DeWalt D28730 Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Outils électroportatifs
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur

If you have questions or comments, contact us.
Pour toute question ou tout commentaire, nous contacter.
Si tiene dudas o comentarios, contáctenos.
1-800-4-DeWALT
Instruction Manual
Guide D’utilisation
Manual de instrucciones
D28730
Chop Saw
Scie à onglets
Sierra de corte
final page size: 8.5 x 5.5 in

ENGLISH
English (original instructions) 1
Français (traduction de la notice d’instructions originale) 10
Español (traducido de las instrucciones originales) 20

ENGLISH
1
English (original instructions)
Definitions: Safety Alert Symbols and Words
This instruction manual uses the following safety alert symbols and words to alert you to hazardous situations and your risk
of personal injury or property damage.
DANGER: Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or seriousinjury.
WARNING: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or seriousinjury.
CAUTION: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderateinjury.
(Used without word) Indicates a safety related message.
NOTICE: Indicates a practice not related to personal injury which, if not avoided, may result in propertydamage.
WARNING: Read all safety warnings and all
instructions. Failure to follow the warnings and
instructions may result in electric shock, fire and/or
seriousinjury.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury, read the
instructionmanual.
If you have any questions or comments about this or
any
DeWALT
tool, call us toll free at:
1-800-4-
DeWALT
(1-800-433-9258).
1
Lock pin
2
Spark deflector screw
3
Spark deflector
4
Base
5
Fence
6
Vise
7
5/16" (8mm) hex key
8
Crank
9
Vise lever
10
Wheel
11
Guard
12
Spindle lock
13
Trigger switch
14
Lock-off lever
15
Fence bolts
16
Mounting holes
17
Operating handle
18
Carrying handle
Fig. A
4
5
6
7
8
10
11
12
17
9
9
16
16
16
13
15
2
3
1
14
18

ENGLISH
2
GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY WARNINGS
WARNING: Read all safety warnings,
instructions, illustrations and specifications
provided with this power tool. Failure to follow all
instructions listed below may result in electric shock,
fire and/or seriousinjury.
SAVE ALL WARNINGS AND
INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE
REFERENCE
The term “power tool” in the warnings refers to your mains-
operated (corded) power tool or battery-operated (cordless)
powertool.
1) Work Area Safety
a ) Keep work area clean and well lit. Cluttered or dark
areas inviteaccidents.
b ) Do not operate power tools in explosive
atmospheres, such as in the presence of
flammable liquids, gases or dust. Power tools
create sparks which may ignite the dust orfumes.
c ) Keep children and bystanders away while
operating a power tool. Distractions can cause you
to losecontrol.
2) Electrical Safety
a ) Power tool plugs must match the outlet. Never
modify the plug in any way. Do not use any
adapter plugs with earthed (grounded) power
tools. Unmodified plugs and matching outlets will
reduce risk of electricshock.
b ) Avoid body contact with earthed or grounded
surfaces such as pipes, radiators, ranges and
refrigerators. There is an increased risk of electric
shock if your body is earthed orgrounded.
c ) Do not expose power tools to rain or wet
conditions. Water entering a power tool will increase
the risk of electricshock.
d ) Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord for
carrying, pulling or unplugging the power tool.
Keep cord away from heat, oil, sharp edges or
moving parts. Damaged or entangled cords increase
the risk of electricshock.
e ) When operating a power tool outdoors, use an
extension cord suitable for outdoor use. Use of
a cord suitable for outdoor use reduces the risk of
electricshock.
f ) If operating a power tool in a damp location
is unavoidable, use a ground fault circuit
interrupter (GFCI) protected supply. Use of a GFCI
reduces the risk of electricshock.
3) Personal Safety
a ) Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use
common sense when operating a power tool. Do
not use a power tool while you are tired or under
the influence of drugs, alcohol or medication. A
moment of inattention while operating power tools
may result in serious personalinjury.
b ) Use personal protective equipment. Always wear
eye protection. Protective equipment such as dust
mask, non-skid safety shoes, hard hat, or hearing
protection used for appropriate conditions will reduce
personalinjuries.
c ) Prevent unintentional starting. Ensure the
switch is in the off position before connecting to
power source and/or battery pack, picking up or
carrying the tool. Carrying power tools with your
finger on the switch or energizing power tools that
have the switch on invitesaccidents.
d ) Remove any adjusting key or wrench before
turning the power tool on. A wrench or a key left
attached to a rotating part of the power tool may
result in personalinjury.
e ) Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and
balance at all times. This enables better control of
the power tool in unexpectedsituations.
f ) Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing or
jewelry. Keep your hair, clothing and gloves
away from moving parts. Loose clothes, jewelry or
long hair can be caught in movingparts.
g ) If devices are provided for the connection of dust
extraction and collection facilities, ensure these
are connected and properly used. Use of dust
collection can reduce dust-relatedhazards.
h ) Do not let familiarity gained from frequent use
of tools allow you to become complacent and
ignore tool safety principles. A careless action can
cause severe injury within a fraction of asecond.
4) Power Tool Use and Care
a ) Do not force the power tool. Use the correct
power tool for your application. The correct power
tool will do the job better and safer at the rate for
which it wasdesigned.
b ) Do not use the power tool if the switch does not
turn it on and off. Any power tool that cannot be
controlled with the switch is dangerous and must
berepaired.
c ) Disconnect the plug from the power source and/
or remove the battery pack, if detachable, from
the power tool before making any adjustments,
changing accessories, or storing power tools.
Such preventive safety measures reduce the risk of
starting the power toolaccidentally.
d ) Store idle power tools out of the reach of children
and do not allow persons unfamiliar with the
power tool or these instructions to operate the
power tool. Power tools are dangerous in the hands
of untrainedusers.
e ) Maintain power tools and accesories. Check
for misalignment or binding of moving parts,
breakage of parts and any other condition
that may affect the power tool’s operation. If
damaged, have the power tool repaired before
use. Many accidents are caused by poorly maintained
powertools.
f ) Keep cutting tools sharp and clean. Properly
maintained cutting tools with sharp cutting edges are
less likely to bind and are easier tocontrol.
g ) Use the power tool, accessories and tool bits, etc.
in accordance with these instructions, taking
into account the working conditions and the

ENGLISH
3
work to be performed. Use of the power tool for
operations different from those intended could result
in a hazardoussituation.
h ) Keep handles and grasping surfaces dry, clean
and free from oil and grease. Slippery handles and
grasping surfaces do not allow for safe handling and
control of the tool in unexpectedsituations.
5) Service
a ) Have your power tool serviced by a qualified
repair person using only identical replacement
parts. This will ensure that the safety of the power
tool ismaintained.
Safety Instructions for Cut-Off Machines
1) Cut-Off Machine Safety Warnings
a ) Position yourself and bystanders away from the
plane of the rotating wheel. The guard helps to
protect the operator from broken wheel fragments
and accidental contact withwheel.
b ) Use only bonded reinforced cut-off wheels for
your power tool. Just because an accessory can
be attached to your power tool, it does not assure
safeoperation.
c ) The rated speed of the accessory must be at least
equal to the maximum speed marked on the
power tool. Accessories running faster than their
rated speed can break and flyapart.
d ) Wheels must be used only for recommended
applications. For example: do not grind with the
side of a cut-off wheel. Abrasive cut-off wheels are
intended for peripheral grinding, side forces applied to
these wheels may cause them toshatter.
e ) Always use undamaged wheel flanges that are of
correct diameter for your selected wheel. Proper
wheel flanges support the wheel thus reducing the
possibility of wheelbreakage.
f ) The outside diameter and the thickness of your
accessory must be within the capacity rating of
your power tool. Incorrectly sized accessories cannot
be adequately guarded orcontrolled.
g ) The arbor size of wheels and flanges must
properly fit the spindle of the power tool. Wheels
and flanges with arbor holes that do not match the
mounting hardware of the power tool will run out
of balance, vibrate excessively and may cause loss
ofcontrol.
h ) Do not use damaged wheels. Before each use,
inspect the wheels for chips and cracks. If the
power tool or wheel is dropped, inspect for
damage or install an undamaged wheel. After
inspecting and installing the wheel, position
yourself and bystanders away from the plane
of the rotating wheel and run the power tool
at maximum no load speed for one minute.
Damaged wheels will normally break apart during
this testtime.
i ) Wear personal protective equipment. Depending
on application, use face shield, safety goggles
or safety glasses. As appropriate, wear dust
mask, hearing protectors, gloves and shop
apron capable of stopping small abrasive or
workpiece fragments. The eye protection must
be capable of stopping flying debris generated by
various operations. The dust mask or respirator must
be capable of filtrating particles generated by your
operation. Prolonged exposure to high intensity noise
may cause hearingloss.
j ) Keep bystanders a safe distance away from
work area. Anyone entering the work area must
wear personal protective equipment. Fragments
of workpiece or of a broken wheel may fly away and
cause injury beyond immediate area ofoperation.
k ) Position the cord clear of the spinning accessory.
If you lose control, the cord may be cut or snagged
and your hand or arm may be pulled into the
spinningwheel.
l ) Regularly clean the power tool’s air vents. The
motor’s fan can draw the dust inside the housing and
excessive accumulation of powdered metal may cause
electricalhazards.
m ) Do not operate the power tool near flammable
materials. Do not operate the power tool while
placed on a combustible surface such as wood.
Sparks could ignite thesematerials.
n ) Do not use accessories that require liquid
coolants. Using water or other liquid coolants may
result in electrocution orshock.
o ) Check damaged parts. Before further use of the
tool, a guard or other part that is damaged should
be carefully checked to determine that it will operate
properly and perform its intended function—check
for alignment of moving parts, binding of moving
parts, breakage of parts, mounting, and any other
conditions that may affect its operation. A guard
or other part that is damaged should be properly
repaired orreplaced.
2) Kickback and Related Warnings
Kickback is a sudden reaction to a pinched or snagged
rotating wheel. Pinching or snagging causes rapid stalling
of the rotating wheel which in turn causes the uncontrolled
cutting unit to be forced upwards toward theoperator.
For example, if an abrasive wheel is snagged or pinched
by the workpiece, the edge of the wheel that is entering
into the pinch point can dig into the surface of the material
causing the wheel to climb out or kick out. Abrasive wheels
may also break under theseconditions.
Kickback is the result of power tool misuse and/or incorrect
operating procedures or conditions and can be avoided by
taking proper precautions as givenbelow.
a ) Maintain a firm grip on the power tool and
position your body and arm to allow you to resist
kickback forces. The operator can control upward
kickback forces, if proper precautions aretaken.
b ) Do not position your body in line with the
rotating wheel. If kickback occurs, it will propel the
cutting unit upwards toward theoperator.
c ) Do not attach a saw chain, woodcarving blade,
segmented diamond wheel or toothed saw
blade. Such blades create frequent kickback and loss
ofcontrol.

ENGLISH
4
d ) Do not “jam” the wheel or apply excessive
pressure. Do not attempt to make an excessive
depth of cut. Overstressing the wheel increases the
loading and susceptibility to twisting or binding of
the wheel in the cut and the possibility of kickback or
wheelbreakage.
e ) When the wheel is binding or when interrupting
a cut for any reason, switch off the power tool
and hold the cutting unit motionless until the
wheel comes to a complete stop. Never attempt
to remove the wheel from the cut while the
wheel is in motion otherwise kickback may
occur. Investigate and take corrective action to
eliminate the cause of wheelbinding.
f ) Do not restart the cutting operation in the
workpiece. Let the wheel reach full speed and
carefully re-enter the cut. The wheel may bind,
walk up or kickback if the power tool is restarted in
theworkpiece.
g ) Support any oversized workpiece to minimize
the risk of wheel pinching and kickback. Large
workpieces tend to sag under their own weight.
Supports must be placed under the workpiece near the
line of cut and near the edge of the workpiece on both
sides of thewheel.
Additional Safety Information
WARNING: ALWAYS use safety glasses. Everyday
eyeglasses are NOT safety glasses. Also use face or
dust mask if cutting operation is dusty. ALWAYS WEAR
CERTIFIED SAFETYEQUIPMENT:
• ANSI Z87.1 eye protection (CAN/CSA Z94.3),
• ANSI S12.6 (S3.19) hearing protection,
• NIOSH/OSHA/MSHA respiratoryprotection.
WARNING: Some dust created by power sanding,
sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction
activities contains chemicals known to the State
of California to cause cancer, birth defects or
other reproductive harm. Some examples of these
chemicalsare:
• lead from lead-based paints,
• crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other
masonry products, and
• arsenic and chromium from chemically-
treatedlumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how
often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to
these chemicals: work in a well ventilated area, and work with
approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are
specially designed to filter out microscopicparticles.
• Avoid prolonged contact with dust from power
sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other
construction activities. Wear protective clothing and
wash exposed areas with soap and water. Allowing
dust to get into your mouth, eyes, or lay on the skin may
promote absorption of harmfulchemicals.
WARNING: Use of this tool can generate and/
or disperse dust, which may cause serious and
permanent respiratory or other injury. Always use
NIOSH/OSHA approved respiratory protection
appropriate for the dust exposure. Direct particles
away from face andbody.
WARNING: Always wear proper personal hearing
protection that conforms to ANSI S12.6 (S3.19)
during use. Under some conditions and duration
of use, noise from this product may contribute to
hearingloss.
• Air vents often cover moving parts and should be
avoided. Loose clothes, jewelry or long hair can be
caught in movingparts.
• An extension cord must have adequate wire size
(AWG or American Wire Gauge) for safety. The smaller
the gauge number of the wire, the greater the capacity
of the cable, that is, 16 gauge has more capacity than 18
gauge. An undersized cord will cause a drop in line voltage
resulting in loss of power and overheating. When using
more than one extension to make up the total length,
be sure each individual extension contains at least the
minimum wire size. The following table shows the correct
size to use depending on cord length and nameplate
ampere rating. If in doubt, use the next heavier gauge. The
lower the gauge number, the heavier thecord.
Minimum Gauge for Cord Sets
Volts
Total Length of Cord in Feet
(meters)
120 V 25 (7.6) 50 (15.2) 100 (30.5) 150 (45.7)
240 V 50 (15.2) 100 (30.5) 200 (61.0) 300 (91.4)
Ampere Rating
American Wire Gauge
More
Than
Not
More
Than
0 6 18 16 16 14
6 10 18 16 14 12
10 12 16 16 14 12
12 16 14 12 Not Recommended
The label on your tool may include the following symbols. The
symbols and their definitions are asfollows:
V ......................... volts
Hz .......................hertz
min ..................... minutes
or DC ......direct current
...................... Class I Construction
(grounded)
…/min ..............per minute
BPM .................... beats per minute
IPM ..................... impacts per minute
RPM .................... revolutions per
minute
sfpm ................... surface feet per
minute
SPM .................... strokes per minute
A ......................... amperes
W ........................watts
or AC ...........alternating current
or AC/DC .... alternating or
direct current
...................... Class II
Construction
(double insulated)
n
o
.......................no load speed
n .........................rated speed
......................earthing terminal
.....................safety alert symbol
.....................visible radiation
..................... wear respiratory
protection
..................... wear eye
protection
..................... wear hearing
protection
..................... read all
documentation
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS FOR
FUTURE USE

ENGLISH
5
Motor
Be sure your power supply agrees with the nameplate
marking. Voltage decrease of more than 10% will cause loss
of power and overheating.
DeWALT
tools are factory tested;
if this tool does not operate, check powersupply.
Connecting to a Power Supply
Connect this product to a 120V, 15A, polarized receptacle.
This appliance has a polarized plug (one blade is wider than
the other). This plug will fit in a polarized outlet only one
way. If the plug does not fit fully in the outlet, reverse the
plug. If it still does not fit, contact a qualified electrician to
install the properoutlet.
WARNING: Do not change the plug in any way.
If the power cord is ever damaged, take the tool
to a D
eWALT
authorized service center for repair
orreplacement.
COMPONENTS (FIG. A)
WARNING: Never modify the power tool or any part
of it. Damage or personal injury couldresult.
Refer to Figure A at the beginning of this manual for a
complete list ofcomponents.
Intended Use
Your chop saw has been designed for the cutting of
variously shaped steelmaterials.It is designed only for use
with reinforced bonded abrasives. Diamond or TCT blades
should not be used with thisunit.
DO NOT use under wet conditions or in presence of
flammable liquids orgases.
Your chop saw is a professional power tool.
DO NOT let children come into contact with the tool.
Supervision is required when inexperienced operators use
thistool.
SPECIFICATIONS
D28730
Voltage 120V~
Frequency 60 Hz
Amps 15
No-load speed 4000/min (rpm)
Wheel diameter 14" (355 mm)
Wheel thickness .12" (3.0 mm)
Arbor size 1" (25.4 mm)
Net weight 34.1 lbs (15.5 kg)
ASSEMBLY AND ADJUSTMENTS
WARNING: To reduce the risk of serious personal
injury, turn unit off and disconnect it from
power source before making any adjustments or
removing/installing attachments or accessories.
An accidental start-up can causeinjury.
Cutting Capacity
The wide vise opening and high pivot point provide cutting
capacity for many large pieces. Use the cutting capacity
chart to determine total maximum size of cuts that can be
made with a newwheel.
CAUTION: CERTAIN LARGE, CIRCULAR OR
IRREGULARLY SHAPED OBJECTS MAY REQUIRE
ADDITIONAL HOLDING MEANS IF THEY CANNOT BE
HELD SECURELY INVISE.
CAUTION: DO NOT CUT MAGNESIUM OR WOOD
WITH THISTOOL.
Maximum Cutting Capacity
NOTE: Capacity shown on chart assumes no wheel wear
and optimum fenceposition.
Workpiece
Shape
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
90° Cutting
angle
A = 4-7/8"
(125 mm)
A = 4-1/2"
(115 mm)
4-1/2" x 5-1/8"
(115 mm x 130 mm)
A = 4-3/4"
(120 mm)
45° Cutting
angle
A = 4-1/2"
(115 mm)
A = 3-13/16"
(98 mm)
3-3/4" x 4-1/8"
(95 mm x 105 mm)
A = 4-1/8"
(105 mm)
OPERATION
WARNING: To reduce the risk of serious personal
injury, turn unit off and disconnect it from
power source before making any adjustments or
removing/installing attachments or accessories.
An accidental start-up can causeinjury.
Proper Hand Position (Fig. B)
WARNING: To reduce the risk of serious personal injury,
ALWAYS use proper hand position as shown.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of serious personal injury,
ALWAYS hold securely in anticipation of a sudden
reaction.
Proper hand position requires one hand on the operating
handle
17
.
Fig. B
17

ENGLISH
6
Carrying the Chop Saw (Fig. A)
Fold down unit to position where you can carry the saw.
Push in lock pin
1
to lock armdown. Always carry the saw
using the carrying handle
18
.
Unlocking (Fig. A)
To unlock tool and raise head, depress motor arm slightly
and pull lock pin
1
out. Motor arm will then pivotupward.
Mounting (Fig. A)
CAUTION: Tool must be supported on stable, level,
non-skid surface to prevent unexpected movement
whenoperating.
1. Drill holes through the work surface that align the base
of the chopsaw.
2. Insert two 5/16" (M10) bolts down through the
mounting holes
16
in the base and through holes
in mounting surface. The approximate length of the
screws should be the thickness of the mounting surface
plus 4" (102mm).
Spark Deflector Adjustment (Fig. A)
WARNING: Do not touch the spark deflector
during or immediately after operation as it
becomes hot and may cause skin burn.
To best deflect sparks away from surrounding persons and
materials, loosen the spark deflector screw
2
, adjust the
spark deflector
3
and then retighten screw. Do not allow
cordset to come into contact with deflector or sparks as
damage to cordset mayoccur.
Lock-Off Trigger Switch (Fig. A)
To turn the saw on, push the lock-off lever
14
to the left,
then depress the lock-off trigger switch
13
. The saw will
run while the switch is depressed. Allow the blade to spin
up to full operating speed before making the cut. To turn
the saw off, release the switch. Keep hands and material
away from the wheel until it has coasted to a stop. Allow
the blade to stop before raising the saw head. There is no
provision for locking the switchon.
Material Clamping and Supporting
(Fig. C, D)
• Angles are best clamped and cut with both legs resting
againstbase.
• A spacer block slightly narrower than the workpiece can
be used to increase wheel utilization (Fig.C).
• Long workpieces must be supported by a block so it will
be level with top of base (Fig. D). The cut off end should
be free to fall downward to avoid wheelbinding.
Diameter of workpiece
Fig. C
Width of space block
Space block
Fig. D
Block
Cut-off end
Vise Operation (Fig. A)
The vise
6
has a quick-travel feature. To release the
vise when it is clamped tightly, turn the crank
8
counterclockwise one or two times to remove clamping
pressure. Lift vise lever
9
up. Pull crank assembly out as far
as desired. Vise may be pushed forward into work without
cranking. Lower vise lever then tighten vise
6
on work by
usingcrank.
Fence Operation (Fig. A, E, F)
WARNING: Turn off and unplug the tool before
making any adjustments or removing or
installing attachments or accessories. Be sure the
trigger switch is in the OFFposition.
The fence
5
can be adjusted two ways: to change desired
cutting angle and to change spacing between the fence
andvise.
To Change the Desired Cutting Angle
Use the 5/16" (8mm) hex key
7
provided to loosen (do
not remove) the two fence bolts
15
. Align the desired
angle indicator line with the slot line
26
in the base
4
.
Securely tighten both fence bolts before use. For more
accurate square cuts, disconnect the power supply, loosen
the two fence bolts, push arm down until wheel extends
into base. Place a square against the wheel and adjust fence
against the square. Securely tighten both fence bolts before
use. When making a miter cut, the vise
6
may not clamp
securely, depending on the thickness of the workpiece and
the miter angle. Other aids (such as spring, bar or C-clamps)
will be necessary to secure the workpiece to the fence when
making thesecuts.

ENGLISH
7
Fig. E
6
5
15
Fig. F
5
15
26
Removal and Installation of Wheels
(Fig. G, H)
WARNING: Turn off and unplug the tool before
making any adjustments or removing or
installing attachments or accessories. Be sure the
trigger switch is in the OFF position. Do not make
any adjustment while the wheel is in motion. Do not
make any adjustment while chop saw is plugged into
powersupply.
WARNING: Use only bonded reinforced cut-off wheels
for your power tool. A bonded reinforced wheel is
defined as a grinding wheel consisting of abrasive
particles bonded together with various substances
specifically for cutting steelmaterials.
WARNING: Always use gloves when
handlingwheels.
WARNING: Handle and store all abrasive wheels
carefully to prevent damage from thermal shock, heat,
mechanical damage, etc. Store in a dry protected area
free from high humidity, freezing temperatures or
extreme temperaturechanges.
WARNING: Do not impact the wheel, and do not use
a wheel that has been dropped or impacted. Do not
use a chipped, deformed or damagedwheel.
1. Push in spindle lock
12
and rotate wheel
10
by hand
until wheel lock lever engages slot in inside flange
27
to lock wheel. Loosen the bolt
19
counterclockwise in
the center of the abrasive wheel with the 5/16" (8mm)
hex key
7
. Bolt has right-handthread.
Fig. G
12
2. Remove the bolt
19
, washer
20
, outside flange
21
and old wheel
10
.
Fig. H
19
20
21
10
27
3. Make sure flange surfaces are clean and flat. Install the
new abrasive wheel by reversing the abovesteps.
4. For safe operation, securely tighten bolt
19
to firmly
secure the abrasive wheel
10
in between inner
18
and
outer flanges
21
. Do not overtightenbolt
19
.
WARNING: Check the work surface that the chop saw
rests on when replacing with a new abrasive wheel. It
is possible that the wheel may contact ANY ITEMS OR
STRUCTURE THAT EXTENDS ABOVE work surface
(under the base) when the arm is fullylowered.
Operation Tips for More Accurate Cuts
• Allow the wheel to do the cutting. Excessive force will
cause the wheel to glaze reducing cutting efficiency
and/or to deflect causing inaccuratecuts.
• Properly adjust fenceangle.
• Make sure material is laying flat acrossbase.
• Properly clamp material to avoid movement
andvibration.
Motor Brush Inspection and Replacement
(Fig. I, J)
BE SURE TOOL IS UNPLUGGED BEFORE INSPECTING
BRUSHES. Brushes should be regularly inspected for wear.
To inspect brushes, unscrew the two end cap screws
22
and remove the end cap
23
. To remove each brush
24
,
first unplug the shunt wire terminal connection
25
. Then

ENGLISH
8
carefully back the brush spring out of the brush box and
remove brush. Brushes should slide freely in brush box.
If brushes are worn down to 5/16" (8 mm) as shown in
FigureJ, they should bereplaced.
To reinstall each brush, carefully back the spring out of the
brush box, insert the brush and return the spring making
sure it is pressing on the brush and not touching the brush
box. Reconnect shunt wire terminal, then replace the end
cap and twoscrews.
Fig. I
23
22
24
25
FIg. J
5/16"
(8mm)
24
MAINTENANCE
WARNING: To reduce the risk of serious personal
injury, turn unit off and disconnect it from
power source before making any adjustments or
removing/installing attachments or accessories.
An accidental start-up can causeinjury.
Cleaning
WARNING: Blow dirt and dust out of all air vents with
clean, dry air at least once a week. To minimize the risk
of eye injury, always wear ANSI Z87.1 approved eye
protection when performingthis.
WARNING: Never use solvents or other harsh
chemicals for cleaning the non-metallic parts of
the tool. These chemicals may weaken the plastic
materials used in these parts. Use a cloth dampened
only with water and mild soap. Never let any liquid
get inside the tool; never immerse any part of the tool
into aliquid.
Accessories
WARNING: Since accessories, other than those
offered by
DeWALT
, have not been tested with this
product, use of such accessories with this tool could be
hazardous. To reduce the risk of injury, only
DeWALT
recommended accessories should be used with
thisproduct.
Recommended accessories for use with your tool
are available at extra cost from your local dealer or
authorized service center. If you need assistance in
locating any accessory, please contact
DeWALT
Industrial
Tool Co., 701East Joppa Road, Towson, MD 21286, call
1-800-4-
DeWALT
(1-800-433-9258) or visit our website:
www.dewalt.com.
Repairs
WARNING: To assure product SAFETY and
RELIABILITY, repairs, maintenance and adjustment
should be performed by a
DeWALT
factory service
center or a
DeWALT
authorized service center. Always
use identical replacementparts.
Register Online
Thank you for your purchase. Register your product nowfor:
• WARRANTY SERVICE: Registering your product will
help you obtain more efficient warranty service in case
there is a problem with yourproduct.
• CONFIRMATION OF OWNERSHIP: In case of
an insurance loss, such as fire, flood or theft, your
registration of ownership will serve as your proof
ofpurchase.
• FOR YOUR SAFETY: Registering your product will
allow us to contact you in the unlikely event a safety
notification is required under the Federal Consumer
SafetyAct.
Register online at www.dewalt.com/register.
Three Year Limited Warranty
DeWALT
will repair, without charge, any defects due to
faulty materials or workmanship for three years from
the date of purchase. This warranty does not cover part
failure due to normal wear or tool abuse. For further detail
of warranty coverage and warranty repair information,
visit www.dewalt.com or call 1-800-4-
DeWALT
(1-800-
433-9258). This warranty does not apply to accessories
or damage caused where repairs have been made
or attempted by others. THIS LIMITED WARRANTY IS
GIVEN IN LIEU OF ALL OTHERS, INCLUDING THE IMPLIED
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, AND EXCLUDES ALL INCIDENTAL
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. Some states do not allow
limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts or the
exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential
damages, so these limitations may not apply to you. This
warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may have
other rights which vary in certain states orprovinces.
In addition to the warranty,
DeWALT
tools are covered
byour:
1 YEAR FREE SERVICE
DeWALT
will maintain the tool and replace worn parts
caused by normal use, for free, any time during the first year
afterpurchase.
90 DAY MONEY BACK GUARANTEE
If you are not completely satisfied with the performance of
your
DeWALT
Power Tool, Laser, or Nailer for any reason, you

ENGLISH
9
can return it within 90 days from the date of purchase with
a receipt for a full refund – no questionsasked.
LATIN AMERICA: This warranty does not apply to products
sold in Latin America. For products sold in Latin America,
see country specific warranty information contained in
the packaging, call the local company or see website for
warrantyinformation.
FREE WARNING LABEL REPLACEMENT: If your warning
labels become illegible or are missing, call 1-800-4-
DeWALT
(1-800-433-9258) for a freereplacement.

FRANÇAIS
10
Définitions : symboles et termes d'alarmes sécurité
Ces guides d'utilisation utilisent les symboles et termes d'alarmes sécurité suivants pour vous prévenir de situations
dangereuses et de risques de dommages corporels ou matériels.
DANGER: indique une situation dangereuse imminente qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, entraînera la mort ou des
blessuresgraves.
AVERTISSEMENT: indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, pourrait entraîner la
mort ou des blessuresgraves.
ATTENTION: indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, pourrait entraîner des
blessures légères oumodérées.
(Si utilisé sans aucun terme) Indique un message propre à la sécurité.
AVIS : indique une pratique ne posant aucun risque de dommages corporels mais qui par contre, si rien n’est fait
pour l’éviter, pourrait poser des risques de dommages matériels.
AVERTISSEMENT : lire tous les avertissements
de sécurité et toutes les directives. Le non-respect
des avertissements et des directives pourrait se
solder par un choc électrique, un incendie et/ou une
blessuregrave.
AVERTISSEMENT : afin de réduire le risque de
blessures, lire le mode d’emploi del’outil.
Pour toute question ou remarque au sujet de cet outil
ou de tout autre outil
DeWALT
, composez le numéro
sans frais : 1-800-4-
DeWALT
(1-800-433-9258).
1
Tige de blocage
2
Vis du déflecteur contre
les étincelles
3
Déflecteur contre les
étincelles
4
Base
5
Guide
6
Étau
7
Clé hexagonale 8mm
(5/16po)
8
Manivelle
9
Levier de l’étau
10
Meule
11
Protecteur
12
Verrou de la tige
13
Gâchette
14
Levier de verrouillage
15
Boulons du guide
16
Trous de montage
17
Poignée de manœuvre
18
Poignée de transport
Français (traduction de la notice d’instructions originale)
Fig. A
4
5
6
7
8
10
11
12
17
9
9
16
16
16
13
15
2
3
1
14
18

FRANÇAIS
11
AVERTISSEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX SUR LA
SÉCURITÉ DES OUTILS
AVERTISSEMENT: lisez tous les avertissements de
sécurité, toutes les instructions, les illustrations
et les caractéristiques fournis avec cet outil
électrique. Ne pas suivre toutes les instructions
comprises aux présentes peut conduire à un choc
électrique, un incendie et/ou des blessuresgraves.
CONSERVER TOUS LES
AVERTISSEMENTS ET TOUTES
LES DIRECTIVES POUR UN
USAGE ULTÉRIEUR
Le terme « outil électrique » cité dans les avertissements se
rapporte à votre outil électrique à alimentation sur secteur
(avec fil) ou par piles (sansfil).
1) Sécurité du lieu de travail
a ) Tenir l’aire de travail propre et bien éclairée.
Les lieux encombrés ou sombres sont propices
auxaccidents.
b ) Ne pas faire fonctionner d’outils électriques
dans un milieu déflagrant, tel qu’en présence de
liquides, de gaz ou de poussières inflammables.
Les outils électriques produisent des étincelles qui
pourraient enflammer la poussière ou lesvapeurs.
c ) Éloigner les enfants et les personnes à proximité
pendant l’utilisation d’un outil électrique. Une
distraction pourrait en faire perdre la maîtrise à
l’utilisateur.
2) Sécurité en matière d’électricité
a ) Les fiches des outils électriques doivent
correspondre à la prise. Ne jamais modifier la
fiche d’aucune façon. Ne jamais utiliser de fiche
d’adaptation avec un outil électrique mis à la
terre. Le risque de choc électrique sera réduit par
l’utilisation de fiches non modifiées correspondant à
laprise.
b ) Éviter tout contact physique avec des surfaces
mises à la terre comme des tuyaux, des
radiateurs, des cuisinières et des réfrigérateurs.
Le risque de choc électrique est plus élevé si votre corps
est mis à laterre.
c ) Ne pas exposer les outils électriques à la pluie ou
à l’humidité. La pénétration de l’eau dans un outil
électrique augmente le risque de chocélectrique.
d ) Ne pas utiliser le cordon de façon abusive.
Ne jamais utiliser le cordon pour transporter,
tirer ou débrancher un outil électrique. Tenir le
cordon éloigné de la chaleur, de l’huile, des bords
tranchants et des pièces mobiles. Les cordons
endommagés ou enchevêtrés augmentent les risques
de chocélectrique.
e ) Pour l’utilisation d’un outil électrique à
l’extérieur, se servir d’une rallonge convenant à
cette application. L’utilisation d’une rallonge conçue
pour l’extérieur réduira les risques de chocélectrique.
f ) S’il est impossible d’éviter l’utilisation d’un
outil électrique dans un endroit humide,
brancher l’outil dans une prise ou sur un circuit
d’alimentation dotés d’un disjoncteur de fuite à
la terre (GFCI). L’utilisation de ce type de disjoncteur
réduit les risques de chocélectrique.
3) Sécurité personnelle
a ) Être vigilant, surveiller le travail effectué et faire
preuve de jugement lorsqu’un outil électrique
est utilisé. Ne pas utiliser d’outil électrique en
cas de fatigue ou sous l’influence de drogues,
d’alcool ou de médicaments. Un simple moment
d’inattention en utilisant un outil électrique peut
entraîner des blessures corporellesgraves.
b ) Utiliser des équipements de protection
individuelle. Toujours porter une protection
oculaire. L’utilisation d’équipements de protection
comme un masque antipoussière, des chaussures
antidérapantes, un casque de sécurité ou des
protecteurs auditifs lorsque la situation le requiert
réduira les risques de blessurescorporelles.
c ) Empêcher les démarrages intempestifs. S’assurer
que l’interrupteur se trouve à la position
d’arrêt avant de relier l’outil à une source
d’alimentation et/ou d’insérer un bloc-piles, de
ramasser ou de transporter l’outil. Transporter
un outil électrique alors que le doigt repose sur
l’interrupteur ou brancher un outil électrique dont
l’interrupteur est à la position de marche risque de
provoquer unaccident.
d ) Retirer toute clé de réglage ou clé avant de
démarrer l’outil. Une clé ou une clé de réglage
attachée à une partie pivotante de l’outil électrique
peut provoquer des blessurescorporelles.
e ) Ne pas trop tendre les bras. Conserver
son équilibre en tout temps. Cela permet
de mieux maîtriser l’outil électrique dans les
situationsimprévues.
f ) S’habiller de manière appropriée. Ne pas porter
de vêtements amples ni de bijoux. Garder les
cheveux, les vêtements et les gants à l’écart des
pièces mobiles. Les vêtements amples, les bijoux ou
les cheveux longs risquent de rester coincés dans les
piècesmobiles.
g ) Si des composants sont fournis pour le
raccordement de dispositifs de dépoussiérage
et de ramassage, s’assurer que ceux-ci sont bien
raccordés et utilisés. L’utilisation d’un dispositif de
dépoussiérage peut réduire les dangers engendrés par
lespoussières.
h ) Ne pas laisser votre connaissance acquise suite
l’utilisation fréquente des outils vous permettre
de baisser la garde et ignorer les principes de
sécurité de l’outil. Un acte irréfléchi peut causer une
blessure grave en une fraction deseconde.

FRANÇAIS
12
4) Utilisation et entretien d’un
outil électrique
a ) Ne pas forcer un outil électrique. Utiliser l’outil
électrique approprié à l’application. L’outil
électrique approprié effectuera un meilleur travail,
de façon plus sûre et à la vitesse pour laquelle il a
étéconçu.
b ) Ne pas utiliser un outil électrique dont
l’interrupteur est défectueux. Tout outil électrique
dont l’interrupteur est défectueux est dangereux et
doit êtreréparé.
c ) Débranchez la fiche de la prise électrique et, si
amovible, retirez le bloc-piles de l’outil avant
d’effectuer tout ajustement, changement et
entreposage de celui-ci. Ces mesures préventives
réduisent les risques de démarrage accidentel de
l’outilélectrique.
d ) Ranger les outils électriques hors de la portée
des enfants et ne permettre à aucune personne
n’étant pas familière avec un outil électrique ou
son mode d’emploi d’utiliser cet outil. Les outils
électriques deviennent dangereux entre les mains
d’utilisateursinexpérimentés.
e ) Gardez les poignées et surfaces d’emprise
propres et libres de tout produit lubrifiant.
Vérifier si les pièces mobiles sont mal alignées ou
coincées, si des pièces sont brisées ou présentent
toute autre condition susceptible de nuire au bon
fonctionnement de l’outil électrique. En cas de
dommage, faire réparer l’outil électrique avant
toute nouvelle utilisation. Beaucoup d’accidents
sont causés par des outils électriques malentretenus.
f ) S’assurer que les outils de coupe sont aiguisés et
propres. Les outils de coupe bien entretenus et affûtés
sont moins susceptibles de se coincer et sont plus
faciles àmaîtriser.
g ) Utiliser l’outil électrique, les accessoires, les
forets, etc. conformément aux présentes
directives en tenant compte des conditions de
travail et du travail à effectuer. L’utilisation d’un
outil électrique pour toute opération autre que celle
pour laquelle il a été conçu estdangereuse.
h ) Garder vos mains et les surfaces de prise sèches,
propres et libres de graisse et de poussière. Les
mains et les surfaces de prise glissante ne permettent
pas la manutention et le contrôle sécuritaires de l’outil
dans les situationsimprévues.
5) Réparation
a ) Faire réparer l’outil électrique par un réparateur
professionnel en n’utilisant que des pièces de
rechange identiques. Cela permettra de maintenir
une utilisation sécuritaire de l’outil électriques.Ne
jamais réparer des blocs-piles endommagés. La
réparation de blocs-piles doit seulement être effectuée
par le fabricant ou les fournisseurs de serviceautorisé.
Consignes de sécurité pour les machines
à tronçonner
1) Avertissements de sécurité pour les
machines à tronçonner
a ) Placez-vous et les passants à l’écart de l’axe de
la meule en rotation. Le protecteur aide à protéger
l’utilisateur des fragments de meules brisées et du
contact accidentel avec lameule.
b ) Utilisez seulement des meules à tronçonner
renforcées agglomérées pour votre outil
électrique. Le fait qu’un accessoire peut être fixé à
votre outil n’assure pas une utilisationsécuritaire.
c ) La vitesse nominale de l’accessoire doit être au
moins égale à la vitesse maximale indiquée sur
l’outil électrique. Les accessoires qui fonctionnent
plus rapidement que leur vitesse nominale peuvent se
briser et voler enéclats.
d ) Les meules doivent être utilisées seulement pour
les applications recommandées. Par exemple:
ne pas meuler avec le côté de la meule de coupe.
Les meules de coupe sont conçues pour le meulage
périphérique, les forces latérales appliquées sur ces
meules peuvent faire en sorte qu’elleséclatent.
e ) Utilisez toujours des brides de meules non
endommagées ayant le bon diamètre pour
la meule sélectionnée. Les brides de meules
appropriées soutiennent la meule réduisant ainsi la
possibilité d’un bris de lameule.
f ) Le diamètre extérieur et l’épaisseur de votre
accessoire doivent être conformes à la capacité
nominale de votre outil. Les accessoires ayant
un format incorrect ne peuvent pas être gardés ou
contrôlés de façonappropriée.
g ) La taille de l’axe des meules et des brides
doit bien s’ajuster s’ajuster à la tige de l’outil
électrique. Les meules et les brides ayant de trous
qui ne correspondent pas au matériel de montage
de l’outil électrique manqueront d’équilibre, vibreront
de façon excessive ou peuvent entraîner une perte
decontrôle.
h ) Ne pas utiliser de meules endommagées. Avant
chaque utilisation, inspectez les meules pour
des copeaux et des fissures. Si vous échappez
l’outil ou une meule, inspectez pour vérifier s’il y
a des dommages ou installez un accessoire non
endommagé. Après avoir inspecté et installé la
meule, placez-vous et les passants à distance
de la zone de rotation de la meule et faites
fonctionner l’outil électrique à une vitesse à vide
pendant une minute. Les meules endommagées se
briseront normalement durant la durée dutest.
i ) Portez un équipement de protection individuelle.
Selon l’application, utilisez un masque de
protection ou des lunettes de sécurité. Selon
les besoins, portez un masque antipoussières,
une protection auditive, des gants et un tablier
pouvant arrêter de petits fragments de la pièce

FRANÇAIS
13
de travail ou abrasifs. La protection des yeuxdoit
être en mesure d’arrêter les débris volants générés
par diverses opérations. Le masque antipoussières
ou le respirateur doit être en mesure de filtrer les
particules générées par votre utilisation. L’exposition
prolongée à du bruit d’intensité élevée peut causer une
perteauditive.
j ) Gardez les passants à une distance sécuritaire
de l’aire de travail. Toute personne entrant dans
l’aire de travail doit porter un équipement de
protection individuel. Les fragments de la pièce
de travail ou d’une meule brisée peuvent s’envoler
et peuvent causer une blessure au-delà de l’aire
immédiate de l’opération.
k ) Placez le cordon à l’écart de l’accessoire en
rotation. Si vous perdez le contrôle, le cordon peut
être coupé ou accroché et votre main ou votre bras
peut être tiré dans la meule enrotation.
l ) Nettoyez régulièrement les évents de l’outil
électrique. Le ventilateur du moteur peut
produire de la poussière à l’intérieur du boîtier et
l’accumulation excessive de métal fritté peut causer
des chocsélectriques.
m ) Ne pas utiliser l’outil électrique près de
matières inflammables. Ne pas utiliser l’outil
électrique pendant qu’il est placé sur une
surface combustible comme le bois. Des étincelles
pourraient enflammer cesmatières.
n ) Ne pas utiliser des accessoires qui nécessitent des
liquides réfrigérants. Utiliser de l’eau ou d’autres
liquides réfrigérants peut entraîner une électrocution
ou un chocélectrique.
o ) Vérifiez les pièces endommagées. Avant
l’utilisation ultérieure de l’outil, un protecteur
ou une autre pièce qui est endommagé doit
être soigneusement vérifié afin de déterminer
s’il fonctionnera bien et s’il effectuera la
fonction prévue. Vérifiez l’alignement des pièces
en mouvement, le bris des pièces, le montage et
tout autre état qui peut affecter son utilisation. Tout
protecteur ou toute pièce endommagé devrait être
adéquatement réparé ouremplacé.
2) Avertissements de recul intempestif
et autres dangers
Le rebond est une réaction soudaine d’une meule en
rotation coincée ou accrochée. Le coinçage ou l’accrochage
entraîne un blocage rapide de la meule en rotation qui à son
tour entraîne l’outil de coupe non contrôlé à être forcé vers
le haut vers l’utilisateur.
Par exemple, si une meule abrasive est accrochée ou
coincée dans la pièce de travail, le bord de la meule qui
est entré dans le point de coincement peut creuser la
surface du matériau causant la chute ou l’éjection de la
meule. Les meules abrasives peuvent aussi se briser dans
cesconditions.
Le rebond est le résultat d’une mauvaise utilisation de
l’outil électrique et/ou de procédures ou de conditions de
fonctionnement incorrectes et il peut être évité en prenant
les précautions appropriées définies ci-dessous :
a ) Maintenez solidement l’outil électrique et placez
votre corps et votre bras pour vous permettre
de résister aux forces des rebonds. L’utilisateur
peut contrôler les forces des rebonds si les précautions
appropriées sontprises.
b ) Ne pas placer votre corps en ligne avec la meule
en rotation. Si un rebond se produit, il poussera
l’unité de coupe vers le haut vers l’utilisateur.
c ) Ne pas fixer une scie à chaîne, une lame de
sculpture de bois, une meule diamantée
segmentée ou une lame de scie dentée. Ces lames
créent des rebonds et une perte de contrôlefréquents.
d ) Ne pas bloquer la meule ou appliquer une
pression excessive. Ne pas tenter de faire
une coupe dont la profondeur est excessive.
Surcharger la meule augmente la charge et la
prédisposition à la torsion ou au coinçage de la meule
dans la coupe et la possibilité de rebond ou de bris de
lameule.
e ) Lorsque la meule se coince ou si vous cessez
une coupe pour quelque raison que ce soit,
éteignez l’outil électrique et tenez l’outil de coupe
sans bouger jusqu’à ce que la meule s’arrête
complètement. Ne jamais tenter de retirer la
meule de la coupe pendant que la meule est en
mouvement sinon un rebond peut se produire.
Examinez-la et prenez des mesures correctives pour
éliminer la cause du coinçage de lameule.
f ) Ne pas redémarrer la coupe dans la pièce à
travailler. Laissez la meule atteindre sa pleine
vitesse et entrez doucement dans la coupe à
nouveau. La meule peut se coincer, s’approcher ou
rebondir si l’outil électrique est redémarré dans la pièce
àtravailler.
g ) Soutenez toute pièce de travail surdimensionnée
afin de réduire le risque de coinçage ou de
rebond de la meule. Les grosses pièces à travailler
ont tendance à s’affaisser sous leur propre poids. Des
supports doivent être placés sous la pièce de travail
près de la ligne de coupe et près du bord de la pièce de
travail des deux côtés de lameule.
Consigne de sécurité supplémentaire
AVERTISSEMENT: porter SYSTEMATIQUEMENT
des lunettes de protection. Les lunettes courantes
NE sont PAS des lunettes de protection. Utiliser aussi
un masque antipoussières si la découpe doit en
produire beaucoup. PORTER SYSTÉMATIQUEMENT UN
ÉQUIPEMENT DE SÉCURITÉ HOMOLOGUÉ:
• Protection oculaire ANSI Z87.1 (CAN/CSA Z94.3);
• Protection auditive ANSI S12.6 (S3.19);
• Protection des voies respiratoires NIOSH/OSHA/
MSHA.
AVERTISSEMENT: les scies, meules, ponceuses,
perceuses ou autres outils de construction peuvent
produire des poussières contenant des produits

FRANÇAIS
14
chimiques reconnus par l’État californien pour causer
cancers, malformations congénitales ou être nocifs au
système reproducteur. Parmi ces produits chimiques,
on retrouve:
• Le plomb dans les peintures à base de plomb;
• La silice cristallisée dans les briques et le ciment,
ou autres produits de maçonnerie; et
• L’arsenic et le chrome dans le bois ayant subi un
traitementchimique.
Le risque associé à de telles expositions varie selon la
fréquence à laquelle on effectue ces travaux. Pour réduire
toute exposition à ces produits: travailler dans un endroit
bien aéré, en utilisant du matériel de sécurité homologué, tel
un masque antipoussières spécialement conçu pour filtrer les
particulesmicroscopiques.
• Limiter toute exposition prolongée avec les
poussières provenant du ponçage, sciage, meulage,
perçage ou toute autre activité de construction.
Porter des vêtements de protection et nettoyer à
l’eau savonneuse les parties du corps exposées. Le
fait de laisser la poussière pénétrer dans la bouche, les
yeux ou la peau peut favoriser l’absorption de produits
chimiquesdangereux.
AVERTISSEMENT: cet outil peut produire et/
ou répandre de la poussière susceptible de causer
des dommages sérieux et permanents au système
respiratoire. Utiliser systématiquement un appareil
de protection des voies respiratoires homologué par
le NIOSH ou l’OSHA. Diriger les particules dans le sens
opposé au visage et aucorps.
AVERTISSEMENT: pendant l’utilisation, porter
systématiquement une protection auditive
individuelle adéquate homologuée ANSI S12.6
(S3.19). Sous certaines conditions et suivant la durée
d’utilisation, le bruit émanant de ce produit pourrait
contribuer à une perte de l’acuitéauditive.
• Prendre des précautions à proximité des évents,
car ils cachent des pièces mobiles. Vêtements amples,
bijoux ou cheveux longs risquent de rester coincés dans
ces piècesmobiles.
• Pour la sécurité de l’utilisateur, utiliser une rallonge
de calibre adéquat (AWG, American Wire Gauge
[calibrage américain normalisé des fils électriques]).
Plus le calibre est petit, et plus sa capacité est grande. Un
calibre16, par exemple, a une capacité supérieure à un
calibre18. L’usage d’une rallonge de calibre insuffisant
causera une chute de tension qui entraînera perte de
puissance et surchauffe. Si plus d’une rallonge est utilisée
pour obtenir une certaine longueur, s’assurer que chaque
rallonge présente au moins le calibre de fil minimum. Le
tableau ci-dessous illustre les calibres à utiliser selon la
longueur de rallonge et l’intensité nominale indiquée sur
la plaque signalétique. En cas de doute, utiliser le calibre
suivant. Plus le calibre est petit, plus la rallonge peut
supporter decourant.
Calibre minimum pour les cordons d'alimentation
Volts
Longueur totale du cordon
d'alimentation en mètre (pieds)
120 V 7,6 (25) 15,2 (50) 30,5 (100) 45,7 (150)
240 V 15,2 (50) 30,5 (100) 61,0 (200) 91,4 (300)
Ampères
AWG
Plus que Pas plus
que
0 6 18 16 16 14
6 10 18 16 14 12
10 12 16 16 14 12
12 16 14 12 Non recommandé
L’étiquette apposée sur votre outil peut inclure les symboles
suivants. Les symboles et leur définition sont indiqués ci-après:
V ......................... volts
Hz ....................... hertz
min ..................... minutes
or DC ...... courant continu
...................... fabrication classe I
(mis à la terre)
…/min .............. par minute
BPM .................... battements par
minute
IPM ..................... impacts par minute
RPM .................... révolutions par
minute
sfpm ................... pieds linéaires par
minute (plpm)
SPM (FPM) ......... fréquence par
minute
A ......................... ampères
W ........................ watts
or AC ........... courant alternatif
or AC/DC .... courant alternatif
ou continu
...................... fabrication classe II
(double isolation)
n
o
....................... vitesse à vide
n ......................... vitesse nominale
...................... borne de terre
...................... symbole
d’avertissement
..................... radiation visible
..................... protection
respiratoire
.....................protection oculaire
.....................protection auditive
..................... lire toute la
documentation
CONSERVER CES CONSIGNES POUR
UTILISATION ULTÉRIEURE
Moteur
S’assurer que le bloc d’alimentation est compatible avec
l’inscription de la plaque signalétique.Une diminution de
tension de plus de 10 % provoquera une perte de puissance
et une surchauffe. Les outils
DeWALT
sont testés en usine; si
cet outil ne fonctionne pas, vérifier l’alimentationélectrique.
Brancher à l’alimentation électrique
Branchez ce produit dans une prise polarisée 120V, 15A.
Cet appareil est muni d’une fiche polarisée (une lame est
plus large que l’autre). Celle-ci ne pourra être branchée dans
une prise polarisée que dans un sens. Si la fiche ne s’insère
pas dans la prise, inversez-la. Si elle ne s’insère toujours
pas, appelez un électricien accrédité pour installer une
priseadéquate.
AVERTISSEMENT: ne jamais modifier la fiche
de quelque façon que ce soit. Si jamais le cordon
d’alimentation est endommagé, apportez l’outil
dans un centre de services autorisé D
eWALT
pour des
réparations ou unremplacement.

FRANÇAIS
15
DESCRIPTION (FIG. A)
AVERTISSEMENT: ne jamais modifier l’outil
électrique ni aucun de ses composants, car il y a
risques de dommages corporels oumatériels.
Reportez-vous en FigureA au début de ce manuel pour
obtenir la liste complète descomposants.
Usage prévu
Votre scie à tronçonner a été conçue pour la coupe de
matériaux en acier de diverses formes. Elle est conçue pour
être utilisée avec des abrasifs renforcés agglomérés. Les
lames diamantées ou TCT ne doivent pas être utilisées avec
cetoutil.
NE PAS les utiliser en milieu ambiant humide ou en
présence de liquides ou de gazinflammables.
Cette scie à tronçonner est un outil électrique professionnel.
NE PAS le laisser à la portée des enfants. Une supervision
est nécessaire auprès de tout utilisateur nonexpérimenté.
CARACTÉRISTIQUES
D28730
Tension
120V~
Fréquence
60 Hz
Ampères
15
Vitesse à vide
4000/min (rpm)
Diamètre de la meule
355 mm (14 po)
Épaisseur de la meule
3.0 mm (.12 po)
Diamètre de l’arbre
25.4 mm (1 po)
Poids net
15.5 kg (34.1 lbs)
ASSEMBLAGE ET AJUSTEMENTS
AVERTISSEMENT: pour réduire le risque de
blessures graves, éteindre l’outil et retirer le
débrancher avant d’effectuer tout réglage
et d’enlever ou d’installer tout accessoire. Un
démarrage accidentel peut provoquer desblessures.
Capacité de coupe
La large ouverture de l’étau et le point de pivotement élevé
offrent une capacité de coupe pour de nombreuses grandes
pièces. Utilisez le tableau de capacité de coupe afin de
déterminer la taille maximale totale des coupes qui peuvent
être faites avec une nouvellemeule.
ATTENTION: CERTAINS OBJETS DE FORMES
GRANDES, CIRCULAIRES OU IRRÉGULIÈRES
PEUVENT NÉCESSITER DES MESURES DE MAINTIEN
SUPPLÉMENTAIRES S’ILS NE PEUVENT PAS ÊTRE TENUS
DE FAÇON SÉCURITAIRE DANS L’ÉTAU.
ATTENTION: NE PAS COUPER LE MAGNÉSIUM OU DE
BOIS AVEC CET OUTIL.
Capacité de coupe recommandée
REMARQUE: La capacité affichée au tableau suppose qu’il
n’y a aucune usure de la meule et que la position du guide
estoptimale.
Forme de
la pièce de
travail
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
Angle de
coupe
à 90°
A = 125 mm
(4-7/8 po)
A = 115 mm
(4-1/2 po)
115 mm x 130 mm
(4-1/2 po x 5-1/8 po)
A = 120 mm
(4-3/4 po)
Angle de
coupe
à 45°
A = 115 mm
(4-1/2 po)
A = 98 mm
(3-13/16 po)
95 mm x 105 mm
(3-3/4 po x 4-1/8 po)
A = 105 mm
(4-1/8 po)
UTILISATION
AVERTISSEMENT: pour réduire le risque de
blessures graves, éteindre l’outil et retirer le
débrancher avant d’effectuer tout réglage
et d’enlever ou d’installer tout accessoire. Un
démarrage accidentel peut provoquer desblessures.
Position correcte des mains (Fig. B)
AVERTISSEMENT: pour réduire tout risque
de dommages corporels graves, adopter
SYSTÉMATIQUEMENT la position des mains illustrée.
AVERTISSEMENT: pour réduire tout risque
de dommages corporels graves, maintenir
SYSTÉMATIQUEMENT l’outil fermement pour
anticiper toute réaction soudaine.
La position correcte des mains requiert une main sur la
poignée principale
17
.
Fig. B
17
Transporter la scie à tronçonner (Fig. A)
Rabattez l’outil à la position où vous pouvez transporter la
scie. Poussez la tige de verrouillage
1
pour verrouiller le
bras vers le bas. Transportez toujours la scie à l’aide de la
poignée de transport
18
.
Déverrouillage (Fig. A)
Pour déverrouiller l’outil et lever la tête, appuyez légèrement
sur le bras du moteur et retirez la tige de verrouillage
1
. Le
bras du moteur pivotera ensuite vers lehaut.
Montage (Fig. A)
ATTENTION : l’outil doit être soutenu sur une
surface stable, plane et antidérapante afin d’éviter un
mouvement inattendu durant l’utilisation.

FRANÇAIS
16
1. Percez des trous dans la surface de travail qui aligne la
base de la scie àtronçonner.
2. Insérez deux boulons 5/16 po (M10) à travers les trous
de montage
16
dans la base et à travers les trous dans
la surface de montage. La longueur approximative
des vis doit correspondre à l’épaisseur de la surface de
montage plus 102mm (4 po).
Ajustement du déflecteur contre les
étincelles (Fig. A)
AVERTISSEMENT : Ne pas toucher le déflecteur
contre les étincelles durant ou immédiatement
après l’utilisation, car il devient chaud et il peut
causer des brûlures de la peau.
Pour mieux dévier les étincelles loin des personnes et des
matériaux dans les environs, dévissez la vis du déflecteur
contre les étincelles
2
, ajustez le déflecteur contre les
étincelles
3
, puis revissez la vis. Ne pas laisser le cordon
entrer en contact avec le déflecteur ou des étincelles
puisque cela peut endommager lecordon.
Gâchette de verrouillage (Fig. A)
Pour mettre la scie en marche, appuyez sur le levier de
verrouillage
14
, puis appuyez sur
13
la gâchette de
verrouillage. La scie fonctionnera tant que vous appuierez
sur la gâchette. Laissez tourner la lame à pleine vitesse de
fonctionnement avant de faire une coupe. Pour éteindre la
scie, relâchez la gâchette. Gardez vos mains et le matériau à
l’écart de la meule jusqu’à ce qu’elle s’arrête. Laissez la lame
s’arrêter avant de lever la tête de la scie. Rien n’est prévu
pour verrouiller la gâchette enmarche.
Serrer et maintenir le matériau
(Fig. C, D)
• Les angles sont mieux serrés et coupés avec les deux
pattes s’appuyant contre labase.
• Un bloc d’espacement légèrement plus étroit que
la pièce de travail peut être utilisé pour augmenter
l’utilisation de la meule (Fig.C).
• Les longues pièces de travail doivent être soutenues par
un bloc pour être au même niveau que le dessus de la
base (Fig. D). L’extrémité tronçonnée doit être libre de
tomber afin d’éviter le coinçage de lameule.
Diamètre de la pièce de travail
Fig. C
Largeur du bloc d’espacement
Bloc
d’espacement
Fig. D
Extrémité
tronçonnée
Bloc
Utilisation de l’étau (Fig. A)
L’étau
6
a une fonction de déplacement rapide. Pour
dégager l’étau lorsqu’il est très serré, tournez la manivelle
8
dans le sens contraire des aiguilles d’une montre un ou deux
fois pour enlever la pression de serrage. Levez le levier de
l’étau
9
. Retirez l’assemblage de la manivelle aussi loin que
vous le désirez. L’étau peut être poussé vers l’avant dans le
travail sans tourner la manivelle. Baissez le levier de l’étau,
puis serrez l’étau
6
sur le travail à l’aide de lamanivelle.
Utilisation du guide (Fig. A, E, F)
AVERTISSEMENT : éteignez et débranchez
l’outil avant d’effectuer tout ajustement ou
de retirer ou d’installer des fixations ou des
accessoires. Assurez-vous que la gâchette est en
positionArrêt.
Le guide
5
peut être ajusté de deux façons: en changeant
l’angle de coupe désiré et en changeant l’espace entre le
guide et l’étau.
Pour changer l’angle de coupe désiré
Utilisez la clé hexagonale 5/16 po (8mm)
7
fournie pour
dévisser (ne pas retirer) les deux boulons du guide
15
.
Alignez la ligne de l’indicateur de l’angle désiré avec la
ligne de la fente
26
dans la base
4
. Serrez solidement les
boulons du guide avant l’utilisation. Pour des coupes carrées
plus précises, débranchez l’alimentation. Dévissez les deux
boulons du guide. Poussez le bras vers le bas jusqu’à ce que
la meule s’étende dans la base. Placez un carré contre la
meule et ajustez le guide contre le carré. Serrez solidement
les boulons du guide avant l’utilisation. Lorsque vous
effectuez une coupe d’onglet, l’étau
6
peut ne pas se serrer
solidement, selon l’épaisseur de la pièce de travail l’angle de
l’onglet. D’autres accessoires aidants (comme un ressort, une
barre ou un étau en C) seront nécessaires pour fixer la pièce
de travail au guide lorsque vous effectuez cescoupes.

FRANÇAIS
17
Fig. E
6
5
15
Fig. F
5
15
26
Retrait et installation des meules
(Fig. G, H)
AVERTISSEMENT : éteignez et débranchez l’outil
avant d’effectuer tout ajustement ou de retirer
ou d’installer des fixations ou des accessoires.
Assurez-vous que la gâchette est en position
Arrêt. Ne pas faire d’ajustement lorsque la meule est
en mouvement. Ne pas faire d’ajustement lorsque la
scie à tronçonner est branchée à l’alimentation.
AVERTISSEMENT : utilisez seulement des meules
à tronçonner renforcées agglomérées pour votre
outil électrique. Une meule renforcée agglomérée
correspond à une meule composée de particules
abrasives agglomérées ensemble avec différentes
substances spécifiquement pour couper des matériaux
enacier.
AVERTISSEMENT : utilisez toujours des gants
lorsque vous manipulez lesmeules.
AVERTISSEMENT : manipulez et remisez tous les
meules abrasives pour prévenir tout dommage de
choc mécanique, de chaleur intensive, etc. Entreposez
dans un endroit protégé de l’humidité, du gel ou de
changements brusques detempérature.
AVERTISSEMENT : ne pas causer d’impact sur la
meule et ne pas utiliser une meule qui été échappée
ou a reçu un impact. Ne pas utiliser une meule écaillée,
déformée ouendommagée.
1. Poussez le verrou de la tige
12
et tournez la meule
10
à la main jusqu’à ce que le levier de verrouillage
s’engage dans la bride interne
27
pour verrouiller la
meule. Dévissez le boulon
19
dans le sens contraire des
aiguilles d’une montre au centre de la meule abrasive
avec une clé hexagonale 8mm (5/16 po)
7
. Le boulon
a un filetage àdroite.
Fig. G
12
2. Retirez le boulon
19
, la rondelle
20
, la bride
externe
21
et la vieille meule
10
.
Fig. H
19
20
21
10
7
3. Assurez-vous que les surfaces des brides sont propres et
plates. Installez la nouvelle meule abrasive en inversant
les étapesprécédentes.
4. Pour une utilisation sécuritaire, vissez solidement le
boulon
19
pour fixer solidement la meule abrasive
10
entre les brides interne
18
et externe
21
. Ne pas trop
serrer le boulon
19
.
AVERTISSEMENT: vérifiez la surface de travail sur
laquelle est déposée la scie à tronçonner lorsque
vous mettez une nouvelle meule abrasive. Il est
possible que la meule puisse entrer en contact avec
TOUT ÉLÉMENT OU STRUCTURE DÉPASSANT
la surface de travail (sous la base) lorsque le bras est
entièrementbaissé.
Conseils d’utilisation pour des coupes plus
précises
• Laissez la meule faire la coupe. Une force excessive
entraînera l’émoussement de la meule réduisant
l’efficacité de la coupe et/ou la déviation entraînant des
coupesimprécises.
• Ajustez bien l’angle duguide.

FRANÇAIS
18
• Assurez-vous que le matériau est déposé à plat contre
labase.
• Serrez bien le matériau afin d’éviter le mouvement et
lavibration.
Inspection et remplacement des brosses
du moteur (Fig. I, J)
ASSUREZ-VOUS QUE L’OUTIL EST DÉBRANCHÉ AVANT
D’INSPECTER LES BROSSES. Les brosses doivent être
régulièrement inspectées pour l’usure. Pour inspecter les
brosses, dévissez les deux vis du capuchon
22
et retirez le
capuchon
23
. Pour retirer chaque brosse
24
, débranchez
d’abord le branchement de la cosse de dérivation
25
.
Puis sortez soigneusement le ressort du porte-brosse et
retirez la brosse. Les brosses doivent glisser librement dans
le porte-brosse. Si les brosses sont usées jusqu’à 8mm
(5/16 po) comme illustré dans la Figure I, elles doivent
êtreremplacées.
Pour réinstaller chaque brosse, sortez soigneusement le
ressort du porte-brosse, insérez la brosse et remettez le
ressort en vous assurant d’appuyer sur la brosse et qu’il
ne touche pas le porte-brosse. Rebranchez la cosse de
dérivation, puis replacez le capuchon et les deuxvis.
Fig. I
23
22
24
25
FIg. J
8mm
(5/16po)
24
MAINTENANCE
AVERTISSEMENT: pour réduire le risque de
blessures graves, éteindre l’outil et retirer le
débrancher avant d’effectuer tout réglage
et d’enlever ou d’installer tout accessoire. Un
démarrage accidentel peut provoquer desblessures.
Nettoyage
AVERTISSEMENT : enlever les saletés et la poussière
hors des évents au moyen d’air comprimé propre et
sec, au moins une fois par semaine. Pour minimiser
le risque de blessure aux yeux, toujours porter une
protection oculaire conforme à la norme ANSI Z87.1
lors dunettoyage.
AVERTISSEMENT : ne jamais utiliser de solvants ni
d’autres produits chimiques puissants pour nettoyer
les pièces non métalliques de l’outil. Ces produits
chimiques peuvent affaiblir les matériaux de plastique
utilisés dans ces pièces. Utiliser un chiffon humecté
uniquement d’eau et de savon doux. Ne jamais laisser
de liquide pénétrer dans l’outil et n’immerger aucune
partie de l’outil dans unliquide.
Accessoires
AVERTISSEMENT : puisque les accessoires autres
que ceux offerts par
DeWALT
n’ont pas été testés
avec ce produit, leur utilisation pourrait s’avérer
dangereuse. Pour réduire le risque de blessures, utiliser
exclusivement les accessoires
DeWALT
recommandés
avec le présentproduit.
Les accessoires recommandés pour cet outil sont vendus
séparément au centre de service de votre région. Pour
obtenir de l’aide concernant l’achat d’un accessoire,
communiquer avec
DeWALT
Industrial Tool Co., 701 East
Joppa Road, Towson, MD 21286 aux États-Unis;
composer le 1 800 433-9258 (1 800 4-
DeWALT
) ou visiter
notre site Web : www.dewalt.com.
Réparations
AVERTISSEMENT: pour assurer la SÉCURITÉ et la
FIABILITÉ du produit, les réparations, l’entretien et
l’ajustement doivent être effectués par un centre de
services de l’usine
DeWALT
ou un centre de services
autorisé
DeWALT
. Utilisez toujours des pièces de
remplacementidentiques.
Registre en ligne
Merci pour votre achat. Enregistrez dès maintenant
votreprodui:
• RÉPARATIONS SOUS GARANTIE: cette carte remplie
vous permettra de vous prévaloir du service de
réparations sous garantie de façon plus efficace dans le
cas d’un probléme avec leproduit.
• CONFIRMATION DE PROPRIÉTÉ: en cas de perte
provoquée par un incendie, une inondation ou un vol,
cette preuve de propriété vous servira de preuve auprès
de votre compagnie d’assurances.
• SÉCURITÉ: l’enregistrement de votre produit
nous permettra de communiquer avec vous dans
l’éventualité peu probable de l’envoi d’un avis de
sécurité régi par la loi fédérale américaine de la
protection desconsommateurs.
Registre en ligne à www.dewalt.com/register.
Garantie limitée de trois ans
DeWALT
réparera, sans frais, tout produit défectueux
causé par un défaut de matériel ou de fabrication pour
une période de trois ans à compter de la date d’achat.
La présente garantie ne couvre pas les pièces dont la
défectuosité a été causée par une usure normale ou
l’usage abusif de l’outil. Pour obtenir de plus amples
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
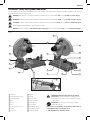 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
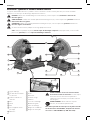 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
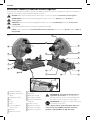 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
DeWalt D28730 Manuel utilisateur
- Catégorie
- Outils électroportatifs
- Taper
- Manuel utilisateur
dans d''autres langues
- English: DeWalt D28730 User manual
- español: DeWalt D28730 Manual de usuario
Documents connexes
-
DeWalt D28730 Manuel utilisateur
-
DeWalt D28710 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
DeWalt D28710 Manuel utilisateur
-
DeWalt DWC860W Manuel utilisateur
-
DeWalt D28715X Manuel utilisateur
-
DeWalt D28715 TYPE2 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Epson D28715 Manuel utilisateur
-
Epson D28715 Manuel utilisateur
-
DeWalt D28720 Manuel utilisateur



































