überhitzen. I2. Schweißstrom.
U2. Sekundärspannung bei Schweißstrom I2.
U1. Bemessungsspeisespannung.
Die Maschine verfügt über eine Funktion für die
automatische Wahl der Speisespannung.
3~ 50/60Hz Dreiphasen-Stromversorgung 50 oder 60 Hz.
I1 max. Dies ist der Höchstwert der Stromaufnahme.
I1 eff. Dies ist der Höchstwert der effektiven Stromauf-
nahme bei Berücksichtigung der relativen
Einschaltdauer.
IP23S Schutzart des Gehäuses.
Die zweite Ziffer 3 gibt an, dass dieses Gerät bei
Niederschlägen zwar im Freien gelagert, jedoch nicht
ohne geeigneten Schutz betrieben werden darf.
Geeignet zum Betrieb in Umgebungen mit
erhöhter Gefährdung.
ANMERKUNGEN:
1-Das Gerät ist außerdem für den Betrieb in
Umgebungen mit Verunreinigungsgrad 3 konzipiert.
(Siehe IEC 60664).
2-Dieses Gerät ist konform mit der Norm IEC 61000-3-12
unter der Voraussetzung, dass die maximal zulässige
Impedanz ZMAX am Verknüpfungspunkt zwischen der
Abnehmeranlage und dem öffentlichen
Versorgungsnetz kleiner oder gleich 0,117(Art. 362) -
0,137 (Art. 360) ist. Es liegt in der Verantwortung des
Installateurs bzw. des Betreibers des Geräts, erforder-
lichenfalls in Absprache mit dem öffentlichen
Energieversorgungsunternehmen sicherzustellen, dass
das Gerät ausschließlich an eine Anlage angeschlos-
sen wird, deren maximal zulässige Netzimpedanz
ZMAX kleiner oder gleich 0,117(Art. 362) - 0,137 (Art.
360) ist.
2.3. BESCHREIBUNG DER SCHUTZEINRICHTUNGEN
2.3.1. Thermischer Schutz
Dieses Gerät wird durch einen Temperaturfühler
geschützt, der, wenn die zulässigen Temperaturen über-
schritten werden, den Betrieb der Maschine sperrt. In die-
sem Zustand bleibt der Lüfter eingeschaltet und die LED
M leuchtet auf.
S

20
2.3.2- Sicherheitsverriegelung Art. 338
Diese Schweißmaschine verfügt über verschiedene
Schutzeinrichtungen, die die Maschine ausschalten,
bevor sie Schaden nehmen kann.
Die Schweißmaschine kann innerhalb der folgenden
Spannungsbereiche arbeiten:
Für Nennspannung 208/220/230V: von 175V bis 270V.
Für Nennspannung 400/440V: von 340V bis 490V.
Achtung: Wenn die Netzspannung nicht innerhalb der
o.g. Werte liegt, leuchtet keine LED auf, doch der
Ventilator wird gespeist.
Wenn die Phasen nicht richtig angeschlossen sind,
erscheinen im Moment der Einschaltung der Maschine
auf dem Display P drei ständig leuchtende Punkte.
Wenn die Spannung bei eingeschalteter Maschine den Wert
von 175 V (U1 = 230 V) bzw. von 340 V (U1 = 400 V) unter-
schreitet, erscheint auf dem Display P das Kürzel E3.
Wenn die Spannung bei eingeschalteter Maschine den
Wert von 275 V (U1 = 230 V) bzw. von 490 V (U1 = 400 V)
überschreitet, erscheint auf dem Display P das Kürzel E4.
In diesen Fällen muss man die Maschine ausschalten und
für die richtige Versorgungsspannung sorgen; dann die
Maschine wieder einschalten. Wenn das Problem beho-
ben wurde, arbeitet die Schweißmaschine wieder ord-
nungsgemäß.
Wenn bei eingeschalteter Maschine auf dem Display P
das Kürzel E2 oder E1 erscheint, die
Versorgungsspannung der Maschine kontrollieren. Sollte
die richtige Versorgungs- spannung vorliegen, bedarf die
Maschine einer Reparatur.
Wenn der Wasserpegel im Kühlaggregat zu niedrig ist,
erscheint auf Display P das Kürzel H2O.
3. INSTALLATION
Sicherstellen, daß die Speisespannung der auf dem
Leistungsschild der Schweißmaschine angegebenen
Bemessungsspannung entspricht.
Das Speisekabel mit einem Stecker mit einem geeigneten
Bemessungsstrom versehen und sicherstellen, daß der
gelb-grüne Schutzleiter an den Schutzkontakt ange-
schlossen ist.
Der Bemessungsstrom des in Reihe mit der Speisung
geschalteten thermomagnetischen Schalters oder der
Sicherungen muß gleich dem von der Maschine aufge-
nommenen Strom I1 sein.
ACHTUNG! Die Verlängerungen bis 30 m müssen einen
Querschnitt von mindestens 2,5 mm2 haben.
3.1. INSTALLATION
Die Installation der Maschine muß durch Fachpersonal
erfolgen. Alle Anschlüsse müssen nach den geltenden
Bestimmungen und unter strikter Beachtung der
Unfallverhütungsvorschriften ausgeführt werden (Norm
CEI 26-10 CENELEC HD 427).
3.2. BESCHREIBUNG DES GERÄTS
AL - Wahltaster Schweißverfahren
Mit diesem Drucktaster wählt man das
Schweißverfahren (Elektroden- oder WIG-Schweißen).
Jede Betätigung entspricht einer Wahl. Die getroffene
Wahl wird durch das Aufleuchten der LEDs neben den
jeweiligen Symbolen angezeigt.
B - LED Elektrodenschweißen (MMA)
Diese Maschine kann alle Arten von umhüllten Elektroden
mit Ausnahme von Elektroden mit Zelluloseumhüllung
verschweißen. Bei diesem Verfahren wird der Strom mit
dem Regler O eingestellt; außerdem kann man die
Funktionen "Arc Force" (LED AN) und "Hot Start" (LED
AM) regeln.
AH - LED WIG-Konstantstromschweißen
AI - LED WIG-Impulsschweißen
Die Impulsfrequenz kann in einem Bereich von 0,16 bis
500 Hz eingestellt werden (LED T); der Impulsstrom und
der Grundstrom können mit den LEDs X bzw. W gewählt
und mit dem Regler O eingestellt werden.
Im Impulsfrequenzbereich von 0,16 bis 1,1 Hz zeigt das
Display P abwechselnd den Impulsstrom (Hauptstrom)
und den Grundstrom an. Die LEDs X und W leuchten
abwechselnd auf; jenseits von 1,1 Hz zeigt das Display P
den Mittelwert der zwei Ströme an und die LEDs X und W
bleiben ständig eingeschaltet.
A - Funktionswahltaster
Jede Betätigung entspricht einer Wahl, die durch das
Aufleuchten der LED C oder D zusammen mit anderen
LEDs signalisiert wird, die das Schweißverfahren anzei-
gen.
C - LED Zünden des Lichtbogens ohne HF
Zum Zünden des Lichtbogens den Brennertaster drücken,
mit der Wolfram-Elektrode das Werkstück berühren und
dann die Elektrode wieder anheben. Diese Bewegung muss
entschieden und rasch ausgeführt werden.
D - LED Zünden des Lichtbogens mit HF
Zum Zünden des Lichtbogens den Brennertaster drü-
cken: ein Zündfunke hoher Spannung/Frequenz zündet
den Lichtbogen.
E -LED WIG-Schweißen 2-Takt (Handbetrieb)
Drückt man den Brennertaster, steigt der Strom in der
zuvor eingestellten Zeit "slope up" an, bis der mit dem
Regler O eingestellt Wert erreicht wird. Löst man den
Brennertaster, sinkt der Strom in der zuvor eingestellten
Zeit "slope down" auf den Wert 0.
In dieser Stellung kann man den zusätzlichen Fußregler
Art. 193 anschließen.
F-LED WIG-Schweißen 4-Takt (Automatikbetrieb)
Dieses Programm unterscheidet sich von der vorherigen
Funktion darin, daß sowohl die Zündung als auch das
Löschen durch Betätigen und Lösen des Brennertasters
gesteuert werden.
G - LED WIG-Schweißen mit
Zweiwertschaltung, 4-Takt (Automatikbetrieb)
Vor dem Zünden des Lichtbogens müssen die zwei ver-
schiedenen Schweißströme eingestellt werden:
Erste Stufe: die Taste R drücken, bis die LED X aufleuch-
tet, und dann den Hauptstrom mit Regler O einstellen.
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
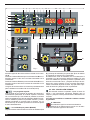 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
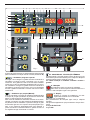 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
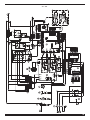 95
95
-
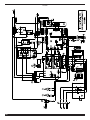 96
96
-
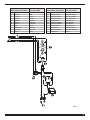 97
97
-
 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
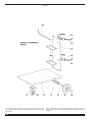 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur
- Ce manuel convient également à
dans d''autres langues
- italiano: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Manuale utente
- English: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T User manual
- español: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Manual de usuario
- Deutsch: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Benutzerhandbuch
- Nederlands: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Handleiding
- português: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Manual do usuário
- dansk: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Brugermanual
- svenska: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Användarmanual
- suomi: Cebora 360 TIG Sound DC 2341/T Ohjekirja
Documents connexes
-
Cebora 341 TIG Sound DC 3240/T Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora 346 TIG Sound AC-DC 2030/M Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora 366 Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora 278 Bi-Welder TIG 1665 DC HF Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora WIN TIG DC 180 M Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora INVERTER TIG Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora 289 Sound MIG 5040/TD Double Pulse Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora TIG SOUND AC-DC 2240/M Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora 287 Sound MIG 3840/T Pulse Manuel utilisateur
-
Cebora 335 Sound MMA 3536/T Cell Manuel utilisateur











































































































