
0
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE

1
QUICKSTART GUIDE
Connect the unit with the electrode pads
Verbinden Sie das Gerät mit den Elektroden
Connectez l’appareil aux électrodes
Conecte el dispositivo a los parches
Place the electrode pads around the area to be treated
Coloque los electrodos alrededor del área a tratar
Placez les électrodes autour de la zone à traiter
Platzieren Sie die Elektroden um den Behandlungsbereich
Press and hold the ON button to switch the device on
Halten Sie die ON-Taste gedrückt, um einzuschalten
Appuyez sur le bouton ON pour allumer l’appareil
Presione y mantenga el botón ON para encenderlo
Regulate the output intensity for each channel
Regulieren Sie die Intensität für jeden Kanal
Réglez l’intensité pour chaque canal
Regule la intensidad en ambos canales
Press and hold the OFF button to switch the device off
Halten Sie die OFF-Taste gedrückt, um auszuschalten
Appuyez sur le bouton OFF pour éteindre l’appareil
Presione y mantenga el botón OFF para apagarlo
ON
Button P
Channel
2 UP
Channel
2 DOWN
Channel
1 UP
Channel
1 DOWN
OFF
Select the programme by pressing the button P
Wählen Sie ein Programm mit der P-Taste
Choisissez le programme avec le bouton P
Seleccione el programa, pulsando el botón P
1
2
3
4
5
6

2
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing perfect EMS. TensCare stands for high-quality,
thoroughly tested products for the applications in the areas of gentle
electrotherapy, muscle toning, continence management and pain relief
during labour.
Please read these instructions for use carefully and keep them for later
use, be sure to make them accessible to other users and observe the
information they contain.
Best regards,
Your TensCare Team

3
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................. 5
2. INTENDED USE ............................................................................................... 5
3. PERFECT EMS FEATURES ............................................................................ 5
4. HOW ‘EMS’ WORKS ........................................................................................ 6
5. HOW ‘TENS’ WORKS ...................................................................................... 7
6. CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS & CAUTIONS ....................................... 8
7. INFORMATION ABOUT THE PROGRAMME SETTINGS ............................. 11
8. PROGRAMMES ............................................................................................. 12
8.1. PROGRAMME SETTINGS ......................................................................... 12
8.2. PRESET PROGRAMMES .......................................................................... 13
8.3. MANUAL PROGRAMMES .......................................................................... 14
8.4. USING THE PROGRAMMES ..................................................................... 14
9. ELECTRODE PADS ....................................................................................... 16
9.1. PAD POSITIONING .................................................................................... 16
9.2. PAD ADVICE .............................................................................................. 17
9.3. EMS ELECTRODE PLACEMENT ............................................................... 18
10. CONTENT ...................................................................................................... 20
11. UNIT INFORMATION ..................................................................................... 21
11.1. CONTROLS & DISPLAY ......................................................................... 21
11.2. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS ................................................................ 22
12. SETTING UP AND USING THE PERFECT EMS .......................................... 24
12.1. INSTALLATION OF BATTERIES ............................................................. 24
12.2. CONNECTING LEAD WIRES .................................................................. 25
12.3. PREPARING FOR SESSION .................................................................. 25
12.4. TRAINING SESSION ............................................................................... 25
12.5. AFTER YOUR TRAINING SESSION ....................................................... 26
13. CLEANING & STORAGE ............................................................................... 26
14. EMC ............................................................................................................... 26
15. DISPOSAL OF WASTE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRODUCTS
(WEEE) .................................................................................................................... 27
16. ACCESSORIES ............................................................................................. 27
17. WARRANTY ................................................................................................... 27
18. TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................... 29
19. GENERAL SPECIFICATION .......................................................................... 30

4
SYMBOLS USED
TYPE BF APPLIED PART: Equipment providing a degree of protection against
electric shock, with isolated applied part. Indicates that this device has conductive
contact with the end user.
This symbol on the unit means “Refer to instructions for use”.
Temperature Limitation: indicates the temperature limits to which the medical
device can be safely exposed.
Lot Number: indicates the manufacturer’s batch code so that the batch or lot can
be identified.
Humidity Limitation: indicates the humidity limits to which the medical device can
be safely exposed.
Serial Number: indicates the manufacturer’s serial number so that a specific
medical device can be identified.
Do not dispose in household waste.
Catalogue Number: indicates the manufacturer’s catalogue number so that the
device can be identified.
Atmospheric Pressure: indicates the atmospheric limits to which the medical
device can be safely exposed.
Manufacturer Symbol
Date of Manufacture: indicates the date which the medical device was
manufactured. This is included within the serial number found on the device
(usually on the back of the device), either as “E/Year/Number” (YY/123456) or
“E/Month/Year/Number” (MM/YY/123456).
CE Mark
Medical Device
This medical device is indicated for home use.
Importer Symbol
This medical device is not water resistant and should be protected from liquids.
The first number 2: Protected against access to hazardous parts with a finger,
and the jointed test finger of 12 mm ø, 80 mm length, shall have adequate
clearance from hazardous parts, and protected against solid foreign objects of
12.5 mm ø and greater.
The second number 2: Protected against vertically falling water drops when
enclosure is tilted up to 15˚. Vertically falling drops shall have no harmful effects
when the enclosure is tilted at any angle up to 15˚ on either side of the vertical.

5
1. INTRODUCTION
Device Description & Principles of
Design
The perfect EMS unit provides muscle
toning, shaping and rehabilitation
through EMS, with additional pain relief
programmes using TENS to relieve
pain from injuries and muscle strain.
It sends a small and gentle stimulation
(similar to your natural nerve impulses)
to the muscles being treated via two or
four auto-adhesive electrode pads, in
order to help you to firm and tone your
body.
Muscle wastage: neuromuscular
facilitation, muscle re-education,
muscle training, prevention/slowing of
atrophy/hypotrophy and reduction of
spasticity.
Sports training: warm up, strength,
speed, power, resistance, endurance
and recovery.
2. INTENDED USE
Perfect EMS is a medical
device designed to be used in
the home healthcare environment to
improve muscle tone and bulk, as well
as provide symptomatic relief and
management of acute or chronic
localised pain and muscle pain. It is
suitable for use by all who can control
the device and understand the
instructions.
Do not use the device for any purpose
other than this intended use.
Warning: Not suitable for use
in children without medical
supervision.
3. PERFECT EMS
FEATURES
•Dual Channel
Two independent channels with four
electrode pads to treat two areas at the
same time.
•Comfortable Stimulation
Gentle stimulation with 90 small steps
of intensity provides fine yet powerful
performance.
•6 Preset Programmes
Including Warm Up, Endurance, Power
and Bulk.
•Manual TENS and EMS
Programmes
Enables the user to easily adjust and
save settings to suit personal needs.
•Treatment Timer
Enables the user to set the session
duration (between 10-90 mins) and
select manual parameters.
•Memory
Features 3 functions: programme
retention (automatically starts in the last
programme used), number of uses and
time of usage.
•Open Circuit Detection
Automatically resets the strength to
zero if the electrode pads are not
correctly applied.
•Automatic Keypad Lock
Automatic keypad locking prevents any
accidental changes in settings.

6
• Detachable Belt Clip
Enables the user to clip the unit onto a
belt.
• Large LCD Screen
Clearly shows the operation of the unit
and the parameters being used.
Note: The electrode pads need
to be applied directly to the skin
before the intensity increase
buttons will operate. If the perfect EMS
detects the unit is not properly
connected to you (for example if the
electrode pads or leads come loose)
then the unit switches the intensity to
zero. This safety feature prevents any
unpleasant changes in output.
4. HOW ‘EMS’ WORKS
E.M.S. stands for Electrical Muscle
Stimulation and has successfully been
used in medical rehabilitation and
training in competitive sports. EMS
produces intensive and effective
muscular contraction.
EMS is a complement to other physical
therapy and should always be
combined with active mobility, strength,
coordination and functional training.
In training, the technology for
electrotherapy is used for all kinds of
muscular exercise - warm-up, strength,
speed, power, resistance, endurance,
recovery and also for rehabilitation.
EMS is well known and works as an
excellent complement to regular
training.
Advantages of EMS
Use of EMS will help to tone and shape
the body by contracting the selected
muscle group. It is particularly
convenient for areas that are famous for
losing their shape and hard to exercise
such as the upper arms and the face.
Successful athletes all over the world
have discovered the advantages of
electrical muscle stimulation, such as
an increase of the local circulation and
the size of the muscle fibres.
How EMS Works
Muscular activity is produced by the
central and peripheral nervous systems
transmitting electrical stimuli to the
muscles of our body. EMS uses
external electrical impulses that work
through the skin to stimulate the nerves
supplying a specific muscle group.
This current then passes into the nerve
fibres controlling that part of the muscle
stimulating it to contract. So, electrical
stimulation (EMS) artificially activates a
muscle for you enabling to exercise the
muscles and, as with any kind of
exercise if performed regularly, build
strength and tone.
Different frequencies have different
effects; low frequencies (1-10 Hz)
coupled with long impulse times, for
example, have a purifying and relaxing
effect through individual contractions,
whereby the circulation in the treated
muscle is simultaneously improved and
removal of metabolic end products is
supported (lymphatic drainage).
In contrast, by means of a rapid
succession of contractions (fibrillation),

7
medium frequencies (20-50 Hz) can put
a high level of strain on the muscle, thus
promoting the muscular structure.
5. HOW ‘TENS’ WORKS
T.E.N.S. stands for Transcutaneous
Electrical Nerve Stimulation. T.E.N.S.
stimulates your body’s own natural
defences against pain, namely the
release of endorphins. TENS is totally
safe and has been used successfully by
thousands of pain sufferers.
TENS sends a gentle stimulation
through the skin which works in
TWO ways:
Pain Gate
It stimulates the
sensory nerves,
which carry touch
and temperature
signals. These
nerves go to the
same connections
in the spine as the
nerves carrying pain. A strong sensory
signal will block the pain signal
travelling up the spine to the brain. This
is known as closing the “Pain Gate” and
takes effect quite quickly after the unit
is switched on. When the gate is open,
pain messages get through to the brain
and we feel pain. When the gate is
closed, these pain messages are
blocked and we do not feel pain.
Evidence suggests that TENS produce
pain relief in a similar way to ‘rubbing
the pain better’. The pain gate can be
closed by activation of
mechanoreceptors through ‘rubbing the
skin’.
Scientifically, the pain gate works by the
release of a chemical in the synapse at
spinal level that inhibits transmission of
pain signal.
Endorphin Release
At low frequency
settings, and
slightly stronger
outputs, TENS
drives the motor
nerves to produce
a small repetitive
muscle
contraction. This is seen by the brain as
exercise, and this promotes the release
of endorphins - your body’s own natural
pain killer. The relief builds up and
normally takes about 40 minutes to
reach a maximum level which can last
for hours after the machine is switched
off.
By using TENS, you can expect to
achieve a significant reduction in pain -
if not complete relief from pain.
• TENS is effective for pain from a very
wide range of causes.
• TENS machines can be used to help
reduce pain from problems in
muscles, joints and nerves.
• It can be also used for people with
musculoskeletal pain such as long-
term (chronic) back pain or knee joint
arthritis. They are also often used for
pain relief in the early stages of
labour (see perfect mamaTENS),
particularly whilst a pregnant woman
remains at home.

8
• TENS may also be used to treat
many types of pain, such as period
pain and endometriosis (see Ova+),
cystitis, sports injuries, fibromyalgia
and neuralgia, plantar fasciitis, post-
operative pain, TMJ disorder,
diabetic neuropathy, osteo-arthritis
and sometimes non-painful
conditions such as travel sickness.
• You can use low frequency (<10 Hz)
programmes on acupuncture points,
to achieve similar effects to
acupuncture.
• With neurogenic pain (caused by
inflamed nerves) such as neuralgia,
TENS may start by increasing the
pain. We recommend that you only
use TENS for these conditions under
medical supervision.
You can safely use TENS as long as it
gives you pain relief. The effect may
wear off after a few hours (this is called
“accommodation”). If this happens, take
a break of an hour or so before trying
again. If you use settings that cause
muscle movement for more than 40
minutes, you may experience aching
muscles a few hours later.
6. CONTRAINDICATIONS,
WARNINGS &
CAUTIONS
In this manual:
A Contraindication is used when a
device should not be used
because the risk of use clearly
outweighs any foreseeable
benefits and may result in serious injury
or death.
Warning is used when failure
to follow the instructions may
result in serious injury or death.
A Caution is used when failure
to follow the instructions may
result in a minor or moderate
injury, or damage to the device or other
property.
Notes are used to provide
clarification or
recommendation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Do NOT use if you have a pacemaker
(or if you have a heart rhythm problem)
or with any electronic medical devices.
Using this unit with electronic medical
devices may cause erroneous
operation of the device. Stimulation in
the direct vicinity of an implanted device
may affect some models.
Do NOT use during the first three
months of pregnancy. It is not known
whether TENS and EMS may affect
foetal development.
Do NOT use on the abdomen in the
later stages of pregnancy. Stop using
immediately if you experience
unexpected contractions.
WARNINGS:
Do NOT use when driving, operating
machinery, or similar actions needing
muscular control. Loose electrode
pads, damaged leads, or sudden
changes in contact may cause brief
involuntary muscle movements.

9
Do NOT use to mask or relieve
undiagnosed pain. This may delay
diagnosis of a progressive condition.
Do NOT use if you have, in the area
being treated: active or suspected
cancer or undiagnosed pain with a
history of cancer. Stimulation directly
through a confirmed or suspected
malignancy should be avoided as it may
stimulate growth and promote spread of
cancer cells.
Do NOT use simultaneously with high
frequency hospital
diagnostic/therapeutic equipment.
Doing so may result in burns at the site
of the electrodes and possible damage
to device.
Do NOT use electrodes on the front of
the neck. Stimulation on the front of the
neck can affect your heart rate or cause
contraction of the throat.
Do NOT use electrodes across the
chest. Very strong stimulation across
the chest may cause an extra heartbeat
and/or rhythm disturbances to your
heart, which could be lethal.
Do NOT use in close proximity (e.g. 1
m) to a shortwave or microwave as this
may produce instability in the stimulator
output.
Do NOT apply near the thorax because
the introduction of electrical current
may increase the risk of cardiac
fibrillation.
Stimulation should not be applied
across or through the head, directly on
the eyes, covering the mouth, on the
front of the neck (especially the carotid
sinus), or from electrodes placed on the
upper back or crossing over the heart.
CAUTIONS:
Caution should be used if you have a
bleeding disorder as stimulation may
increase blood flow to the stimulated
region.
Caution should be used if you have
suspected or diagnosed epilepsy as
electrical stimulation may affect seizure
threshold.
Caution should be observed when
using the device at the same time as
being connected to monitoring
equipment with body worn electrode
pads. It may interfere with the signals
being monitored.
Caution should be used following
recent surgical procedures. Stimulation
may disrupt the healing process.
Caution Do not permit use by children
unable to understand the instructions or
persons with cognitive disabilities, i.e.;
Alzheimer’s disease or dementia.
Caution Keep away from children
under 5 years of age, pets and pests.
Long lead wires - risk of strangulation in
infants.
Caution: should be observed when
using the Perfect EMS at high strength
settings. Perfect EMS has a Yellow
LED light on output socket which
means the output will exceed 10 mA
(R.M.S) or 10 V (R.M.S) averaged over
any period of 1 sec. Prolonged use at
high settings may cause muscle injury
or tissue inflammation.
Caution Not intended for use in an
oxygen rich environment.
Caution Not intended for use in
conjunction with flammable
anaesthetics or flammable agents.
Caution The patient is an intended
operator.

10
Caution Do not service and maintain
the device while in use with a patient
Caution Maintenance and all repairs
should only be carried out by an
authorized agency. The manufacturer
will not be held responsible for the
results of maintenance or repairs by
unauthorized persons.
If necessary, we will provide circuit
diagrams, component part lists or other
information that will assist authorized
service personnel to repair the device.
Caution The operator should not touch
the patient at the same time when
touching the battery output.
Caution There are no user serviceable
parts. No modification of this equipment
is allowed.
DO NOT PLACE ELECTRODE PADS:
• On skin, which does not have normal
sensation. If the skin is numb too
great a strength may be used, which
could result in skin inflammation.
• On broken skin. The electrode pads
could encourage infection.
• On the front of the neck. This could
cause the airway to close, giving
breathing problems. May cause
sudden drop in blood pressure
(vasovagal response).
• Over the eyes. May affect eyesight
or cause headaches.
• Across the front of the head. Effect
on patients who have had strokes or
seizures is not known. May affect
your sense of balance. The effects of
stimulation on the brain are
unknown.
ELECTRODE PADS CAUTION:
Caution: Do not ignore any allergic
reaction to the electrode pads: If a skin
irritation develops, stop using the
device, as this type of electrodes may
not be suitable for you. Alternative
electrode pads specially made for
sensitive skin are available (see E-696-
SS).
Caution: Do not use this device with
leads or electrode pads other than
those recommended by the
manufacturer. Performance may vary
from specification. Electrodes with
smaller surface area may cause tissue
irritation.
Caution: Do not use high intensity
settings if electrodes are smaller than
50x50mm.
Note: Electrode pads supplied
have no measurable latex
content.
TO KEEP YOUR DEVICE IN GOOD
WORKING ORDER, OBSERVE THE
FOLLOWING ADDITIONAL
CAUTIONS:
Caution: Do not immerse your device
in water or place it close to excessive
heat such as a fireplace or radiant
heater or sources of high humidity such
as a nebulizer or kettle as this may
cause it to cease to operate correctly.
Caution: Keep the device away from
sunlight, as long-term exposure to
sunlight may affect the rubber causing
it to become less elastic and crack.
Caution: Keep the device away from
lint and dust, as long-term exposure to
lint or dust may affect the sockets or
cause the battery connector to develop
a bad contact.
Caution: Temperature & Relative
Humidity of storage:
-25°C to +70°C, up to 93% R.H.
Temperature & Relative Humidity of

11
transportation: -25°C to +70°C, up to
93% R.H.
Caution: Do not attempt to open or
modify the unit. This may affect the safe
operation of the unit and will invalidate
the warranty.
Note: There are no known side
effects to use and long-term
use is not harmful. However,
the device works your muscles and
unaccustomed amounts of exercise
may produce muscle ache. If this
happens, simply reduce the strength of
the machine or allow your muscles to
rest until the aching disappears.
7. INFORMATION ABOUT
THE PROGRAMME
SETTINGS
Each programme has its own
combination of Frequency and Pulse
Width settings which allow for different
muscle groups to be exercised and
toned through the electrode pads.
• Frequency (measured in Hz -
pulses per second)
For EMS programmes:
Low frequencies (1-10 Hz) have a
purifying and relaxing effect through
individual contractions.
Medium frequencies (20-50 Hz) can put
a high level of strain on the muscle, thus
promoting the muscular structure.
For TENS programmes:
Pain gate: A high frequency of 110 Hz
is good at blocking pain signals.
Endorphin release: A low frequency of
4 or 10 Hz allows for the release of
endorphins, the body’s natural
morphine-like substances.
• Pulse Width (measured in μs -
millionths of a second)
The perfect EMS unit has pulse widths
of 50 to 350 μs. Generally speaking, the
higher the pulse width, the more
"aggressive" the stimulation feels, if the
pulse width is set high enough, it will
usually elicit a muscle contraction,
which is required for an effective toning
of the muscle group selected.
For the TENS programmes (pain relief),
it is not desired to elicit a muscle
contraction, however Pulse Rate is
important because different frequency
settings target different nerve groups
and the setting will determine if the
"Gate Theory" or "Endorphin Theory" of
TENS will be used.
• Work/Rest
All the EMS programmes (see A to H)
are intermittent.
Once you have reached a comfortable
level, 5 seconds after you stop pressing
the button, the intermittent Work/Rest
phase will start.
For each programme, the unit will go
through a stimulation phase (Work) for
1-40 seconds, followed by a phase
without stimulation (Rest) for a similar
time.
This is to allow your muscles to recover
from exercise and avoid fatigue.
During the Work period (W), the unit will
generate contractions, try to contract
the muscle voluntarily at the time to get
the best possible results.
This cycle Work/Rest will continue for
the duration of the programme
selected.

12
W and R are displayed on the screen.
• Ramp
RAMP is the time in seconds taken to
move up and down between zero and
the set stimulation strength (i.e. the time
taken to move between the Work
stimulation and the Rest period). The
perfect EMS offers Ramp periods from
0 to 5 seconds.
• Constant and Burst Modes
Constant mode is when the sensation is
continuous versus Burst mode when
the sensation, as its name implies, is
one of on and off. Constant mode is
often used for acute pain via Pain Gate
effect whereas Burst mode is useful in
chronic pain relief. Burst gives a
combination of Pain Gate and
Endorphin Release, but the squeezing
feeling may not be as comfortable. The
stimulation intensity will need to be
relatively high. In Constant mode, the
sensation is continuous and is more of
a tingling pins and needles type. See
programmes S and T.
8. PROGRAMMES
8.1. PROGRAMME SETTINGS
Prog
Muscle group
Description
Special Feature
A
Preset EMS
All
Warm up: Helps preparing
the muscles before an active
training by stimulating the
surface muscle fibres.
For all users
B
Preset EMS
Large (e.g.:
Abdominal,
Buttocks & Hips,
Thighs,
Bust/Pectorals*)
Endurance: Firming up
muscles working mainly on
slow-twitch fibres.
For all users
C
Preset EMS
Large (e.g.:
Abdominal,
Buttocks & Hips,
Thighs,
Bust/Pectorals*)
Power: Toning up working
mainly on fast-twitch fibres.
For all users
D
Preset EMS
Large (e.g.:
Abdominal,
Buttocks & Hips,
Thighs,
Bust/Pectorals*)
Definition and Bulk: Defining
muscles in the selected area
working mainly on explosive
fibres. Grows muscles size.
For advanced users
wanting to improve results
E
Preset EMS
Small (e.g.:
Arms, Calves)
Endurance: Firming up
muscles working mainly on
slow-twitch fibres.
For all users exercising
small muscles.
To start exercise of weak or
atrophied large muscles.

13
* Specifically designed breast electrode pads (see E-CMR60130) are available.
Note: These programmes must be used in combination with a healthy diet
and regular active exercises.
8.2. PRESET PROGRAMMES
Perfect EMS has six different, specially
developed EMS programmes (A to F),
two manual EMS programmes (G and
H) and two manual TENS programmes
(S and T).
To choose the programme that suits
your needs, please see section 8.1., for
the electrode pads positioning, please
see section 9.3.
This will depend greatly on what you
are looking to achieve and on the
selected muscle group.
F
Preset EMS
Small (e.g.:
Arms, Calves)
Power: Toning up working
mainly on fast-twitch fibres.
For all users exercising
small muscles.
To start exercise of weak or
atrophied large muscles.
G
Manual EMS
Manual programme for
Muscle Toning
H
Manual EMS
Manual programme for
Muscle Toning
S
Manual TENS
Manual programme for Pain
Relief
Constant mode –
Recommended for acute
pain
T
Manual TENS
Manual programme for Pain
Relief
Burst mode –
Recommended for chronic
pain
Prog
Frequency
(Hz)
Pulse Width
(μs)
Work (s)
Rest (s)
Ramp (s)
A
10
300
Constant
B
20
250
5
10
1
C
50
250
3
6
2
D
75
250
5
10
1
E
20
100
5
15
1
F
50
100
3
6
1
G
Select 1-80
Select 50-350
Select 1-40
Select 0-40
Select 0-5
H
Select 1-80
Select 50-350
Select 1-40
Select 0-40
Select 0-5
S
Select 1-120
Select 50-250
Constant
T
Select 1-120
Select 50-250
2 Hz Burst

14
8.3. MANUAL PROGRAMMES
In the EMS manual programmes (G and
H) you can select and change the
following parameters using the T timer
button:
Parameter Display Symbol
to Change Flashes
Frequency Hz
Pulse Width μs
Ramp Time (seconds)
Work Time (seconds) W
Rest Time (seconds) R
Treatment Timer (minutes) min
In the TENS manual programmes (S
and T) you can select and change the
following parameters using the T timer
button:
Parameter Display Symbol
to Change Flashes
Frequency Hz
Pulse Width μs
Constant / Burst C/B
Treatment Timer (minutes) min
1. Press the P key until you reach
programme G, H, S or T.
2. Press the T key. The Hz symbol will
flash next to the number at the
bottom centre of the screen.
3. Press CH1▲ or CH1▼ to adjust the
setting.
You can select a frequency from 1 to
80 Hz in programmes G and H, and
1 to 120 Hz in programmes S and T.
4. Press the T key again to save your
change and advance to the next
setting µs.
You can select a pulse width from 50
to 350 µs in programmes G and H,
and 50 to 250 µs in programmes S
and T.
5. Press the T key to select Ramp.
You can select a ramp from 0 to 5 s
in programmes G and H only.
6. Press the T key to select Work Time.
You can select a work time from 1 to
40 s in programmes G and H only.
7. Press the T key to select Rest Time.
You can select a rest time from 0 to
40 s in programmes G and H only.
8. Press the T key to select C or B.
C = Constant B = Burst in
programmes S and T only.
9. Finally, you can select the
Treatment Timer. Continuous, 10,
20, 30, 45, 60 or 90 minutes.
10. Press T once more to return to
start using.
See section 7 for more information on
the choice of settings.
8.4. USING THE
PROGRAMMES
• TENS PROGRAMMES
There is not one programme for a
particular condition, and the best choice
varies from one person to another, even
if they have the same type of pain.
Each user needs to select both the
programme and the positioning of the
electrode pads that is best for them.
You may need to try a few
CH1
CH2
Hz

15
positions/programmes before finding
the one that suits you.
TENS can be used for as long as it is
necessary. Continuous treatment is
fine, but the electrode pads should be
repositioned regularly (at least every 12
hours) to allow the skin to be exposed
to the air.
The Endorphin Release works better
when the strength is high enough to
cause small muscle contractions. Best
results are achieved with a session
duration between 20 and 40 minutes.
Longer use may cause muscle ache.
• EMS PROGRAMMES
Abs, hip, thigh:
EMS can help improving body toning
and body shaping by generating
passive muscle contractions in the
selected area.
It may improve your general fitness
levels as well as achieving a thinner
silhouette by building up the muscles.
Bust:
Electrical Stimulation can build,
strengthen, and firm the pectoral
muscles giving bulk and lift.
• Exercise and massage therapy to
enhance the size and shape of your
breasts
• Natural method to enhance your all-
natural body
Note: For improved comfort,
use this programme with the
breast electrode pads* (see E-
CMR60130).
*Sold separately.
Arm:
The upper arms often get saggy and
flabby especially in women with the
triceps (back of the upper arm). It is
commonly referred to as “Bingo Wings”
or “Bat Wings”. It is tricky to tone this
muscle group and some women find
this area ungraceful or even
embarrassing.
Perfect EMS helps to tone, firm and lift
the triceps and the biceps as it allows
you to generate contractions in this
specific muscle group.
Calf:
Most people are aiming for thin but
muscly legs with a harmonious balance
between the size of the thighs and the
size of the calves. Often, the calves are
either too skinny with only little muscle
mass or too big with a long muscle
mass especially around the ankle.
The aim is to tone, shape and lift the
calves’ muscles to achieve slender legs
with improved definition of the muscles
as well as a slimming effect on the
ankles
Recommended use:
Generally, 3 sessions per week, over a
period of 4 to 6 weeks, gives good initial
results depending on the body shaping,
toning, sports training or rehabilitation
and recovery needs.
GENERAL ADVICE:
Ideally, use perfect EMS once every
two days for each muscle with a day of
rest in between. It is possible to work on
pairs of muscles, for example thighs
and abdominal muscles, treating one
set one day and the other the next day.

16
Warning: Working on too
many muscles at the same
time is not recommended.
Increase the intensity until you feel a
very smooth tensing under the pads,
there should be little visible movement.
Use a low intensity for the first session
to help you to understand how the
machine works.
During the programme and over the
next few days the intensity should be
increased gradually to produce marked,
but not painful muscle contractions.
Once good results have been obtained
the sessions may be reduced to once or
twice a week until the user feels that
optimum body shaping has been
achieved.
Note: The stimulation should
remain comfortable and
relaxing at all times.
9. ELECTRODE PADS
9.1. PAD POSITIONING
The electrode pads must always be
used in pairs (two electrode pads on
each channel), so that the signal can
flow in a circuit.
Electrode placement for TENS:
• TENS works one vertebra at a time.
You need to stimulate the sensory
nerves that enter the spine at the
same level as the nerve carrying
your pain. Since you don’t know
exactly where your nerves are, the
easiest way is to apply the electrode
pads around/near the source of the
pain.
• TENS activates the nerves best if it
travels along the nerve rather than
across it. So place one pad further
from the spine than the source of the
pain, and one closer.
• The nerves wrap around the limbs
and torso, so you may have to try a
few positions before you get the best
effect.
• If the pain is in, or close to, your
spine you can place one pad either
side of the spine.
• You may feel more sensation in one
pad than the other. This is normal –
it depends on where the electrode
pads are in relation to your nerves.
Note: See examples of
positioning in the instructions
enclosed with your electrode
pads.
Electrode placement for EMS is very
important for obtaining the best
results:
Place two electrode pads over the bulk
of the muscle, with one electrode over
the muscle’s motor point. The motor
point is the area on the skin that is
located closest to the motor nerve’s
entry into the muscle – about 1/3 of the
way down the muscle from the spine.
Here, it is easiest to trigger a
contraction by electrical stimulation.
Experiment by moving the electrode
pads across the skin until you locate the
point over the muscle that gives the
cleanest contraction. In the examples in
section 9.3., the electrode pads are
marked +ve (red) and -ve (black) to

17
match the red and black leads. One of
the electrode pads should be
positioned over the motor point.
Large muscle groups may require
stimulation with two channels, that is,
four electrodes simultaneously.
When exercising smaller muscles, take
care to adjust the intensity level slowly
as the motor nerves may be more
sensitive and using smaller electrode
pads increases the current density.
You may feel more sensation in one
pad than the other. This is normal – it
depends on where the electrode pads
are in relation to your nerves.
Use the square electrode pads (see E-
CM5050) for all areas.
For the bust area, it is recommended to
use the optional breast electrode pads for
improved comfort (see E-CMR60130*).
*Sold separately.
Always check that the unit is OFF
before attaching or removing
electrode pads.
Perfect EMS resets strength to zero
if the pad or lead is disconnected
from your body. This is to prevent
sudden changes in sensation when
the pad is re-connected.
9.2. PAD ADVICE
• The electrode pads supplied are
reusable but for single patient use.
The adhesive is a peelable hydrogel
(water based).
• In order to obtain the best
conductivity through the electrode
pads always ensure that they are in
good condition and tacky.
• Before use make sure your skin is
clean and dry.
• Peel the electrode pads from their
protective plastic shield by holding
and lifting one corner of the pad and
pulling. Do not pull on the pigtail wire
of the pad.
• After use always replace the
electrode pads on the plastic liner
and replace them in the re-sealable
plastic bag.
• If the electrode pads dry out, then it
is best to buy a replacement pack. In
an emergency, it may be possible to
restore some of the tackiness of the
pad by adding a tiny drop of water on
each pad and spreading around. If
too much water is added, the
electrode pad will become too soft. If
that happens then it is suggested in
order to try and re-establish some
adhesiveness, to place them sticky
side up in a refrigerator for a few
hours.
• In very hot weather the gel on the
electrode pads may become soft. In
such cases place them, still on their
plastic liners and in their pouch into
a fridge until they return to their
normal condition.
• The electrode pads provided are
latex-free.
• Replace the electrode pads when
they lose their stickiness.
Poor connection may cause
discomfort and skin irritation.
• Storage life of an unopened pack of
electrode pads is 2 years. This may
be affected by very high
temperatures or very low humidity.

18
9.3. EMS ELECTRODE PLACEMENT
The electrode pads placement is specific to the area being treated. Please refer to the
placement guidelines below.
Note: The + electrode pad needs to be plugged in to the red lead wire
connector, the – refers to the one for the black lead wire connector.
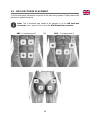
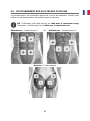
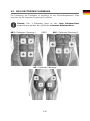
ABS – Pad placement 1 OR ABS – Pad placement 2
HIP – Pads placement

19
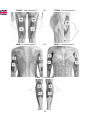
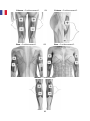
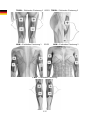
THIGH – Pad placement 1 OR THIGH – Pad placement 2
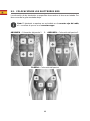
ARM – Pad placement 1 OR ARM – Pad placement 2
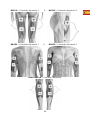
CALF – Pad placement
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
La page est en cours de chargement...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
-
 125
125
-
 126
126
-
 127
127
-
 128
128
-
 129
129
-
 130
130
-
 131
131
-
 132
132
-
 133
133
-
 134
134
dans d''autres langues
- English: TensCare Perfect EMS User manual
- español: TensCare Perfect EMS Manual de usuario
- Deutsch: TensCare Perfect EMS Benutzerhandbuch
Documents connexes
-
 TensCare Sports TENS 2 Manuel utilisateur
TensCare Sports TENS 2 Manuel utilisateur
-
 TensCare UNICARE Manuel utilisateur
TensCare UNICARE Manuel utilisateur
-
 TensCare TENS ONE Manuel utilisateur
TensCare TENS ONE Manuel utilisateur
-
TensCare TENS One Mode d'emploi
-
TensCare I-CM50100PM Manuel utilisateur
-
TensCare E-BF155 Manuel utilisateur
-
 TensCare SONIC STIM+ Manuel utilisateur
TensCare SONIC STIM+ Manuel utilisateur
-
 TensCare SURE+ Manuel utilisateur
TensCare SURE+ Manuel utilisateur
-
 TensCare ALIVIA Manuel utilisateur
TensCare ALIVIA Manuel utilisateur
-
 TensCare ELISE 2 Manuel utilisateur
TensCare ELISE 2 Manuel utilisateur
Autres documents
-
Sanitas SEM 43 Guide de démarrage rapide
-
Beurer EM 59 Heat Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Beurer EM 49 Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Beurer EM 49 Instructions For Use Manual
-
 Compex Wireless Manuel utilisateur
Compex Wireless Manuel utilisateur
-
Sanitas DIGITAL EMS TENS Le manuel du propriétaire
-
Compex RUNNER Manuel utilisateur
-
Drive Medical Padded Swivel Seat Cushion Manuel utilisateur
-
Beurer EM 59 Manuel utilisateur
-
Beurer EM 50 Manuel utilisateur













































































































































