
Miller
The
Power
ofBlue.
0M188
895
November
1997
Eff.
w/Serial
Number
~<H413143
Processes
~
MIG
(GMAW)
Welding
Rux
Cored
(FCAW)
Welding
Description
Wire
Feeder
22A
&
24A

Thank
you
and
congratulations
on
choosing
Miller.
Now
you
can
get
the
job
done
and
get
it
done
right.
We
know
you
dont
have
time
to
do
it
any
other
way.
Thats
why
when
Niels
Miller
first
started
building
arc
welders
in
1929,
he
made
sure
his
products
offered
long-lasting
value
and
superior
quality.
Like
you,
his
customers
couldnt
afford
anything
less.
Miller
products
had
to
be
more
than
the
best
they
could
be.
They
had
to
be
the
best
you
could
buy.
Today,
the
people
that
build
and
sell
Miller
products
continue
the
tradition.
Theyre
just
as
committed
to
providing
equipment
and
service
that
meets
the
high
standards
of
quality
and
value
established
in
1929.
This
Owners
Manual
is
designed
to
help
you
get
the
most
out
of
your
Miller
products.
Please
take
time
to
read
the
Safety
precautions.
They
will
help
you
protect
yourself
against
potential
hazards
on
the
worksite.
Weve
made
installation
and
operation
quick
and
easy.
With
Miller
you
can
count
on
years
of
reliable
service
with
proper
maintenance.
And
if
for
______________
some
reason
the
unit
needs
repair,
theres
a
Troubleshooting
section
that
will
help
you
figure
out
what
the
problem
is.
The
parts
list
will
then
help
you
to
decide
which
exact
part
you
may
need
to
fix
the
problem.
Warranty
and
service
information
for
your
particular
model
are
also
provided.
~
-,
~
Miller
Electric
manufactures
a
full
line
of
welders
and
welding
related
equipment.
For
information
on
other
quality
Miller
products,
contact
your
local
Miller
distributor
O~\
to
receive
the
latest
full
line
catalog
or
individual
catalog
sheets.
To
locate
your
nearest
distributor
call
1-800-4-A-Miller.
From
Miller
to
You
4~(IFIIII1
I
IREGISTERED
I
QUALITY
SYSTEM
Muur~fliI~mEluip~iI
iuigi~ii~kiliW.toh.
l1~g2tuIIl
tO
~l
~I
mi
~u~y
y~e
~ibiL

CaN
1-8004A-MLLER
for
your
local
P~MNer
dl~rtbutor.
Your
distributor
gives
you
Service
You
always
get
the
fast,
reliable
response
you
need.
Most
replacement
parts
can
be
in
your
hands
in
24
hours.
Support
Need
fast
answers
to
the
tough
welding
questions?
Contact
your
distributor.
The
expertise
of
the
distributor
and
Miller
is
there
to
help
you,
every
step
of
the
way.
Miller
offers
a
Technical
Manual
which
provides
more
detailed
service
and
pails
information
for
your
unit
To
obtain
a
Technical
Manual,
contact
your
local
distributor.
Your
distributor
can
also
supply
you
with
Welding
Process
Manuals
such
as
SMAW,
GTAW,
GMAW,
and
GMAW-P
For
practical
information
on
welding,
process
applica
tions,
and
Miller
products,
visit
our
website
at
uw~siwsIk~m
1
3
3
4
5
5
5
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
11
11
11
12
12
12
13
13
14
15
16
17
18
18
19
19
19
20
20
22
23
TABLE
OF
CONTENTS
SECTION
1
-
SAFETY
PRECAUTiONS
-
READ
BEFORE
USING
1-1.
Symbol
Usage
1-2.
Arc
Welding
Hazards
1-3.
Additional
Symbols
For
Installation,
Operation.
And
Maintenance
1-4.
Principal
Safety
Standards
1-5.
EMF
Information
SECTION
1
-
CONSIGNES
DE
SECURITE
-
LIRE
AVANT
UTILISAT1ON
1-1.
Signification
des
symboles
1-2.
Dangers
relatifs
au
soudage
a
Iarc
1-3.
Dangers
supplØmentaires
en
relation
avec
linstallation,
is
fonctionnement
et
Ia
maintenance
1-4.
Principales
normes
de
sØcuritØ
1-5.
Information
sur
les
champs
ØlectromagnØtiques
SECTION
2
-
DEFINITIONS
2-1.
Warning
Label
Definitions
2-2.
Rating
Label
For
CE
Products
2-3.
Symbols
And
Definitions
SECTION
3
-
INSTALLATION
3-1.
Specifications
3-2.
Site
Selection
3-3.
Gun
Recommendation
Table
3-4.
Equipment
Connection
Diagrams
3-5.
14-Pin
Receptacle,
Shielding
Gas
And
Optional
Volt
Sense
Lead
3-6.
14-Pin
Receptacle
Information
3-7.
Connecting
Welding
Gun
And
Weld
Cable
3-8.
Optional
Meter
Circuit
Board
Settings
3-9.
Motor
Start/Burnback
Control
3-10.Installing
Wire
Guide
And
Drive
Roll
3-11.
Installing
And
Threading
Welding
Wire
SECTION
4-
OPERATION
4-1.
Front
Panel
Controls
4-2.
Optional
Side
Panel
Controls
SECTION
5-
MAINTENANCE
&
TROUBLESHOOTING
5-1.
Routine
Maintenance
5-2.
Overload
Protection
5-3.
Troubleshooting
SECTION
6
-
ELECTRICAL
DIAGRAM
SECTION
7
-
PARTS
LIST
OPTIONS
AND
ACCESSORIES
WARRANTY


Declaration
of
Conformity
for
European
Community
(CE)
Products
N
OTE
~
This
information
is
provided
for
units
with
CE
certification
(see
rating
label
on
unit).
Manufacturer~s
Name:
Miller
Electric
Mfg.
Co.
Manufacturer~s
Address:
1635
W.
Spencer
Street
Appleton,
WI
54914
USA
Declares
that
the
product:
22A
A~fl
d
24A
con
forms
to
the
following
Directives
and
Standards:
Directives
Low
Voltage
Directive:
73/23/EEC
Electromagnetic
Compatibility
(EMC)
Directive:
89/336/EEC
Machinery
Directives:
89/392/EEC,
91/368/EEC,
93/C
133/04,
93/68/EEC
Standards
Arc
Welding
Equipment
Part
I:
Welding
Power
Sources:
IEC
974-1
(April
1995
-
Draft
Revision)
Arc
Welding
Equipment:
Wirefeed
Systems:
IEC
974-4
(May
1995
-
Draft
Revision)
Degrees
of
Protection
Provided
By
Enclosures
(IP
Code):
IEC
529:1989
Insulation
Coordination
For
Equipment
With
Low-Voltage
Systems:
Part
I:
Principles,
Requirements
and
Tests:
IEC
664-1:
1992
Electromagnetic
Compatibility,
(EMC):
EN
50199
European
Contact:
Mr.
Luigi
Vacchini,
Managing
Director
MILLER
Europe
S.P.A.
Via
Privata
Iseo
20098
San
Giuliano
Milanese,
Italy
Telephone:
39(02)98290-1
Fax:
39(02)
98281
-552
dec_conl
1/96


SECTION
1
-
SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS
-
READ
BEFORE
USING
scm
_nd_5i~7
A
The
symbols
shown
below
are
used
throughout
this
manual
to
call
attention
to
and
identify
possible
hazards.
When
you
seethe
symbol,
watch
out,
and
follow
the
related
instructions
to
avoid
the
hazard.
The
safety
information
given
below
Is
only
a
summary
of
the
more
complete
safety
information
found
In
the
Safety
Standards
listed
in
Section
1-4.
Read
and
follow
all
Safety
Standards.
A
Only
qualified
persons
should
install,
operate,
maintain,
and
repair
this
unit.
A
During
operation,
keep
everybody,
especially
children,
away.
Touching
live
electrical
parts
can
cause
fatal
shocks
or
severe
burns.
The
electrode
and work
circuit
is
electrically
live
whenever
the
output
is
on.
The
input
power
circuit
and
machine
internal
circuits
are
also
live
when
power
is
on.
In
semiautomatic
or
automatic
wire
welding,
the
wire,
wire
reel,
drive
roll
housing,
and
all
metal
parts
touching
the
welding
wire
are
electrically
live.
Incorrectly
installed
or
improperly
grounded
equipment
is
a
hazard.
Do
not
touch
live
electrical
parts.
Wear
dry,
hole-free
insulating
gloves
and
body
protection.
Insulate
yourself
from
work
and
ground
using
dry
insulating
mats
or
covers
big
enough
to
prevent
any
physical
contact
with
the
work
or
ground.
Do
not
use
AC
output
in
damp
areas,
if
movement
is
confined,
or
if
there
is
a
danger
of
falling.
Use
AC
output
ONLY
if
required
for
the
welding
process.
If
AC
output
is
required.
use
remote
output
control
if
present
on
unit.
Disconnect
input
power
or
stop
engine
before
installing
or
servicing
this
equipment.
Lockout/tagout
input
power
according
to
OSHA29
CFR
1910.147
(see
Safety
Standards).
Properly
install
and
ground
this
equipment
according
to
its
Owners
Manual
and
national,
state,
and
local
codes.
Always
verify
the
supply
ground
-
check
and
be
sure
that
input
power
cord
ground
wire
is
properly
connected
to
ground
terminal
in
disconnect
box
or
that
cord
plug
is
connected
to
a
properly
grounded
receptacle
outlet.
When
making
input
connections,
attach
proper
grounding
conductor
first
-
double-check
connections.
Frequently
inspect
input
power
cord
for
damage
or
bare
wiring
-
replace
cord
immediately
if
damaged
-
bare
wiring
can
kill.
Turn
off
all
equipment
when
not
in
use.
Do
not
use
worn.
damaged.
undersized,
or
poorly
spliced
cables.
Do
not
drape
cables
over
your
body.
If
earth
grounding
of
the
workpiece
is
required,
ground
it
directly
with
a
separate
cable
-
do
not
use
work
clamp
or
work
cable.
Do
not
touch
electrode
if
you
are
in
contact
with
the
work,
ground,
or
another
electrode
from
a
different
machine.
Use
only
well-maintained
equipment.
Repair
or
replace
damaged
parts
at
once.
Maintain
unit
according
to
manual.
Wear
a
safety
harness
if
working
above
floor
level,
Keep
all
panels
and
covers
securely
in
place.
Clamp
work
cable
with
good
metal-to-metal
contact
to
work
piece
or
worktable
as
near
the
weld
as
practical.
Insulate
work
clamp
when
not
connected
to
workplace
to
prevent
contact
with
any
metal
object.
Do
not
connect
more
than
one
electrode
or
work
cable
to
any
single
weld
output
terminal.
SIGNIFICANT
DC
VOLTAGE
exists
after
removal
of
Input
power
on
Inverters.
Turn
Off
inverter,
disconnect
input
power,
and
discharge
input
capacitors
according
to
instructions
in
Maintenance
Section
before
touching
any
parts.
-
Welding
produces
fumes,
and
gases.
Breathing
~
these
fumes
and
gases
can
be
hazardous
to
your
health.
Keep
your
head
out
of
the
fumes.
Do
not
breathe
the
fumes.
If
inside,
ventilate
the
area
and/or
use
exhaust
at
the
arc
to
remove
welding
fumes
and
gases.
If
ventilation
is
poor,
use
an
approved
air-supplied
respirator.
Read
the
Material
Safety
Data
Sheets
(MSDSs)
and
the
manufacturers
instructions
for
metals,
consumables,
coatings,
cleaners,
and
degreasers.
Work
in
a
confined
space
only
if
it
is
well
ventilated,
or
while
wearing
an
air-supplied
respirator.
Always
have
a
trained
watch-
person
nearby.
Welding
fumes and
gases
can
displace
air
and
lower
the
oxygen
level
causing
injury
or
death.
Be
sure
the
breathing
air
is
safe.
Do
not
weld
in
locations
near
degreasing,
cleaning,
or
spraying
operations.
The
heat
and
rays
of
the
arc
can
react
with
vapors
to
form
highly
toxic
and
irritating
gases.
Do
not
weld
on
coated
metals,
such
as
galvanized,
lead,
or
cadmium
plated
steel,
unless
the
coating
is
removed
from
the
weld
area,
the
area
is
well
ventilated,
and
if
necessary,
while
wearing
an
air-supplied
respirator.
The
coatings
and
any
metals
containing
these
elements
can
give
off
toxic
fumes
if
welded.
1-1.
Symbol
Usage
a
Means
Warning~
Watch
Out!
There
are
possible
hazards
with
this
procedure!
The
possible
hazards
are
shown
in
the
adjoining
symbols.
A
Marks
as
ecial
satat
messa
a
g
~
Means
~Note;
not
safety
related,
This
group
of
symbols
means
Warning!
Watch
Out!
possible
ELECTRIC
SHOCK,
MOVING
PARTS,
and
HOT
PARTS
hazards.
Consult
symbols
and
related
instructions
below
for
necessary
actions
to
avoid
the
hazards.
1~2
Arc
Welding
Hazards
OM-186
895
Page
1

ARC~
RAYS
can
burn
eyos
and
skin
1~4
Arc
rays
from
the
welding
process
produce
intense
visible
and
invisible
(ultraviolet
and
infrared)
rays
that
can
burn
eyes
and
skin.
Sparks
fly
off
from
the
weld.
Wear
a
welding
helmet
fitted
with
a
proper
shade
of
filter
to
protect
your
face
and
eyes
when
welding
or
watching
(see
ANSI
Z49.1
and
Z87.l
listed
in
Safety
Standards).
Wear
approved
safety
glasses
with
side
shields
under
your
helmet.
Use
protective
screens
or
barriers
to
protect
others
from
flesh
and
glare;
warn
others
not
to
watch
the
arc.
Wear
protective
clothing
made
from
durable,
flame-resistant
material
(leather
and
wool)
and
foot
protection.
Welding
on
closed
containers,
such
as
tanks,
drums,
or
pipes,
can
cause
them
to
blow
up.
Sparks
can
fly
off
from
the
welding
arc.
The
flying
sparks,
hot
workpiece,
and
hot
equipment
can
cause
fires
and
burns.
Accidental
contact
of
electrode
to
metal
objects
can
cause
sparks,
explosion,
overheating,
or
fire.
Check
and be
sure
the
area
is
safe
before
doing
any
welding.
S
S
Protect
yourself
and
others
from
flying
sparks
and
hot
metal.
Do
not
weld
where
flying
sparks
can
strike
flammable
material.
Remove
all
flammables
within
35
ft
(10.7
m)
of
the
welding
arc.
If
this
is
not
possible,
tightly
cover
them
with
approved
covers.
Be
alert
that
welding
sparks
and
hot
materials
from
welding
can
easily
go
through
small
cracks
and
openings
to
adjacent
areas.
Watch
for
fire,
and
keep
a
fire
extinguisher
nearby.
Be
aware
that
welding
on
a
ceiling,
floor,
bulkhead,
or
partition
can
cause
lire
on
the
hidden
side.
Do
not
weld
on
closed
containers
such
as
tanks,
drums,
or
pipes,
unless
they
are
properly
prepared
according
to
AWS
F4.
1
(see
Safety
Standards).
Connect
work
cable
to
the
work
as
close
to
the
welding
area as
practical
to
prevent
welding
current
from
traveling
long,
possibly
unknown
paths
and
causing
electric
shock
and
fire
hazards.
Do
not
use
welder
to
thaw
frozen
pipes.
Remove
stick
electrode
from
holder
or
cut
off
welding
wire
at
contact
tip
when
not
in
use.
Wear
oil-free
protective
garments
such
as
leather
gloves,
heavy
shirt,
cuffless
trousers,
high
shoes,
and
a
cap.
Remove
any
combustibles,
such
as
a
butane
lighter
or
matches.
from
your
person
before
doing
any
welding.
7
FI~YiN~
METAL
can
Injure
eyes
Welding,
chipping,
wire
brushing,
and
grinding
cause
sparks
and
flying
metal.
As
welds
cool,
they
can
throw
off
slag.
Wear
approved
safety
glasses
with
side
shields
even
under
your
welding
helmet.
Pacemaker
wearers
keep
away.
Wearers
should
consult
their
doctor
before
___________
going
near
arc
welding,
gouging,
or
spot
welding
operations.
NOISE
can
damagQ
hearing
Noise
from
some
processes
or
equipment
can
damage
hearing.
Wear
approved
ear
protection
it
noise
level
is
high.
Shielding
gas
cylinders
contain
gas
under
high
pressure.
If
damaged,
a
cylinder
can
explode.
Since
gas
cylinders
are
normally
part
of
the
welding
process,
be
sure
to
treat
them
carefully.
Protect
compressed
gas
cylinders
from
excessive
heat,
mechanical
shocks,
slag,
open
flames,
sparks,
and
arcs.
Install
cylinders
in
an
upright
position
by
securing
to
a
stationary
support
or
cylinder
rack
to
prevent
failing
or
tipping.
Keep
cylinders
away
from
any
welding
or
other
electrical
circuits.
Never
drape
a
welding
torch
over
a
gas
cylinder.
Never
allow
a
welding
electrode
to
touch
any
cylinder.
Never
weld
on
a
pressurized
cylinder
-
explosion
will
result.
Use
only
correct
shielding
gas
cylinders,
regulators,
hoses,
and
fittings
designed
for
the
specific
application;
maintain
them
and
associated
parts
in
good
condition.
Turn
face
away
from
valve
outlet
when
opening
cylinder
valve.
Keep
protective
cap
in
place
over
valve
except
when
cylinder
is
in
use
or
connected
for
use.
Read
and
follow
instructions
on
compressed
gas
cylinders.
associated
equipment,
and
CGA
publication
P-i
listed
in
Safety
Standards.
Shut
off
shielding
gas
supply
when
not
in
use.
Always
ventilate
confined
spaces
or
use
approved
air-supplied
respirator.
Do
not
touch
hot
parts
bare
handed.
Allow
cooling
period
before
working
on
gun
or
torch.
4
OM-186
895
Page
2

Do
not
overload
building
wiring
-
be
sure
power
supply
system
is
properly
sized,
rated,
and
protected
to
handle
this
unit.
Use
lifting
eye
to
lift
unit
only,
NOT
running
gear,
gas
cylinders,
or
any
other
accessories.
Use
equipment
of
adequate
capacity
to
lift
and
support
unit.
If
using
lift
forks
to
move
unit,
be
sure
forks
are
long
enough
to
extend
beyond
opposite
side
of
unit.
Reduce
current
or
reduce
duty
cycle
before
starting
to
weld
again.
Do
not
block
or
filter
airflow
to
unit.
Have
only
qualified
persons
familiar
with
electronic
equipment
perform
this
installation.
The
user
is
responsible
for
having
a
qualified
electrician
promptly
correct
any
interference
problem
resulting
from
the
installation.
If
notffied
by
the
FCC
about
interference,
stop
using
the
equipment
at
once.
Have
the
installation
regularly
checked
and
maintained.
Keep
high-frequency
source
doors
and
panels
tightly
shut,
keep
spark
gaps
at
correct
setting,
and
use
grounding
end
shielding
to
minimize
the
possibility
of
interference.
Do
not
press
gun
trigger
until
instructed
to
do
so.
Do
not
point
gun
toward
any
part
of
the
body,
other
people,
or
any
metal
when
threading
welding
wire.
To
reduce
possible
interference,
keep
weld
cables
as
short
as
possible,
close
together.
and
down
low,,
such
as
on
the
floor.
Locate
welding
operation
100 meters
from
any
sensitive
elec
tronic
equipment.
Be
sure
this
welding
machine
is
installed
and
grounded
according
to
this
manual.
If
interference
still
occurs,
the
user
must
take
extra
measures
such
as
moving
the
welding
machine,
using
shielded
cables,
using
line
filters,
or
shielding
the
work
area.
Safety
in
Welding
and
Cuffing,
ANSI
Standard
Z49.
1,
from
American
Welding
Society,
550
NW.
LeJeune
Rd,
Miami
FL
33126
Safety
and
Health
Standards,
OSHA
29
CFR
1910,
from
Superinten
dent
of
Documents.
U.S.
Government
Printing
Office,
Washington,
D.C.
20402.
Recommended
Safe
Practices
for
the
Preparation
for
Welding
and
Cutting
of
Containers
That
Have
Held
Hazardous
Substances,
American
Welding
Society
Standard
AWS
F4.
1,
from
American
Welding
Society,
550
N.W.
LeJeune
Rd.
Miami,
FL
33126
National
Electrical
Code.
NFPA
Standard
70,
from
National
Fire
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
Safe
Handling
of
Compressed
Gases
in
Cylinders.
CGA
Pamphlet
P-I,
from
Compressed
Gas
Association,
1235
Jefferson
Davis
Highway,
Suite
501,
Arlington,
VA
22202.
Code
for
Safety
in
Welding
and
Cutting,
CSA
Standard
Wi
17.2,
from
Canadian
Standards
Association,
Standards
Sales,
178
Rexdale
Boulevard,
Rexdale,
Ontario,
Canada
M9W
I
R3.
Safe
Practices
For
Occupation
And
Educational
Eye
And
Face
Protection,
ANSI
Standard
Z87.
1,
from
American
National
Standards
Institute,
1430
Broadway,
New
York,
NY
10018.
Cutting
And
Welding
Processes,
NFPA
Standard
51
B,
from
National
Fire
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
Do
not
install
or
place
unit
on,
over,
or
near
combustible
surfaces.
Do
not
install
unit
near
flammables.
Keep
away
from
moving
parts
such
as
fans.
Keep
all
doors,
panels,
covers,
and
guards
closed
and
securely
in
place.
High-frequency
(HF)
can
interfere
with
radio
navigation,
safety
services,
computers,
and
communications
equipment.
Allow
cooling
period;
follow
rated
duty
cycle.
S
~,
~
~
Put
on
grounded
wrist
strap
BEFORE
handling
boards
or
parts.
Use
proper
static-proof
bags
and
boxes
to
store,
move,
or
ship
PC
boards.
1111111
MOVING
PARTS
can
cause
InJury~
Keep
away
from
moving
parts.
Keep
away
from
pinch
points
such
as
drive
rolls.
Electromagnetic
energy
can
interfere
with
sensitive
electronic
equipment
such
as
computers
and
computer-driven
equipment
such
as
robots.
Be
sure
all
equipment
in
the
welding
area
is
electromagnetically
compatible.
OM-186
895
Page
3

Welding
current,
as
it
flows
through
welding
cables,
will
cause
electro
magnetic
fields.
There
has
been
and
still
is
some
concern
about
such
fields.
However,
after
examining
more
than
500
studies
spanning
17
years
of
research,
a
special
blue
ribbon
committee
of
the
National
Research
Council
concluded
that:
The
body
of
evidence,
in
the
committees
judgment,
has
not
demonstrated
that
exposure
to
power-
frequency
electric
and
magnetic
fields
is
a
human-health
hazard.
However,
studies
are
still
going
forth
and
evidence
continues
to
be
examined.
Until
the
final
conclusions
of
the
research
are
reached,
you
may
wish
to
minimize
your
exposure
to
electromagnetic
fields
when
welding
or
cutting.
To
reduce
magnetic
fields
in
the
workplace,
use
the
following
procedures:
3.
Do
not
coil
or
drape
cables
around
your
body.
4.
Keep
welding
power
source
and
cables
as
far
away
from
opera
tor
as
practical.
5.
Connect
work
clamp
to
workpiece
as
close
to
the
weld
as
possible.
About
Pacemakers:
Pacemaker
wearers
consult
your
doctor
first.
If
cleared
by
your
doctor,
then
following
the
above
procedures
is
recommended.
Considerations
About
Welding
And
The
Effects
Of
Low
Frequency
1.
Keep
cables
close
together
by
twisting
or
taping
them.
Electric
And
Magnetic
Fields
2.
Arrange
cables
to
one
side
and
away
from
the
operator.
OM-186
895
Page
4

SECTION
1
-
CONSIGNES
DE
SECURITE
-
LIRE
AVANT
UTI
LISATION
som
_nd_tre
5/97
14.
SIgnification
des
symboles
a
Signifle
Mise
en
garde!
Soyez
vigilant!
Cette
procedure
prØsente
des
risques
de
danger!
Ceux-ci
sont
identifies
par
des
symboles
adjacents
aux
directives.
A
Idontifie
un
message
do
sØcuritØ
partlculler.
~
Sign/ifs
NOTA
nest
pas
re/at/f
ala
sØcur/tØ.
r,g
*d
Ce
groupe
de
sym
boles
signifle
Mise
en
garde!
Soyez
vigilant
lIly
a
des
risques
do
danger
relies
aux
0-IOCS
ELECTRIQUES,
aux
PIECES
EN
MOUVEMENTet
aux
PIECES
CHAUDES.
Reportez-vous
auxsymboles
et
aux
directives
ci-dessous
afin
de
connaltre
les
mesures
a
prendre
pour
Łviter
tout
danger.
1-2k
Dangers
relatifs
au
soudags
a
raw
A
Los
symbolos
prØsontØs
cl-api-Is
sont
utlllsIs
tout
au
long
du
present
manuel
pour
attiror
votro
attention
ot
IdentIfIer
los
risquos
do
danger.
Lorsquo
vous
voyoz
un
symbolo,
aoyoz
vigilant
ot
sulvox
los
dlroctlvea
montlonnIoa
afin
dCvltor
tout
danger.
Los
conslgnos
do
aIcurlt
prIaontØos
cl-aprIs
no
font
quo
rØsumor
llnformatlon
contonuo
dana
los
normos
do
aØcurltI
InumCrIos
I
Ia
section
1-4.
Voullloz
lIro
ot
rospoctor
toutos
cos
normos
do
aCcuritC.
A
LInatallatlon,
lutlllaatlon,
lontrotlon
ot
lea
reparations
no
dol
vent
Itro
conflØs
quI
dos
poraonnos
quallfiCos.
A
Au
cours
do
lutlllsatlon,tonlrtouto
porsonno
I
lCcart
ot
plus
par
tlcullCromont
los
onf
ants.
_
.~
Un
simple
contact
avec
des
piŁces
electriques
peut
provoquer
une
electrocution
ou
des
blessures
graves.
Lelectrode
et
le
circuit
de
soudage
sont
sous
tension
des
que
lappareil
est
sur
ON.
Le
circuit
dentrŁe
et
les
circuits
intemes
de
lappareil
sont
Łgalement
sous
tension
ace
moment-la.
En
soudage
semi-automatique
ou
automatique,
Ia
fil,
Is
dŁvidoir,
le
logement
des
galets
dentraInement
et
los
piŁces
mŁtalliques
en
contact
avec
Is
fil
de
soudage
sont
sous
tension.
Des
matŁriels
mai
installes
ou
mat
mis
a
Ia
terre
prŁsentent
un
danger.
Ne
jamais
toucher
les
piŁces
Łlectriques
sous
tension.
Porter
des
gants
et
des
vŁtements
de
protection
secs ne
comportant
pas
de
trous.
Sisoler
de
Ia
piŁce
et
de
Ia
terre
au
moyen
de
tapis
ou
dautres
moyens
isolants
suffisamment
grands
pour
empŁcher
le
contact
phy
sique
Łventuel
avec
Ia
piŁce
ou
Ia
terre.
Ne
pas
so
servir
do
source
Łlectrique
acourant
electrique
dans
les
zones
humides,
dans
las
endroits
confines
ou
ia
o
on
risque
de
tomber.
Se
servir
dune
source
Øloctrique
acourant
Łlectrique
UNIQUEMENT
si le
procŁdŁ
de
soudage
le
demande.
Si
lutilisation
dune
source
Łlectrique
acourant
Łlectrique
savŁre
nŁces
saire,
se
servir
de
Ia
fonction
do
tØlŁcommande
si
lappareil
en
est
ŁquipŁ.
Couper
lalimentation
ou
arrŁter
le
moteur
avant
de
procŁder
a
linstal
lation,
a
Ia
reparation
ou
a
lentretien
de
lappareil.
Deverrouiller
lalimentation
salon
Ia
norme
OSHA
29
CFR
191
0.147
(voir
normes
de
sŁcuritŁ).
Installer
et
mettre
ala
terre
correctement
cet
appareil
conformŁment
a
son
manuel
dutilisation
at
aux
codes
nationaux,
provinciaux
at
municipaux.
Toujours
verifier
Ia
terra
du
cordon
dalimentation
-
Verifier
at
sassu
rer
qua
Ia
fil
de
terre
du
cordon
dalimentation
est
bien
raccordŁ
a
Ia
borne
de
terre
du
sectionneur
ou
qua
Ia
fiche
du
cordon
est
raccordŁe
a
une
prise
correctement
mise
a
Ia
terra.
En
effectuant
las
raccordements
dentrŁe
fixer
dabord
le
conducteur
do
mise
a
Ia
terre
appropriŁ
at
contre-vŁrifier
las
connexions.
Verifier
frequemment
Ia
cordon
dalimentation
pour
voir
sil
nest
pas
endommagŁ
ou
dŁnudŁ
-
remplacer
le
cordon
immŁdiatement
s11
est
endommagŁ
-
un
cable
dŁnudŁ
peut
provoquer
une
electrocution.
Mettre
lappareil
hors
tension
quand
on
ne
lutilise
pas.
Ne
pas
utiliser
des
cables
uses,
endommagŁs,
de
grosseur
insutfi
sante
ou
mal
ŁpissŁs.
Ne
pas
enrouler
les
cables
autour
du
corps.
Si
Ia
piŁce
soudŁe
doit
Łtre
mise
ala
terra,
Ia
faire
directement
avec
un
cable
distinct
-
ne
pas
utiliser
le
connecteur
do
piŁce
ou
Ia
cable
de
retour.
Ne
pas
toucher
lŁlectrode
quand
on
est
en
contact
avec
Ia
piŁce,
Ia
terra
ou
une
electrode
provenant
dune
autre
machine.
Nutiliser
quun
materiel
en
bon
Łtat.
RŁparer
ou
remplacer
sur-le
champ
les
piŁces
endommagŁes.
Entretenir
lappareil
conformement
ace
manuel.
o
Porter
un
harnais
de
sŁcuritŁ
quand
on
travaille
en
hauteur.
o
Maintenir
solidement
en
place
tous
les
panneaux
et
capots.
o
Fixer
Is
cable
do
retour
de
faon
a
obtenir
un
bon
contact
metal-metal
avec
Ia
piŁce
a
souder
ou
Ia
table
da
travail,
le
plus
prŁs
possible
do
Ia
soudure.
lsoler
Ia
pince
do
masse
quand
pas
mis
a
Ia
piŁce
pour
Łviter
Is
contact
avec
tout
objet
mØtallique.
ily
a
DU
COURANT
CONTINU
IMPORTANT
dans
los
convertlsseurs
aprØs
Ia
suppression
do
lailmenta
tion
Ølectrlque.
o
ArrŁter
les
convertisseurs,
debrancher
Is
courant
Łlectrique,
et
dŁ
charger
les
condensateurs
dalimentation
selon
les
instructions
indiquees
dans
Ia
partie
entretien
avant
de
toucher
las
piŁces.
.
LES
FUMEES
ET
LES
GAZ
pouvent
~
Mm
dangorewc
La
soudage
gŁnŁro
des
fumŁes
at
des
gaz.
Leur
=9
-
inhalation
peut
Łtre
dangereux
pour
votre
sante.
_____________
o
Eloigner
votre
tŒte
des
fumŁes.
Ne
pas
respirer
es
fumŁes.
A
lintŁneur,
ventiler
Ia
zone
et/ou
utiliser
un
Łchappement
au
ni
veau
do
larc
pour
lŁvacuation
des
fumŁes
at
des
gaz
de
soudage.
Si
Ia
ventilation
est
insuffisante,
utiliser
un
respirateur
a
alimenta
tion
dair
homologuŁ.
Ure
lea
specifications
do
sŁcuritŁ
des
matŁriaux
(MSDSs)
at
les
ins
tructions
du
tabricant
concemant
los
mŁtaux,
las
consommables,
los
revŁtements,
las
nettoyants
at
es
dŁgraisseurs.
Travailler
dans
un
espace
fermŁ
seulement
sil
est
bien
ventile
ou
en
portant
un
respirateur
a
alimentation
dair.
Demander
toujours
a
un
surveillant
dment
formŁ
de
so
tenir
a
proximite.
Des
fumees
at
des
gaz
do
soudage
peuvent
dŁplacer
lair
et
abaisser
le
niveau
doxygŁne
provoquant
des
blessures
ou
des
accidents
mortals.
Sassurer
qua
lair
de
respiration
ne
prŁsente
aucun
danger.
Ne
pas
souder
dans
des
endroits
situes
a
proximite
dopŁrations
de
dŁgraissage,
de
nettoyage
ou
do
pulvŁrisation.
La
chaleur
at
las
rayons
de
arc
peuvent
rŁagir
en
presence
de
vapeurs
at
former
des
gaz
hautement
toxiques
at
irritants.
Ne
pas
souder
des
mŁtaux
munis
dun
revØtement,
tels
qua
lacier
galvanisŁ,
plaque
en
p10mb
ou au
cadmium
a
moms
qua
le
revŒte
ment
nait
ŁtŁ
enlevŁ
dans
Ia
zone
da
soudure,
qua
lendroit
soit
bien
ventilŁ,
et
si
necessaire,
en
portant
un
raspirateur
a
alimanta
tion
dair.
Les
revŁtemants
et
tous
las
mŁtaux
renfermant
ces
ŁlŁ
ments
peuvent
dØgager
des
fumees
toxiques
en
cas
de
soudage.
OM-186
895
PageS

Le
rayonnement
de
Iarc
du
procede
de
soudage
I
gØnØre
des
rayons
visibles
et
invisibles
intenses
(ultraviolets
et
intrarougos)
susceptibles
do
provoquer
des
brUlures
dons
los
yeux
et
sur
Ia
peau.
Des
Øtincelles
sont
projetØos
pendant
le
soudage.
Porter
un
casque
do
soudage
muni
dun
Øcran
do
filtre
appropne
pour
protØger
votre
visage
et
vos
yeux
pendant
le
soudage
ou
pour
rogar
der
(voir
ANSI
Z49.1
et
Z87.1
ØnumØrØ
dons
lea
normes
do
sØcuntØ).
Porter
des
protections
approuvØs
pour
les
oreilles
si le
niveau
sondre
est
trop
ØlevØ.
Utdlsor
dos
Øcrans
ou
des
barriŁres
pour
protØgor
des
tiers
de
lØclair
et
do
lØblouissement;
demander
aux
autres
personnes
de
no
pas
re
garder
arc.
Porter
dos
vØtements
de
protection
constituØ
dons
une
matiŁre
dura
ble,
resistant
au
feu
(cuir
ou
lamb)
et
une
protection
dos
pieds.
(~
~
tncendteouune~xptos1on
Le
soudage
eftectuØ
sur
dos
conteneurs
fermØs
tels
quo
des
reservoirs,
tambours
ou
des
conduites
pout
provoquer
leur
Øclatement.
Des
Øtincelles
peuvent
Øtro
projotØes
do
larc
do
souduro.
La
projection
dØtincel
lea,
dos
piŁces
chaudes
ot
des
Øquipoments
chauds
peut
provoquer
dos
incendios
et
des
brOluros.
Le
contact
accidentel
do
lØloctrodo
avec
dos
objets
metalliques
pout
provoquer
dos
Øtincolles,
une
explosion,
un
surchauffement
ou un
incendie.
Avant
do
commencor
le
soudage,
verifier
et
sassurer
quo
lendroit
no
prØsonto
pas
do
danger.
So
proteger
ot
dautres
porsonnes
do
Ia
projection
dØtincelles
et
do
metal
chaud.
No
pas
soudor
dons
un
endroit
l
oU
dos
Øtincellos
pouvont
tomber
sur
des
substances
inflammablos.
Deplacertoutos
los
substances
inflammables
a
uno
distance
do
10,7
m
do
Iarc
do
soudage.
En
cas
dimpossibilitØ
los
recouvrir
soignouse
ment
avec
dos
protections
homologues.
Des
Øtincolles
ot
des
matØnaux
chauds
du
soudage
pouvont
facile-
mont
passer
dana
dautres
zones
en
traversant
do
petites
fissures
et
des
ouvertures.
Survoillor
tout
dØclenchemont
dincendie
et
tonir
un
extinctour
a
proxi
mite.
Le
soudago
offoctuØ
sur
un
plafond,
plancher,
paroi
ou
separation
pout
dØcloncher
un
incendie
de
lautre
ctØ.
No
pas
offectuor
10
soudage
sur
des
contoneurs
formØs
tols
quo
des
rØsorvoirs,
tambours,
ou
conduites,
a
mains
quils
naient
ØtØ
prØpa
rØs
corroctement
conformOment
a
AWS
F4.1
(voir
los
normes
do
sØcuritØ).
Branchor
Ia
cØble
sur
Ia
piŁce
10
plus
prŁs
possible
do
Ia
zone
do
sou
dage
pour
Øvitor
le
transport
du
courant
sur
une
longuo
distance
par
dos
chomins
inconnus
Øventuols
on
provoquant
des
risques
dØlec
trocution
ot
dincendio.
No
pas
utilisor
le
paste
do
soudago
pour
degeler
dos
conduites
go
lees.
En
cas
do
non
utilisation,
enlevor
Ia
baguette
dØlectrodo
du
porte
electrode
ou
coupor
10
fil
a
Ia
pointo
de
contact.
Porter
des
vØtoments
do
protection
dŁpourvus
dhu~e
tols
quo
dos
gants
en
cuir,
uno
chemise
en
matØriau
lourd,
des
pantalons
sans
re
vors,
des
chaussures
hautos
ot
un
couvro
chef.
Avant
do
souder,
retirer
touto
substance
combustible
do
vos
pochos
telles
quun
allumeur
au
butane
ou
des
allumottes.
ProtØger
los
bouteilles
do
gaz
compnmØ
dune
chalour
excessive,
dos
chocs
mecaniques,
du
laitier,
dos
flammes
ouvertes,
des
Øtin
cellos
et
des
arcs.
Placer
los
boutoillos
debout
en
los
fixant
dons
un
support
station-
noire
ou
dons
un
porte-bouteilles
pour
los
ompØcher
do tomber
ou
do
so
ronvorser.
Tenir
los
bouteilles
eloignØes
des
circuits
do
soudage
ou
autros
cir
cuits
electnquos.
No
iamais
placer
une
torcho
do
soudago
sur
une
bouteille
a
gaz.
Une
electrode
do
soudage
no
daft
jamais
entrer
on
contact
avoc
uno
boutoille.
Ne
jamais
souder
uno
bouteille
prossurisØe
-
risque
doxplosion.
Utiliser
soulomont
dos
boutoillos
do
gaz
protecteur,
regulatours,
tuyaux
et
raccords
convenables
pour
cette
application
specifiquo;
los
maintonir
ainsi
quo
los
ØlØmonts
associØs
on
ban
Øtat.
No
pas
tenir
Ia
tØto
en
face
do
Ia
sortio
on
ouvrant
Ia
soupape
do
a
boutoillo.
Maintonir
le
chapeau
do
protection
sur
Ia
soupapo,
sauf
on cas
dutilisation
ou
do
branchement
de
Ia
bouteillo.
Lire
ot
suivro
los
instructions
concernant
tea
bouteillos
do
gaz
com
prime,
los
equipomonts
associØs
et
los
publications
P-i
CGA
Ønu
mØrØes
dans
es
normes
de
sØcuritØ.
Former
lalimentation
du
gaz
protecteur
en
cas
do
non
utiloation.
Veiller
toujours
a
bien
aØrer
los
espaces
confines
ou so
servir
dun
respi
ratour
dadduction
dair
homologuØ.
Ne
pas
toucher
des
parties
chaudos
a
mains
nues
PrØvoir
une
pØriode
do
refroidissoment
avant
dutiliser
le
pistolet
ou
Ia
torcho.
Porteurs
do
stimulateur
cardiaque,
restoz
a
dlatance.
Los
portours
dun
stimulateur
cardiaque
doivent
dabord
consulter
leur
mØdocin
avant
do
sapprocher
des
operations
do
soudage
a
Iarc.
do
gougoage
ou
do
soudage
par
points.
La
bruit
des
processus
et
des
Øquipemonts
pout
affecter
Iouio.
Porter
des
protections
approuvØs
pour
lea oreilles
si
le
nrveau
sandro
eat
trop
ØlevØ.
Des
bouteillos
do
gaz
protectour
contiennent
du
gaz
sous
haute
prossion.
Si
uno
boutoillo
ost
ondomma
gee,
0110
pout
explosor.
Du
fait
quo
lea
boutoillos
do
gaz
font
normalemont
paftie
du
procØdØ
de
soudage,
los
manipuler
avec
precaution.
Lo
soudago,
IØcailloment,
0
passage
do
Ia
piŁce
a
Ia
brosse
en
fit
do
for,
otto
meulago
gØnŁront
dos
etinceues
et
dos
particutes
mØtalliquos
volan
tes.
Pendant
Ia
periodo
do
roftoidissoment
des
souduros.
ellos
risquent
do
projoter
du
laitior.
Porter
dos
lunottos
do
sØcuritØ
avoc
Øcrans
latØraux
ou
un
Øcran
facial.
OM-186
895
Page
6

Utilisor
lanneau
do
levage
uniquement
pour
sou
lever
lappareil,
NON
PAS
los
chariot,
les
bouteil
los
do
gaz
ou
tout
autre
accossoire.
Utilisor
un
engin
dune
capacitØ
appropnØo
pour
soulever
lappareil.
En
utilisant
des
fourches
do
levage
pour
dØplacer
lunitØ,
sassurer
que
los
fourches
sont
suffisamment
longues
pour
dØpasser
du
ctØ
oppose
do
lappareil.
PrØvoir
une
penode
de
refroidissement,
respec
ter
le
cycle
operatoire
nominal.
RØduire
le
courant
ou
10
cycle
opØratoire
avant
do
recommancer
10
soudage.
No
pas
obstruer
los
passages
dan
du
posto.
k~
peuvontondommagor
los
c~rcuks
Im
Etablir
Ia
connoxion
avec
Ia
barrette
do
terre
avant
do
manipuler
dos
cartes
ou
des
piŁces.
Utilisor
des
pochettos
ot
des
boites
antistatiquos
pour
stocker,
dØplacer
ou
oxpØdier
des
caries
do
circuits
linprimes.
0
provoquer
des
bIessures~
No
pas
sapprocher
des
organes
mobiles.
No
pas
sapprocher
des
points
do
coincement
tels
quo
des
rouleaux
do
commando.
S
L~:F.~~I~/:..fc.INNEMEN
Hi..IJTE
:~.
____
J
QUENCE
~KI9
rtsquo
dG
provoquor
Le
rayonnement
haute
froquence
pout
provoquer
des
interferences
avec
los
Øquipemonts
do
ra
dio-navigation
ot
do
communication,
los
services
do
sØcuritØ
et
los
ordinatours.
Demander
seulement
a
des
personnes
qualifiŁes
familiansØes
avoc
des
Øquipements
Ølectroniquos
do
faire
fonctionner
installa
tion.
Lutilisatour
est
tenu
do
faire
comgor
rapidement
par
un
Ølectricien
qualiflŁ
los
interferences
resultant
do
linstallation.
Si
0
FCC
signale
des
interferences,
arrØter
immØdiatement
lappa
roil.
Effectuer
reguliŁrement
10
contrlo
ot
lentretien
do
linstallation.
Maintenir
soigneusement
fermØs
los
portes
ot
les
panneaux
des
sources
do
haute
frØquonce,
maintonir
los
Øclatours
a
une
distance
correcte
et
utilisor
une
terre
et et
un
blindage
pour
rØduire
los
inter
fØrences
Øventuelles.
1
~
I
LØnorgio
eloctromagnetiquo
risque
do
provoquer
des
interferences
pour
lØquipement
electroniquo
sensible
tel
quo
es
ordinateurs
et
lequipement
commandØ
par
ordinateur
tel
quo
lea
robots.
Veiller
ace
quo
tout
lØquipement
do
Ia
zono
do
soudage
soit
com
patible
electromagnØtiquement.
Pour
rØduire
Ia
possibilitØ
dinterfØrence,
maintenir
los
cables
do
soudago
aussi
courts
que
possible,
es
grouper,
et
los
poser
aussi
bas
quo
possible
(ox.
par
terre).
Veiller
a
soudor
Ł
une
distance
do
100
metres
do
tout
equipement
electroniquo
sensible.
Veillor
a
ce
quo
ce
poste
do
soudago
soit
pose
et
mis
Ł
Ia
terre
conformØment
a
ce
mode
domploi.
En
cas
dinterfØrences
aprŁs
avoir
pris
los
mesures
prØcØdentes,
ii
incombe
a
Iutilisateur
do
prendro
dos
mesures
supplØmentaires
telles
quo
10
dØplacoment
du
poste,
Iutilisation
do
cables
blindØs,
lutilisation
do
filtres
do
ligne
ou
Ia
pose
do
protecteurs
dans
Ia
zone
do
travail.
A
4
No
pas
placer
Iappareil
sur,
au-dessus
ou
a
proximitŁ
de
surfaces
infllammablos.
We
pas
installer
lappareil
a
proximitØ
de
produits
inflammables
No
pas
surcharger
installation
Ølectriquo
-
sassurer
quo
lalimon
tation
est
correctement
dimensionnØ
et
protØgØ
avant
do
mettre
Iappareil
en
service.
Roster
a
lØcart
des
organes
mobiles
comme
le
vontilateur.
Maintenir
formØs
ot
fixement
on
place
los
portes,
panneaux,
recouvroments
et
dispositifs
do
protection.
L~jFLQ~~CESS~
SURcHAiJF~ER
I~EQtJtPEMENT
No
pas
appuyer
sur
Ia
gachetto
avant
den
avoir
recu
linstruction.
Ne
pas
diriger
le
pistolet
vers
sd,
dautres
per
sonnes
ou
toute
piŁce
mØcaniquo
en
engageant
le
fil
de
soudage.
Porteurs
do
stimulateur
cardiaque,
restez
a
dis
tance.
Los
porteurs
dun
stimulateur
cardiaquo
doivent
dabord
consultor
leur
mØdocin
avant
do
sappro
cher
des
operations
do
soudage
a
arc,
do
gou
geage
ou
de
soudage
par
points.
OM-186
895
Page
7

Safety
ann
Health
Sandards,
OSHA
29
CFR
1910,
du
Superintendent
of
Documents,
U.S.
Government
Printing
Office,
Washington,
D.C.
20402.
Recommer,dedSafe
Practice
for
the
Preparation
for
Welding
and
Cut
ting
of
Containers
That
Have
Held
Hazardous
Substances,
norme
AWS
F4.
1,
de
lAmerican
Welding
Society,
550
N.W.
Lejaune
Rd.
Mia
mi
FL
33126
National
EleciTical
Code,
NFPA
Standard
70,
de
Ia
National
Fire
Pro
tection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
DonnØes
sur
le
soudage
Ølectrique
et
sur
las
effats,
pour
lorganisme,
des
champs
magnØtiques
basse
frØquence
La
courant
de
soudage,
pendant
son
passage
dens
es
cables
de
sou
dage,
causera
des
champs
ØlectromagnØtiques.
II
y
a
eu
et
il
y
a
encore
un
certain
souci
a
propos
de
tels
champs.
Cependant,
aprŁs
avoir
examine
plus
de
500
etudes
qui
ont
ØtØ
faites
pendant
une
pØ
node
de
recherche
de
17
ans,
un
comitØ
special
ruban
bleu
du
National
Research
Council
a
conclu:
taccumulation
de
preuvas,
sui
vent
le
jugement
du
comitØ,
na
pas
dØmontrØ
que
lexposition
aux
champs
magnØtiques
et
champs
Ølectriques
a
haute
frØquence
reprØ
sente
un
risque
a
Ia
sante
humaine.
Toutefois,
des
etudes
sont
toujours
en
cours
et
las
preuves
continuent
a
Œtre
examinØes.
En
at
tendant
qua
lea
conclusions
finales
de
Ia
recherche
soient
Øtablies,
il
vous
serait
souhaitable
de
rØduire
votre
exposition
aux
champs
Ølec
tromagnØtlques
pendant
le
soudage
ou
le
coupage.
Safe
Handling
of
Compressed
Gases
in
Cylinders,
CGA
Pamphlet
P-i,
de
Ia
Compressed
Gas
Association,
1235
Jefferson
Davis
High
way,
Suite
501,
Arlington,
VA
22202.
RŁgles
de
sØcuritØ
en
soudage,
coupage
etprocØdØs
connexes,
nor
ma
CSA
Wi
17.2,
de
lAssociation
canadienne
de
normalisation,
yenta
de
normes,
178
Rexdale
Boulevard,
Rexdale
(Ontario)
Canada
M9W
1
R3.
Safe
Practices
For
OccupaiionAnd
Educational
EyeAnd
Face
Protec
tion,
norma
ANSI
Z87.
1,
de
lAmerican
National
Standards
Institute,
1430
Broadway,
New
York,
NY
10018.
Cutting
and
Welding
Processes,
norme
NFPA
51
B,
de
Ia
National
Fire
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
1
Garder
las
cØbles
ensembles
en
las
torsadant
ou en
lea
attacharit
avec
du
ruben
adhØsif.
2
Mettre
tous
las
cØbles
du
ctØ
oppose
de
lopØrateur.
3
Ne
pas
courber
pas
et
ne
pas
entourer
pas
lea
cØbles
autour
de
votra
corps.
4
Garder
le
posta
da
soudaga
at
las
cØbles
Ia
plus
loin
possible
de
vous.
5
Relier
Ia
pince
de
masse
le
plus
prŁs
possible
de
Ia
zone
da
soudura.
Conslgnes
relatives
aux
stlmuiateurs
cardlaques
Las
personnes
qui
portent
un
stimulateur
cardiaque
doivant
avant
tout
consultar
laur
docteur.
Si
vous
Œtes
dØclarØ
apte
par
votre
docteur,
ii
eat
alors
recommandØ
de
respecter
lea
consignes
ci-dessus.
Safety
in
Welding
and
Cuffing,
norma
ANSI
Z49.
1,
de
IAmerican
Wel
ding
Society,
550
N.W.
Lajaune
Ad,
Miami
FL
33126
Afin
de
rØduire
lea
champs
ØlectromagnØtiquas
dens
lenvironnement
da
travail,
respecter
las
consignes
suivantes
OM-186
895
Page
8

SECTION
2-
DEFINITIONS
A.
Warning!
Watch
Out!
There
are
possible
hazards
as
shown
by
the
symbols.
B.
Drive
rolls
can
injure
fingers.
C.
Welding
wire
and
drive
parts
are
at
welding
voltage
during
operation
-
keep
hands
and
metal
objects
clear.
1
Electric
shock
can
kill.
1.1
Wear
dry
insulating
gloves.
Do
not
touch
electrode
with
bare
hand.
Do
not
wear
wet
or
damaged
gloves.
1.2
Protect
yourself
from
electric
shock
by
insulating
yourself
from
work
and
ground.
1.3
Disconnect
input
plug
or
power
before
working
on
machine.
2
Breathing
welding
fumes
can
be
hazardous
to
your
health.
2.1
Keep
your
head
out
of
the
fumes.
2.2
Use
forced
ventilation
or
local
exhaust
to
remove
the
fumes.
2.3
Use
ventilating
fan
to
remove
fumes.
3
Welding
sparks
can
cause
explosion
or
fire.
3.1
Keep
flammables
away
from
welding.
Dont
weld
near
flammables.
3.2
Welding
sparks
can
cause
fires.
Have
a
fire
extinguisher
nearby
and
have
a
watch
person
ready
to
use
it.
3.3
Do
not
weld
on
drums
or
any
closed
containers.
4
Arc
rays
can
burn
eyes
and
injure
skin.
4.1
Wear
hat
and
safety
glasses.
Use
ear
protection
and
button
shirt
collar.
Use
welding
helmet
with
correct
shade
of
filter.
Wear
complete
body
protection.
5
Become
trained
and
read
the
instructions
before
working
on
the
machine
or
welding.
6
Do
not
remove
or
paint
over
(cover)
the
label.
2-1.
Warning
Label
Definitions
OM-186
895
Page
9

2-2.
Rating
Label
For
CE
Products
ST-i
78
794-A
2-3.
Symbols
And
Definitions
NOTE
~
Some
symbols
are
found
only
on
CE
products.
1
On
~J
Off
Input
(~3..
Output
A
Amperes
~~J
Volts
uh\~,
Alternating
Current
)(
Duty
Cycle
I
P
Hz
Hertz
Circuit
Breaker
010
Wire
Feed
I
0~0
Jog
t~J1
Primary
Voltage
Gas
Metal
Arc
Welding
(GMAW)
jJ
ELD~
Une
Connection
Purge
~
Spot
Weld
Time
Spot
Weld
1~
Continuous
Weld
t
Burnback
Time
ti
Preflow
Time
t2
Poslllow
Time
React
Instructions
U2
Load
Voltage
Primary
Current
12
Rated
Current
~J1
Primary
Voltage
OM-186
895
Page
10

3-1.
Specifications
SECTION
3-
INSTALLATION
Type
of
input
Power
Welding
Power
Source
Type
Wire
Feed
Speed
Range
Wire
Diameter
Range
Welding
Circuit
Rating
IP
Rating
Overall
Dimensions
Weight
24
Volts
AC
Single
Phase
7
Amperes
50/60
Hz
Constant
Voltage
(CV)
DC
With
14-Pin
And
Conta~or
Control
1.9
To
16.5
mpm
(75
to
650
ipm)
0.6
To
2
mm
(.023
To
5/64
in)
Max
Spool
Weight:
27kg
(60
Ib)
100
Volts,
500
Amperes,
100%
Duty
Cycle
IP
23
Length:
572
mm
(22-1/2
in)
Width:
267mm
(10-1/2
in)
Height:
305
mm
(12
in)
15.9
kg
(35
Ib)
3-2.
Site
Selection
Choose
slot
that
allows
all
rubber
feet
to
sit
securely
on
top
of
weld
ing
power
source.
5
Wire
Spool/Reel
6
Gas
Cylinder
(Customer
Supplied)
Welding
Power
Source
Do
not
put
feeder
where
welding
wire
hIts
cyiinder.
A
Do
not
move
or
operate
equipment
when
it
could
tip.
Ufting
Handle
Manually
use
handie
to
move
or
briefly
lift
feeder.
A
Do
not
use
lifting
hook
or
other
devices
to
lift
or
suspend
feeder
by
the
handie.
1
Wire
Feeder
6
2
Ufting
Eye
3
Rubber
Feet
4
Slot
7
A
8
A
ST-801
920-A
/
Ref.
ST-i
52
468-A
/
ST-I
55242
/
ST-801
91
9-A
/
SA-188
674
OM-186
895
Page
11

3-3.
Gun
Recommendation
Table
Process
Gun
GMAW
-
Hard
or
Corded
Wires
M25
Or
M40
FCAW
-
Self-Shielding
Wires
GA-4OGL
3-4.
Equipment
Connection
Diagrams
5
3-5.
14-Pin
Receptacle,
Shielding
Gas
And
Optional
Volt
Sense
Lead
F!!
~
Tools
Needed:
~r
5/8,11/l6in
1
Gas
Hose
With
5/8-18
Right-
hand
Thread
Fittings
(Cus
tomer
Supplied)
2
14
Pin
Receptacle
RC9
Use
interconnecting
cord
to
make
connection
to
welding
power
source.
3
Power
Switch
Ref.
ST-801
921
-A
rrI~1r*
d
1
3
CV
Welding
Power
Source
With
24
VAC
Power
2
CV
Welding
Power
Source
Without
24
VAC
Power
115
Volts
AC
/24
Volts
AC
Power
Adapter
14-Pin
Contro
Cord
Weld
Cable
Work
4
5
6
/
OM-186
895
Page
12

3-6.
14-Pin
Receptacle
Information
REMOTE
~
Pln*
Pin
information
A
24
volts
ac
with
respect
to
pin
G.
B
Contact
closure
to
A
completes
24
volts
ac
contactor
control
circuit.
G
Circuit
common
for
24
volts
AC
circuit.
C
+10
volts
dc
output
to
remote
control
with
respect
to
pin
0.
D
Remote
control
circuit
common.
E
0
to
+10
volts
dc
input
command
signal
from
remote
control
with
respect
to
pin
D.
F
Current
feedback:
0
to
10
volts
dc,
1
V/100
A
H
Voltage
feedback:
0
to
10
volts
dc,
1
V/i
0
arc
volts
*The
remaining
pins
are
not
used.
Ref.
S.0004-A
3-7.
Connecting
Welding
Gun
And
Weld
Cable
OM-186
895
Page
13

3-8.
Optional
Meter
Circuit
Board
Settings
1
Meter
Circuit
Board
2
DlPSwitchS2
3
Potentiometer
Ri
8
4
Receptacle
RC1
6
Wiring
harness
with
free-hanging
plug
PLG42
connects
to
Rd
6.
For
voltage
feedback
from
volta!
sensing
lead,
connect
plug
PLG43
from
unit
wiring
harness
to
PLG42.
For
voltage
feedback
from
welding
power
source
to
wire
feeder
14-pin
receptacle,
connect
plug
PLG41
from
unit
winng
harness
to
PLG42.
Tools
Needed:
cI:II:::::J====:n
1/4
in
Voltage
Sensing
Function
Arc
Voltage
Sensing
Using
Voltage
Sensing
Lead
For
Welding
Power
Source
That
Does
Not
Support
Pins
F
And H
II
F
I
2
Arc
Voltage
Sensing
Using
Feedback
From
Welding
Power
Source
That
Does
Support
Pins
F
And
H
Meters/Minute
Inches/Minute
X
Means
switch
position
does
not
affect
specified
function.
I
Means
switch
must
be
in
this
position.
OM-186
895
Page
14
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
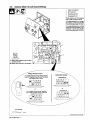 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
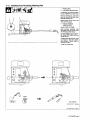 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
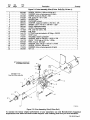 33
33
-
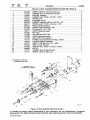 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
Miller I-22A Le manuel du propriétaire
- Catégorie
- Système de soudage
- Taper
- Le manuel du propriétaire
dans d''autres langues
- English: Miller I-22A Owner's manual
Documents connexes
-
Miller DS-64M Swingarc Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller KJ148959 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller CP-252TS Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller Mark VI Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller MATIC 400 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller KH577834 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller KH419746 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller TOUCH SENSOR Manuel utilisateur
-
Miller KJ164358 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Miller KH391014 Le manuel du propriétaire













































